由激肽释放酶-激肽系统产生的活性肽。 它是炎症调节因子,也被认为是几种血管和肾功能以及神经调节因子。
编号:122160
CAS号:58-82-2/227-781-2/6846-03-3
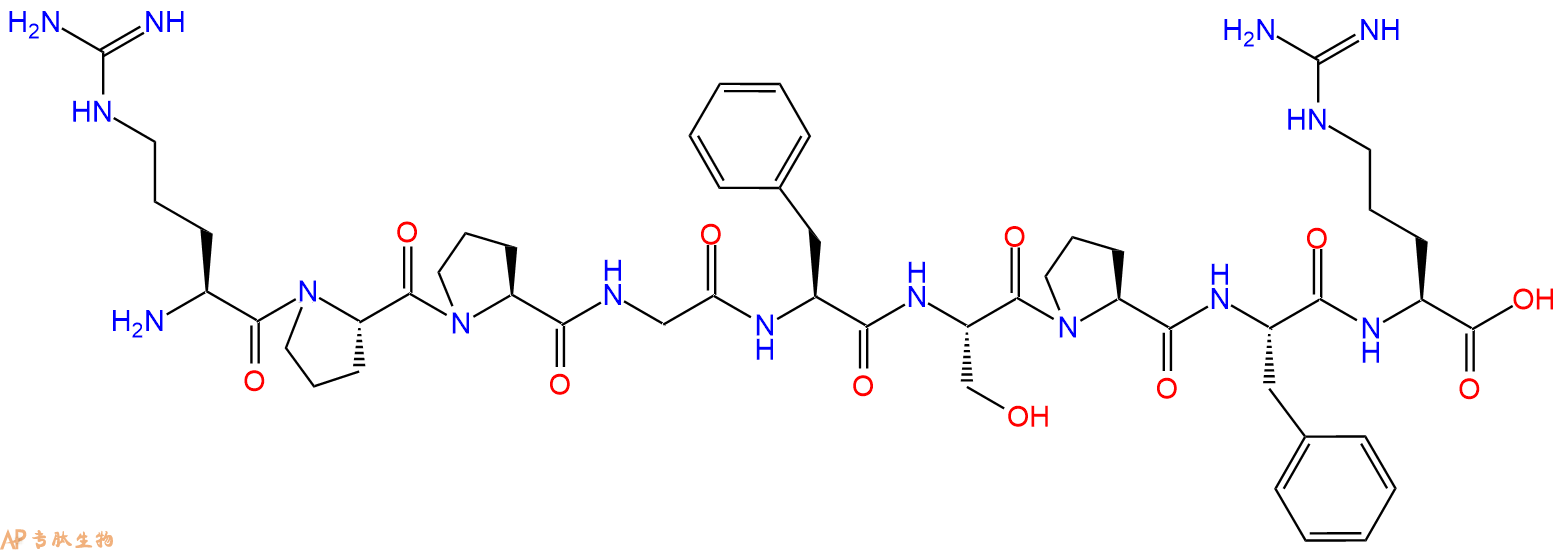
单字母:H2N-RPPGFSPFR-OH
| 编号: | 122160 |
| 中文名称: | 缓激肽Bradykinin |
| 英文名: | Bradykinin |
| CAS号: | 58-82-2/227-781-2/6846-03-3 |
| 单字母: | H2N-RPPGFSPFR-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Arg精氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 9 |
| 分子式: | C50H73N15O11 |
| 平均分子量: | 1060.21 |
| 精确分子量: | 1059.56 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 2.97 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.26 |
| 疏水性值: | -1.04 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 消光系数: | - |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 生成周期: | 2-3周 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 抑制剂相关肽(Inhibitor Peptide) 缓激肽(Bradykinin) 炎症研究 |
Bradykinin是由激肽释放酶-激肽系统产生的活性肽。 它是炎症调节因子,也被认为是几种血管和肾功能以及神经调节因子。
Bradykinin is an active peptide that is generated by the kallikrein-kinin system. It is a inflammatory mediator and also recognized as a neuromediator and regulator of several vascular and renal functions.
该肽是血管紧张素I转换酶(ACE I)的抑制剂,来源于缓激肽。ACE I部分抑制肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统(RAAS),该系统调节血压并可能介导高血压。ACE I利用锌和氯依赖性机制将血管紧张素I转化为具有生物活性的肽血管紧张素II。
This peptide is an inhibitor for Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE I), derived from Bradykinin. ACE I partially suppresses the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and may mediate hypertension. ACE I converts angiotensin I to the biologically active peptide angiotensin II using a zinc- and chloride- dependent mechanism.
定义
酶是用于生化反应的非常有效的催化剂。它们通过提供较低活化能的替代反应途径来加快反应速度。酶作用于底物并产生产物。一些物质降低或什至停止酶的催化活性被称为抑制剂。
发现
1965年,Umezawa H分析了微生物产生的酶抑制剂,并分离出了抑制亮肽素和抗痛药的胰蛋白酶和木瓜蛋白酶,乳糜蛋白酶抑制的胰凝乳蛋白酶,胃蛋白酶抑制素抑制胃蛋白酶,泛磷酰胺抑制唾液酸酶,乌藤酮抑制酪氨酸羟化酶,多巴汀抑制多巴胺3-羟硫基嘧啶和多巴胺3-羟色胺酶酪氨酸羟化酶和多巴胺J3-羟化酶。最近,一种替代方法已应用于预测新的抑制剂:合理的药物设计使用酶活性位点的三维结构来预测哪些分子可能是抑制剂1。已经开发了用于识别酶抑制剂的基于计算机的方法,例如分子力学和分子对接。
结构特征
已经确定了许多抑制剂的晶体结构。已经确定了三种与凝血酶复合的高效且选择性的低分子量刚性肽醛醛抑制剂的晶体结构。这三种抑制剂全部在P3位置具有一个新的内酰胺部分,而对胰蛋白酶选择性最高的两种抑制剂在P1位置具有一个与S1特异性位点结合的胍基哌啶基。凝血酶的抑制动力学从慢到快变化,而对于胰蛋白酶,抑制的动力学在所有情况下都快。根据两步机理2中稳定过渡态络合物的缓慢形成来检验动力学。
埃米尔•菲舍尔(Emil Fischer)在1894年提出,酶和底物都具有特定的互补几何形状,彼此恰好契合。这称为“锁和钥匙”模型3。丹尼尔·科什兰(Daniel Koshland)提出了诱导拟合模型,其中底物和酶是相当灵活的结构,当底物与酶4相互作用时,活性位点通过与底物的相互作用不断重塑。
在众多生物活性肽的成熟过程中,需要由其谷氨酰胺(或谷氨酰胺)前体形成N末端焦谷氨酸(pGlu)。游离形式并与底物和三种咪唑衍生抑制剂结合的人QC的结构揭示了类似于两个锌外肽酶的α/β支架,但有多个插入和缺失,特别是在活性位点区域。几种活性位点突变酶的结构分析为针对QC相关疾病5的抑制剂的合理设计提供了结构基础。
作用方式
酶是催化化学反应的蛋白质。酶与底物相互作用并将其转化为产物。抑制剂的结合可以阻止底物进入酶的活性位点和/或阻止酶催化其反应。抑制剂的种类繁多,包括:非特异性,不可逆,可逆-竞争性和非竞争性。可逆抑制剂 以非共价相互作用(例如疏水相互作用,氢键和离子键)与酶结合。非特异性抑制方法包括最终使酶的蛋白质部分变性并因此不可逆的任何物理或化学变化。特定抑制剂 对单一酶发挥作用。大多数毒药通过特异性抑制酶发挥作用。竞争性抑制剂是任何与底物的化学结构和分子几何结构非常相似的化合物。抑制剂可以在活性位点与酶相互作用,但是没有反应发生。非竞争性抑制剂是与酶相互作用但通常不在活性位点相互作用的物质。非竞争性抑制剂的净作用是改变酶的形状,从而改变活性位点,从而使底物不再能与酶相互作用而产生反应。非竞争性抑制剂通常是可逆的。不可逆抑制剂与酶形成牢固的共价键。这些抑制剂可以在活性位点附近或附近起作用。
功能
工业应用中, 酶在商业上被广泛使用,例如在洗涤剂,食品和酿造工业中。蛋白酶用于“生物”洗衣粉中,以加速蛋白质在诸如血液和鸡蛋等污渍中的分解。商业上使用酶的问题包括:它们是水溶性的,这使得它们难以回收,并且一些产物可以抑制酶的活性(反馈抑制)。
药物分子,许多药物分子都是酶抑制剂,药用酶抑制剂通常以其特异性和效力为特征。高度的特异性和效力表明该药物具有较少的副作用和较低的毒性。酶抑制剂在自然界中发现,并且也作为药理学和生物化学的一部分进行设计和生产6。
天然毒物 通常是酶抑制剂,已进化为保护植物或动物免受天敌的侵害。这些天然毒素包括一些已知最剧毒的化合物。
神经气体( 例如二异丙基氟磷酸酯(DFP))通过与丝氨酸的羟基反应生成酯,从而抑制了乙酰胆碱酯酶的活性位点。
参考
1、Scapin G (2006). Structural biology and drug discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des., 12(17):2087–2097.
2、Krishnan R, Zhang E, Hakansson K, Arni RK, Tulinsky A, Lim-Wilby MS, Levy OE, Semple JE, Brunck TK (1998). Highly selective mechanism-based thrombin inhibitors: structures of thrombin and trypsin inhibited with rigid peptidyl aldehydes. Biochemistry, 37 (35):12094-12103.
3、Fischer E (1894). Einfluss der configuration auf die wirkung der enzyme. Ber. Dt. Chem. Ges., 27:2985–2993.
4、Koshland DE (1958). Application of a theory of enzyme specificity to protein synthesis. PNAS., 44 (2):98–104.
5、Huang KF, Liu YL, Cheng WJ, Ko TP, Wang AH (2005). Crystal structures of human glutaminyl cyclase, an enzyme responsible for protein N-terminal pyroglutamate formation. PNAS., 102(37):13117-13122.
6、Holmes CF, Maynes JT, Perreault KR, Dawson JF, James MN (2002). Molecular enzymology underlying regulation of protein phosphatase-1 by natural toxins. Curr Med Chem., 9(22):1981-1989.
Definition
Enzymes are very efficient catalysts for biochemical reactions. They speed up reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway of lower activation energy. Enzyme acts on substrate and gives rise to a product. Some substances reduce or even stop the catalytic activities of enzymes are called inhibitors.
Discovery
In 1965, Umezawa H analysed enzyme inhibitors produced by microorganisms and isolated leupeptin and antipain inhibiting trypsin and papain, chymostatin inhibiting chymotrypsin, pepstatin inhibiting pepsin, panosialin inhibiting sialidases, oudenone inhibiting tyrosine hydroxylase, dopastin inhibiting dopamine 3-hydroxylase, aquayamycin and chrothiomycin inhibiting tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine J3-hydroxylase . Recently, an alternative approach has been applied to predict new inhibitors: rational drug design uses the three-dimensional structure of an enzyme's active site to predict which molecules might be inhibitors 1. Computer-based methods for identifying inhibitor for an enzyme have been developed, such as molecular mechanics and molecular docking.
Structural Characteristics
The crystal structures of many inhibitors have been determined. The crystal structures of three highly potent and selective low-molecular weight rigid peptidyl aldehyde inhibitors complexed with thrombin have been determined. All the three inhibitors have a novel lactam moiety at the P3 position, while the two with greatest trypsin selectivity have a guanidinopiperidyl group at the P1 position that binds in the S1 specificity site. The kinetics of inhibition vary from slow to fast with thrombin and are fast in all cases with trypsin. The kinetics are examined in terms of the slow formation of a stable transition-state complex in a two-step mechanism 2.
Emil Fischer in 1894 suggested that both the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes that fit exactly into one another.This is known as "the lock and key" model 3. Daniel Koshland suggested induced fit model where substrate and enzymes are rather flexible structures, the active site is continually reshaped by interactions with the substrate as the substrate interacts with the enzyme 4.
N-terminal pyroglutamate (pGlu) formation from its glutaminyl (or glutamyl) precursor is required in the maturation of numerous bioactive peptides. The structure of human QC in free form and bound to a substrate and three imidazole-derived inhibitors reveals an alpha/beta scaffold akin to that of two-zinc exopeptidases but with several insertions and deletions, particularly in the active-site region. The structural analyses of several active-site-mutant enzymes provide a structural basis for the rational design of inhibitors against QC-associated disorders 5.
Mode of Action
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. Enzymes interact with substrate and convert them into products. Inhibitor binding can stop a substrate from entering the enzyme's active site and/or hinder the enzyme from catalyzing its reaction. There are a variety of types of inhibitors including: nonspecific, irreversible, reversible - competitive and noncompetitive. Reversible inhibitors bind to enzymes with non-covalent interactions like hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and ionic bonds. Non-specific methods of inhibition include any physical or chemical changes which ultimately denature the protein portion of the enzyme and are therefore irreversible. Specific Inhibitors exert their effects upon a single enzyme. Most poisons work by specific inhibition of enzymes. A competitive inhibitor is any compound which closely resembles the chemical structure and molecular geometry of the substrate. The inhibitor may interact with the enzyme at the active site, but no reaction takes place. A noncompetitive inhibitor is a substance that interacts with the enzyme, but usually not at the active site. The net effect of a non competitive inhibitor is to change the shape of the enzyme and thus the active site, so that the substrate can no longer interact with the enzyme to give a reaction. Non competitive inhibitors are usually reversible. Irreversible Inhibitors form strong covalent bonds with an enzyme. These inhibitors may act at, near, or remote from the active site .
Functions
Industrial application, enzymes are widely used commercially, for example in the detergent, food and brewing industries. Protease enzymes are used in 'biological' washing powders to speed up the breakdown of proteins in stains like blood and egg. Problems using enzymes commercially include: they are water soluble which makes them hard to recover and some products can inhibit the enzyme activity (feedback inhibition) .
Drug molecules, many drug molecules are enzyme inhibitors and a medicinal enzyme inhibitor is usually characterized by its specificity and its potency. A high specificity and potency suggests that a drug will have fewer side effects and less toxic. Enzyme inhibitors are found in nature and are also designed and produced as part of pharmacology and biochemistry 6.
Natural poisons are often enzyme inhibitors that have evolved to defend a plant or animal against predators. These natural toxins include some of the most poisonous compounds known.
Nerve gases such as diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) inhibit the active site of acetylcholine esterase by reacting with the hydroxyl group of serine to make an ester.
References
Scapin G (2006). Structural biology and drug discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des., 12(17):2087–2097.
Krishnan R, Zhang E, Hakansson K, Arni RK, Tulinsky A, Lim-Wilby MS, Levy OE, Semple JE, Brunck TK (1998). Highly selective mechanism-based thrombin inhibitors: structures of thrombin and trypsin inhibited with rigid peptidyl aldehydes. Biochemistry, 37 (35):12094-12103.
Fischer E (1894). Einfluss der configuration auf die wirkung der enzyme. Ber. Dt. Chem. Ges., 27:2985–2993.
Koshland DE (1958). Application of a theory of enzyme specificity to protein synthesis. PNAS., 44 (2):98–104.
Huang KF, Liu YL, Cheng WJ, Ko TP, Wang AH (2005). Crystal structures of human glutaminyl cyclase, an enzyme responsible for protein N-terminal pyroglutamate formation. PNAS., 102(37):13117-13122.
Holmes CF, Maynes JT, Perreault KR, Dawson JF, James MN (2002). Molecular enzymology underlying regulation of protein phosphatase-1 by natural toxins. Curr Med Chem., 9(22):1981-1989.
Definition
Bradykinin is a nonapeptide that is mainly found in animal preparations that are treated with the venom of the snake, Bothrops jararaca1,2. It dialates blood vessels that in turn leads to decrease in blood pressure2. Bradykinin analogs are slightly modified structural derivatives of bradykinin that perform similar functions as bradykinin3.
Discovery
Bradykinin was discovered in the blood plasma of animals that were treated with the venom from the Brazilian snake, Bothrops jararaca1,2. The discovery was part of a study that was related to toxicology of snake bites. Bradykinin analogs were synthesized by solid-phase techniques in 1975 and their function was studied in rats and rabbits3.
Classification
Bradykinin is a 9 amino acid peptide that belongs to the kinin family of proteins4. It has homologs in several animals including other snakes, frog, dog and humans4.
Structural Characteristics
Bradykinin has the sequence Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg3. Several analogs of bradykinin have been synthesized. They are also nanopeptides containing substitutions of various amino acids of bradykinin. For example two analogs of bradykinin were synthesized one with 7-beta-homo-L-proline and the other with 8-beta-homo-L-phenylalanine substitutions3. It was found that both of them are resistant to enzymatic degradation3.
Mode of action
Bradykinin binds to two different kinin G protein coupled receptors- B1 and B25. Upon binding to these receptors it induces conversion of GTP to GDP which in turn triggers the conversion ATP to cAM which then acts as a second messenger resulting in the activation of genes. B1 receptor is expressed as a result of tissue injury and is found to play a role in inflammation while B2 receptor participates in the vasodilatory role of bradykinin5,6. Bradykinin analogs function is a similar fashion although depending on their structure they might have varying affinities to the receptors compared to bradykinin7. Also analogs of bradykinin have been synthesized that are specific to one of these receptors7.
Functions
Bradykinin is a potent endothelium-dependent vasodilator, causes contraction of non-vascular smooth muscle, increases vascular permeability and also is involved in the mechanism of pain. Bradykinin also causes natriuresis, contributing to a drop in blood pressure8. Bradykinin raises internal calcium levels in neocortical astrocytes causing them to release glutamate9. Overactivation of bradykinin is thought to play a role in a rare disease called Hereditary Angioedema, also known as Hereditary Angio-Neurotic Edema10.
Some analogs of bradykinin have been found to have prolonged hypotensive action compared to bradykinin (Eg: beta-H-Pro-bradykinin)3. Some analogs have relative or even lower potencies compared to bradykinin (Eg: HArg1-Bradykinin and HArg9 Bradykinin)7. Other analogs have been studied for their potential of finding bradykinin antagonists that might be useful in the treatment of angio-neurotic edema.
References
1. Partridge, SM (1948). (Title or abstract not available), Biochem. J., 42, 238.
2. Allen PK, Kusumam J, Yoji S, Yoshitaka N, Berhane G, Sesha R and Michael S (1998). Bradykinin formation: Plasma and tissue pathways and cellular interactions. Clinical reviews in allergy and immunology, 16, 4, 403-429.
3. Ondetti MA, Engel SL (1975). Bradykinin analogs containing beta.-homoamino acid, J. Med. Chem.,18 (7), 761–763.
4. Roseli A, Gomes S, Jair RC, Luis J and Valdemar H (1996). Met-Lys-Bradykinin-Ser, the kinin released from human kininogen by human pepsin. Immunopharmacology, 32, 76-79.
5. Peter GM, Amrita A, and Mauro P (2000). Association between Kinin B1 Receptor Expression and Leukocyte Trafficking across Mouse Mesenteric Postcapillary Venules. J Exp. Med., 192, 367-380.
6. Duchene J, Lecomte F, Ahmed S, Cayla C, Pesquero J, Bader M, Perretti M and Ahluwalia A, (2007). A Novel Inflammatory Pathway Involved in Leukocyte Recruitment: Role for the Kinin B1 Receptor and the Chemokine CXCL5. J Immunol., 179, 4849-4856.
7. Max ES, Phyllis AL (1974). Synthesis and pharmacology of homoarginine bradykinin analog. J. Med. Chem., 17 (11), pp 1227–1228.
8. Dendorfer A, Wolfrum S, Wagemann M, Qadri F, Dominiak P, (2001). Pathways of bradykinin degradation in blood and plasma of normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol., 280:H2182
9. Kuoppala A, Lindstedt KA, Saarinen J, Kovanen PT, Kokkonen JO (2000). Inactivation of bradykinin by angiotensin-converting enzyme and by carboxypeptidase N in human plasma. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 278(4):H1069-74.
10. Bas M, Adams V, Suvorava T, Niehues T, Hoffmann TK, Kojda G (2007). Nonallergic angioedema: role of bradykinin. Allergy, 62(8):842-56.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.3892/or.2014.3366 | Bradykinin stimulates IL-6 production and cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.autneu.2015.07.006 | Afferent fibers involved in the bradykinin-induced cardiovascular reflexes from the ovary in rats | 下载 |
| 10.1159/000438526 | Exogenous Bradykinin Inhibits Tissue Factor Induction and Deep Vein Thrombosis via Activating the eNOS/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling Pathway | 下载 |
| 10.1161/01.cir.95.5.1115 | Role of bradykinin in mediating vascular effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in humans | 下载 |
多肽H2N-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg-COOH的合成步骤:
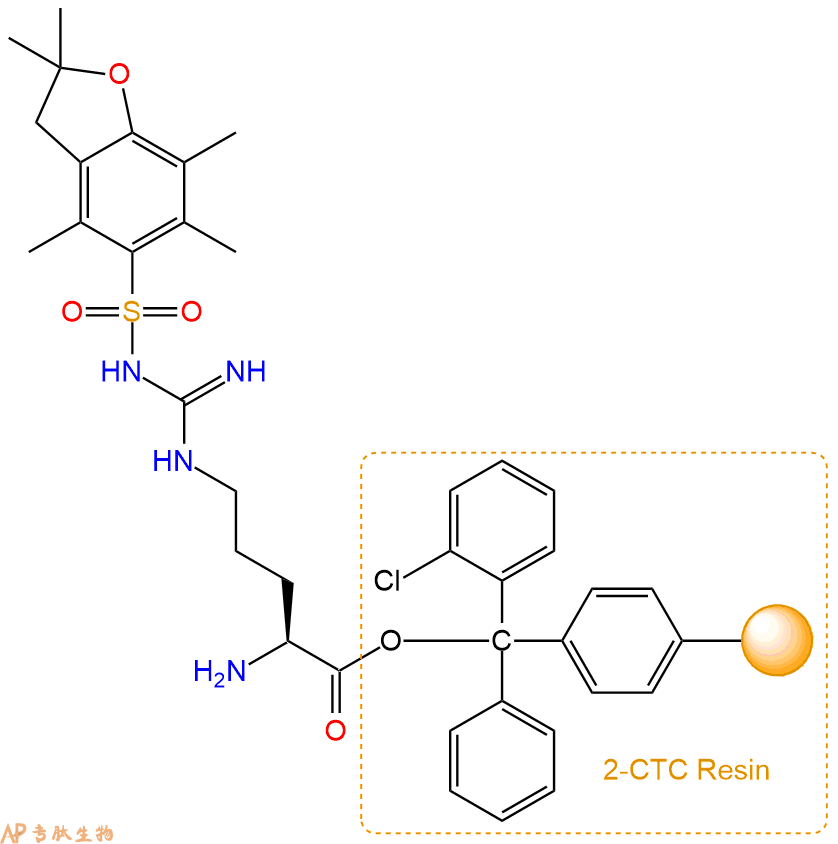
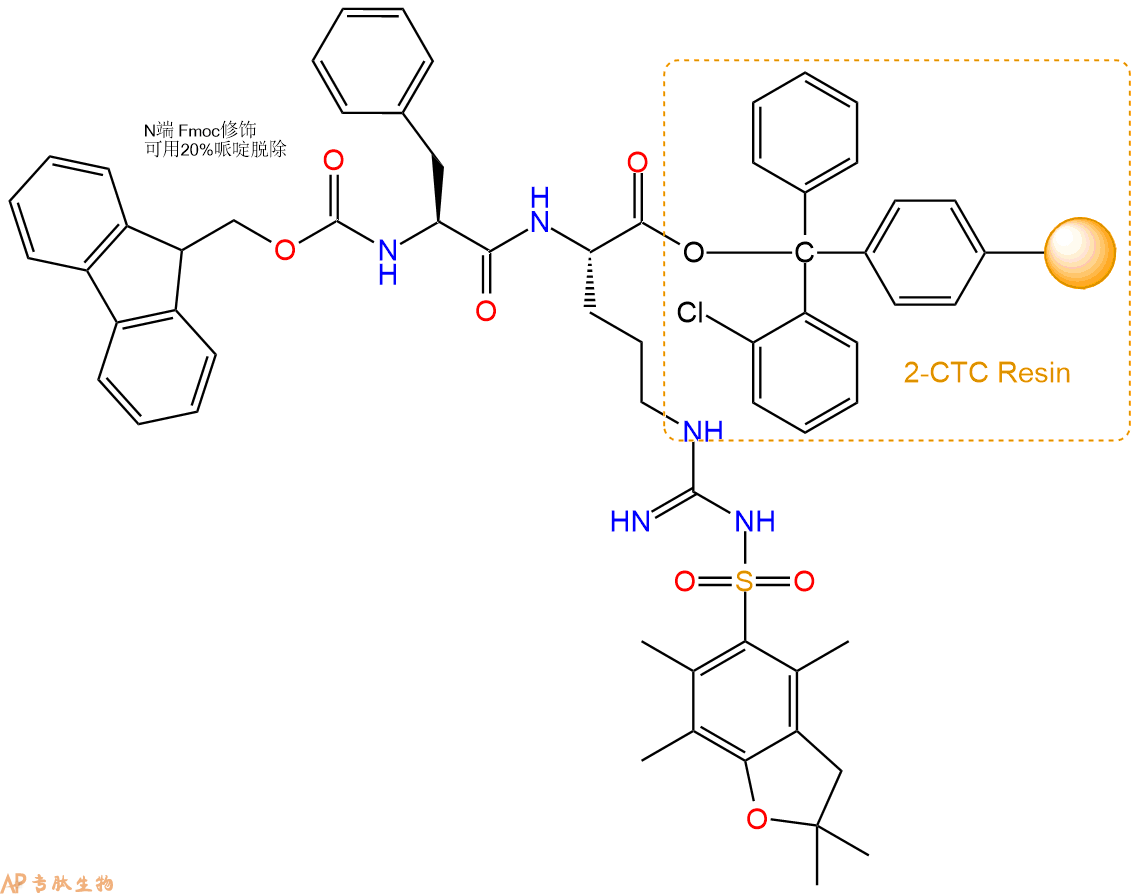
1、合成CTC树脂:称取0.17g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为0.65mmol/g)和0.13mmol Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入0.33mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
3、缩合:取0.33mmol Fmoc-Phe-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入0.66mmol DIPEA,0.31mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
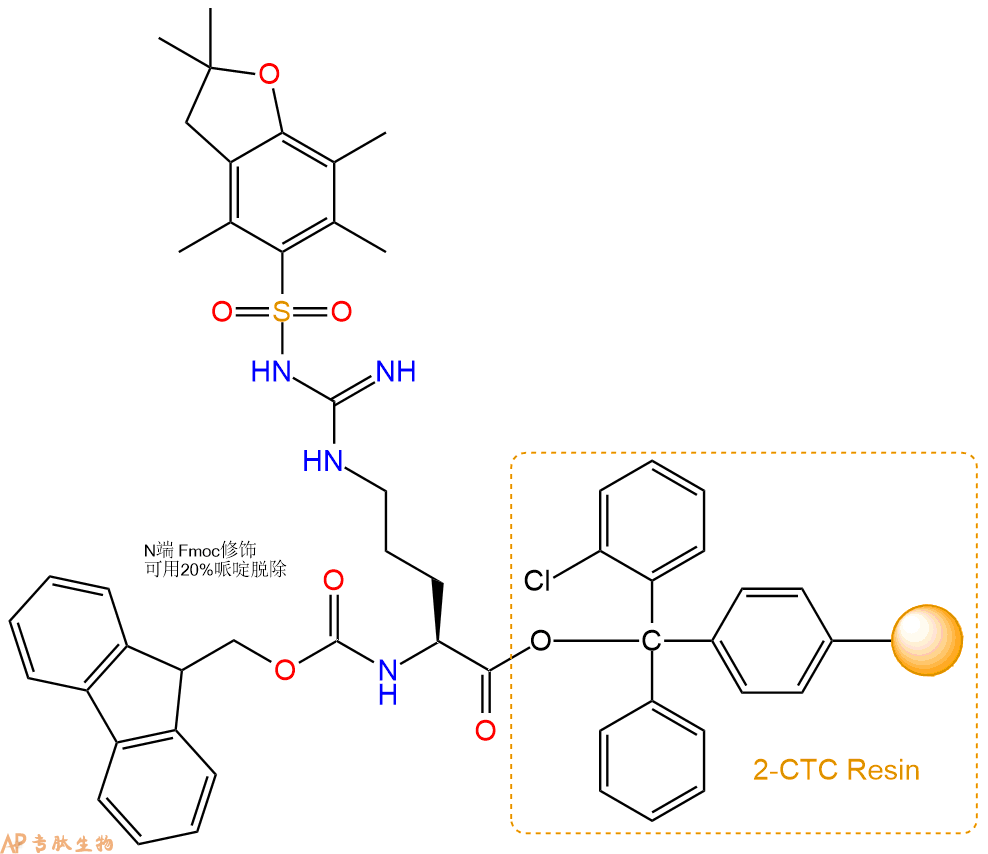
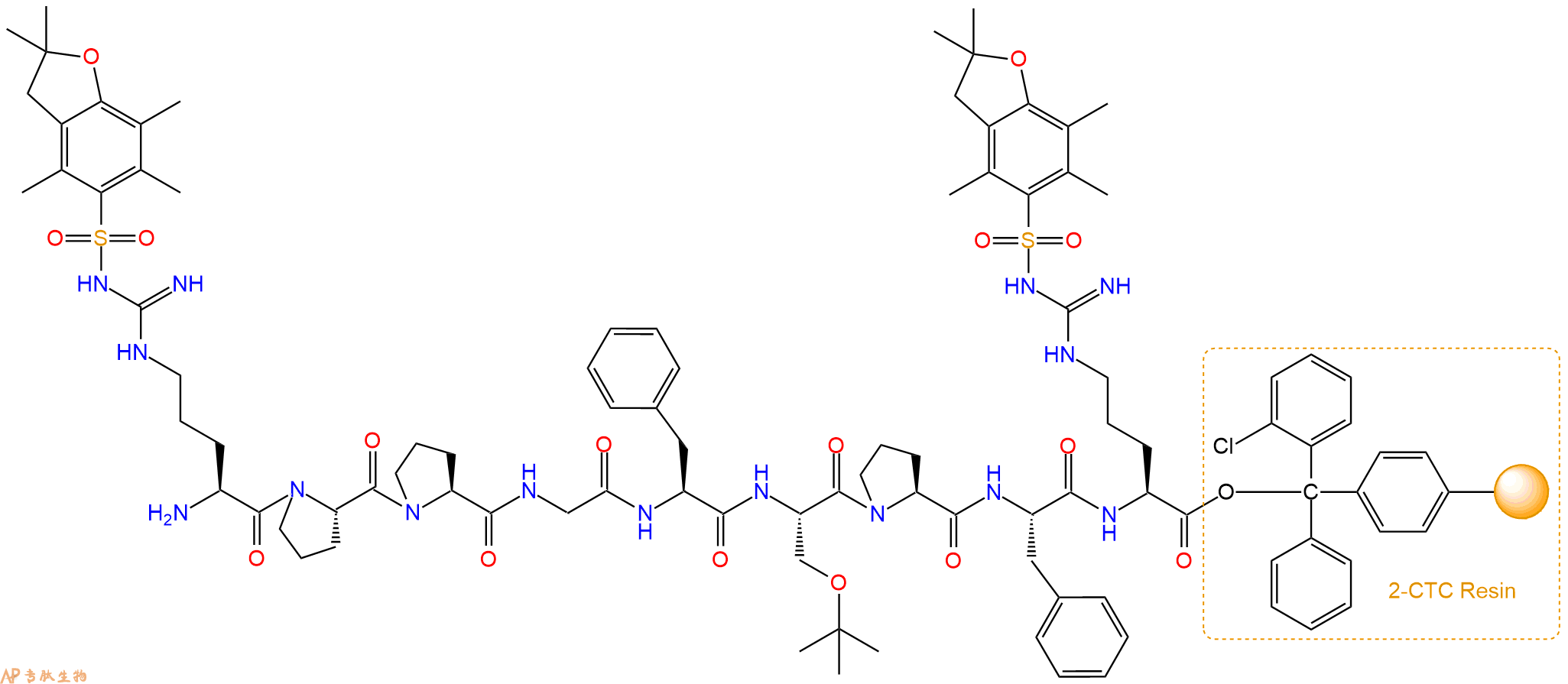
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Phe-Arg(Pbf)-CTC Resin,结构如下:
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%、TFA:H2O=97.5%:2.5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。