Katacalcin (PDN 21) 是一种有效的具有降低血钙效应的多肽激素。
编号:186322
CAS号:85916-47-8
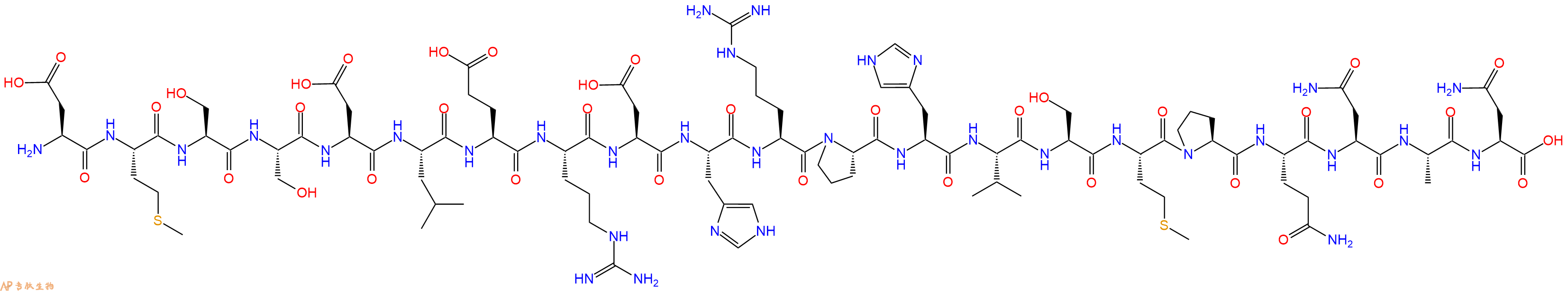
单字母:H2N-DMSSDLERDHRPHVSMPQNAN-OH
| 编号: | 186322 |
| 中文名称: | 钙抑肽、Katacalcin |
| 中文同义词: | 抗钙素 |
| 英文名: | Katacalcin |
| CAS号: | 85916-47-8 |
| 单字母: | H2N-DMSSDLERDHRPHVSMPQNAN-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -His组氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -His组氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Ala丙氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 21 |
| 分子式: | C97H154N34O36S2 |
| 平均分子量: | 2436.6 |
| 精确分子量: | 2435.07 |
| 等电点(PI): | 6.51 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | -0.55 |
| 酸性基团个数: | -1.8 |
| 碱性基团个数: | 亲水 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.63684210526316 |
| 疏水性值: | -1.52 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 闪点: | 0 M-1cm-1 |
| 消光系数: | - |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 降钙素(Calcitonins) |
Katacalcin (PDN 21) 是一种有效的具有降低血钙效应的多肽激素。
Katacalcin (PDN 21) is a potent plasma calcium-lowering peptide[1].
Definition
Calcitonin is a 32-amino acid linear polypeptide hormone produced primarily by the parafollicular cells in humans and ultimobranchial body in many other animals1. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Calcitonin is a product of the CALC1 gene and is initially produced as a precursor1.
Discovery
Calcitonin was purified in 1962 by Copp and Cheney2. While it was initially considered a secretion of the parathyroid glands, it was later identified as the secretion of the C-cells of the thyroid gland 3 .
Classification
CALC1 gene belongs to a superfamily of related protein hormone precursors that includes islet amyloid precursor protein, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and the precursor of adrenomedullin 4 .
Structural Characteristics
Human calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide and is formed from procalcitonin (Cleavage products: Calcitonin, Katalin and a protein fragment)5. It has an N-terminal disulphide bridge and a C-terminal proline amide residue, shown to potently inhibit bone resorption5. Alternative splicing of the gene coding for calcitonin produces a distantly related peptide of 37 amino acids, called calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) 5.
Mode of action
Calcitonin exerts its functions by binding to calcitonin receptor that is a G-protein coupled receptor. Upon binding, the receptor triggers the formation of cAMP, a second messenger which in turn activates various signaling pathways in the target cell (Eg: Osteoblasts) 6 .
Functions
Calcitonin is mainly involved in the metabolism of Ca and phosphorous in the cell. Calcitonin secretion is stimulated by rise in Ca levels in the body. It inhibits Ca intake by the intestine and also prevent loss of Ca from the bones during pregnancy and lactation7It also inhibits osteoclast activity in the bones8. This property of calcitonin is utilized for treatment of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis and recently has been tried for bone metastasis1.Procalcitonin is released during severe infection where it is involved in Ca homeostasis. It is also used as a marker for sepsis8.
References
1. Inzerillo AM, Zaidi M, Huang CL (2004). Calcitonin: physiological actions and clinical applications. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab., 17(7), 931-40.
2. Copp DH, Cheney B (1962). Calcitonin-a hormone from the parathyroid which lowers the calcium-level of the blood. Nature, 193, 381–2.
3. Stevenson JC, Evans IM (1981). Pharmacology and therapeutic use of calcitonin. Drugs, 21(4), 257-72.
4. Zaidi M, Inzerillo AM, Moonga BS, Bevis PJ, Huang CL (2002). Forty years of calcitonin--where are we now? A tribute to the work of Iain Macintyre, FRS, Bone, 30(5), 655-63.
5. Andreotti G, Méndez BL, Amodeo P, Morelli MA, Nakamuta H, Motta A (2006). "Structural determinants of salmon calcitonin bioactivity: the role of the Leu-based amphipathic alpha-helix". J. Biol. Chem., 281 (34), 24193–203.
6. Purdue BW, Tilakaratne N, Sexton PM (2002). Molecular pharmacology of the calcitonin receptor. Recept. Channels, 8 (3-4), 243–55.
7. Woodrow JP, Sharpe CJ, Fudge NJ, Hoff AO, Gagel RF, Kovacs CS (2006). Calcitonin plays a critical role in regulating skeletal mineral metabolism during lactation. Endocrinology, 147(9), 4010-21.
8. BalcI C, Sungurtekin H, Gürses E, Sungurtekin U, Kaptanoglu B (2003). Usefulness of procalcitonin for diagnosis of sepsis in the intensive care unit. Crit Care, 7 (1), 85–90
Definition
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide with potent receptor mediated vasodilatory and cardioexcitatory properties1.
Discovery
It was discovered when alternative processing of RNA transcripts from the calcitonin gene were shown to result in the production of distinct mRNAs encoding CGRP2. A human form of CGRP was isolated from thyroid tissue of patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma3.
Classification
CGRP belongs to the regulatory-peptide family that also includes adrenomedullin and amylin4.
Structural Characteristics
CGRP consists of an amino-terminal disulphide bridge linked loop between amino acids 2 and 7 followed by alpha helix between amino acids 8 and 18 and a poorly defined turn between residues 19 and 215. The carboxy and amino terminals of CGRP can interact independently with its receptors5.
Mode of action
CGRP exerts its function by binding to two G-protein coupled receptors, CGRP1 and CGRP2. One of the major functions of CGRP is vasodilation of cardiac muscles5. In order to achieve this, CGRP first binds to CGRP1 receptor which results in the production of cAMP which in turn activates Protein Kinase A (PKA)6. PKA phosphorylates and opens potassium channels that cause relaxation of muscles6.
Functions
CGRP is widely distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems5. It produces vascular relaxation via binding to CGRP1 receptor5. Studies in mice have shown that CGRP may play a role in controlling blood pressure5. CGRP also protects tissue injury through its vasodilatory functions. Through its activity as a vasodilator, CGRP influence the activity of inflammatory cells by recruiting more cells at the site of inflammation7. CGRP plays a role in migraine as it is found that its levels raise during painful phases of the disease8. CGRP plays a protective role in cardiac tissue. The infusion of CGRP is beneficial in increasing cardiac output and lowering blood pressure in patients with congestive heart failure5.
References
1. Tortorella C, Macchi C, Forneris M and Nussdorfer GG (2001). Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), acting via CGRP type 1 receptors, inhibits potassium-stimulated aldosterone secretion and enhances basal catecholamine secretion from rat adrenal gland. Int. J Mol. Med., 8(3), 261-4.
2. Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES and Evans RM (1982). Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature, 298, 240–244.
3. Aiyar N, Rand K, Elshourbagy NA, Zeng Z, Adamou JE, Bergsma DJ, and Li Y (1996). A cDNA encoding the Calcitonin Generelated peptide type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem., 271, 11325–11329.
4. Bell D and McDermott BJ (1996). Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the cardiovascular system: characterization of receptor populations and their (patho)physiological significance. Pharmacol Rev., 48, 253–288.
5. Susan DB and Andrew DG (2004). Vascular Actions of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide and Adrenomedullin. Physiol Rev., 84, 903-934.
6. Hirata Y, Takagi Y, Takata S, Fukuda Y, Yoshimi H, and Fujita T (1988). Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor in cultured vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun., 151, 1113–1121.
7. Lambrecht BN (2001). Immunologists getting nervous: neuropeptides, dendritic cells and T cell activation. Respir Res., 2, 133–138.
8. Durham, P (2006). Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and migraine. Headache, 48: S3–8.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.10.1872 | Involvement of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase A and pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins in the migratory response of human CD14+ mononuclear cells to katacalcin | 下载 |
| 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91387-9 | Katacalcin: a new plasma calcium-lowering hormone | 下载 |