| 编号: | 131311 |
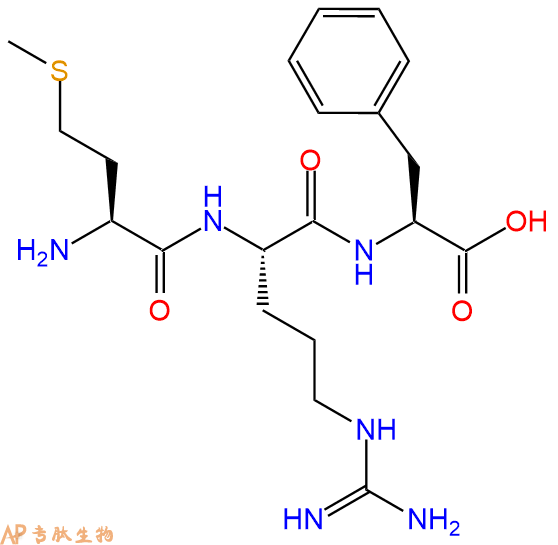
| 中文名称: | 三肽Met-Arg-Phe |
| 英文名: | Met-Arg-Phe |
| CAS号: | 67368-25-6 |
| 单字母: | H2N-MRF-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 3 |
| 分子式: | C20H32N6O4S1 |
| 平均分子量: | 452.57 |
| 精确分子量: | 452.22 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 1.97 |
| 平均亲水性: | -0.26666666666667 |
| 疏水性值: | 0.07 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 消光系数: | - |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 生成周期: | 2-3周 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 酶底物肽(Substrate Peptide) 三肽 FMRF/RFamide 多肽 |
Caspase酶对应的底物,Caspases(半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶,半胱氨酸依赖性天冬氨酸定向蛋白酶)是一类蛋白酶家族,其功能与凋亡(程序性细胞死亡),坏死和发烧(炎症)的过程密切相关。
什么是胱天蛋白酶?
胱天蛋白酶(Caspases)是含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶,它们是为细胞凋亡的主要介质。多种受体,例如TNF-α 受体,FasL受体,TLR和死亡受体,以及Bcl-2和凋亡抑制剂(IAP)蛋白家族参与并调节该caspase依赖性凋亡途径。一旦Caspase受到上游信号(外部或内在)刺激被激活,即会参与执行下游蛋白底物的水解作用,并触发一系列事件,导致细胞分解,死亡,吞噬作用和细胞碎片的清除。
人Caspases酶
人的Caspases家族基于序列相似性和生物学功能等共性主要可分为三大类:第一类由具有长胱天蛋白酶募集结构域的“炎症”胱天蛋白酶组成,他们对P4位上的较大的芳香族或疏水性残基具有亲和力。第二类由具有短的前体结构域的“细胞凋亡效应”胱天蛋白酶组成,而第三类由具有长的前提结构域的Pap位置具有亮氨酸或缬氨酸底物亲和力的“凋亡引发剂”胱天蛋白酶组成(表1)。
表1. 人胱天蛋白酶的功能分类:
| 细胞死亡途径 | 半胱天冬酶类型 | 酵素 | 物种 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 启动器 | Caspases 2 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 启动器 | Caspases 8 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 启动器 | Caspases 9 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 启动器 | Caspases 10 | 人的 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 效应器 | Caspases 3 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 效应器 | Caspases 6 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞凋亡 | 效应器 | Caspases 6 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞焦亡 | 炎性的 | Caspases 1 | 人与鼠 |
| 细胞焦亡 | 炎性的 | Caspases 4 | 人的 |
| 细胞焦亡 | 炎性的 | Caspases 5 | 人的 |
启动器Caspase和效应器Caspase酶
根据其在凋亡胱天蛋白酶途径中的作用,胱天蛋白酶可分为两类:启动器和效应器Caspase酶。启动器和效应器Caspas酶都具有由小亚基和大亚基组成的催化位点,Caspase酶的识别位

凋亡启动器Caspase酶,例如caspase-2,-8,-9和-10可以启动caspase激活级联反应。Caspase-8对于形成死亡诱导信号复合物(DISC)是必不可少的,并且在激活后,Caspase-8激活下游效应子Caspase(例如Caspase 3)并介导线粒体中细胞色素c的释放。Caspase-8已被证明对IETD肽序列具有相对较高的底物选择性。凋亡效应胱天蛋白酶例如Caspase-3,-6和-7虽然不负责启动级联途径,但是当被激活时,它们在级联的中间和后续步骤中起着不可或缺的作用。Caspase-3(CPP32 / apopain)是关键效应器,因为它放大了来自启动器Caspase的信号,使用对Caspase-3有选择性的DEVD肽序列对活化的Caspase-3进行检测,可以检测Caspase-3的活性。
Caspase酶底物和抑制剂
Caspase底物和抑制剂由两个关键成分组成:Caspase识别序列和信号产生或蛋白酶抑制基序。不同Caspase识别序列不同,一般由三个或四个氨基酸组成(表2)。Caspase酶识别序列的N端通常有乙酰基(Ac)或碳苯甲氧基(Z)基团修饰,以增强膜的通透性。对应的Caspase识别特定的肽序列为其酶促反应切割位点,释放产生信号或抑制信号的基序。Caspase的显色和荧光底物均以相似的方式起作用,其中底物的信号或颜色强度与蛋白水解活性成正比。
表2. Caspase的底物及其序列
| 多肽 | 氨基酸序列 | 对应的Caspase的种类 |
| IETD | Ile-Glu-Thr-Asp | Caspase 8,颗粒酶B |
| DEVD | Asp-Glu-Val-Asp | Caspase 3、6、7、8或10 |
| LEHD | Leu-Glu-His-Asp | Caspase 9 |
| VAD | Val-Ala-Asp | Caspase 1、2、3、6、8、9或10 |
Caspase酶的显色底物
Caspase的显色底物是有Caspase识别序列及生色基团组成,常见的生色团有pNA(对硝基苯胺或4-硝基苯胺),可使用酶标仪或分光光度计在405 nm处进行光密度检测。
表3. Caspase的显色底物
| 底物 | Caspase | 吸收(nm) | 颜色 |
| Ac-DEVD-pNA * CAS 189950-66-1 * | 半胱天冬酶3 | 405 nm | 黄色 |
| Z-DEVD-pNA | 半胱天冬酶3 | 405 nm | 黄色 |
| Z-IETD-pNA * CAS 219138-21-3 * | 半胱天冬酶8,颗粒酶B | 405 nm | 黄色 |
Caspase的荧光底物
Caspase的荧光底物的结构包含与半胱天冬酶识别相关的荧光团,例如7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素(AMC),7-氨基-4-三氟甲基香豆素(AFC), Rhodamine 110(R110)或ProRed™620。R110的Caspase底物比基于香豆素的Caspase底物(例如AMC和AFC)更敏感,但由于两步裂解过程,其动态范围更窄。 建议将R110标记的Caspase底物用于终点法测定,而将AMC和AFC标记的 Caspase底物用于动力学测定。

图.从左到右,分别是AMC(7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素),AFC(7-氨基-4-三氟甲基香豆素),Rhodamine 110(R110)和ProRed™620的激发和发射光谱。
表4.荧光半胱天冬酶底物。
| 底物名称 | 对应的Caspase | Ex(nm) | Em(nm) | ε¹ | Φ² |
| Ac-DEVD-AFC * CAS 201608-14-2 * | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 376 | 482 | 17000 | 0.53 |
| Ac-DEVD-AMC * CAS 169332-61-0 * | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 341 | 441 | 19000 | N / D |
| Z-DEVD-AFC | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 376 | 482 | 17000 | 0.53 |
| Z-DEVD-AMC * CAS 1135416-11-3 * | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 341 | 441 | 19000 | N / D |
| Z-DEVD-ProRed™620 | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 532 | 619 | N / D | N / D |
| (Z-DEVD)2 -R110 * CAS 223538-61-2 * | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 500 | 522 | 80000 | N / D |
| Z-DEVD-ProRed™620 | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 532 | 619 | N / D | N / D |
| Ac-IETD-AFC * CAS 211990-57-7 * | 半胱天冬酶8,颗粒酶B | 376 | 482 | 17000 | 0.53 |
| Z-IETD-AFC * CAS 219138-02-0 * | 半胱天冬酶8,颗粒酶B | 376 | 482 | 17000 | 0.53 |
注意:
1.ε=在其最大吸收波长处的摩尔消光系数(单位= cm -1M -1)。
2.Φ=水性缓冲液(pH 7.2)中的荧光量子产率。
Caspase抑制剂
Caspase抑制剂能与Caspase的活性位点结合并形成可逆或不可逆的连接,通常,Caspase抑制剂的结构由Caspase识别序列,诸如醛(-CHO)或氟甲基酮(-FMK)的官能团组成。具有醛官能团的胱天蛋白酶抑制剂是可逆的,而具有FMK的抑制剂是不可逆的。半胱天冬酶底物和抑制剂都具有较小的细胞毒性作用,因此,它们是研究半胱天冬酶活性的有用工具。
表5. 可逆和不可逆的Caspase酶抑制剂
| 抑制剂 | Caspase的种类 | 是否可逆 | Ex(nm) | Em(nm) |
| Ac-DEVD-CHO * CAS 169332-60-9 * | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 可逆的 | -- | -- |
| Ac-IETD-CHO * CAS 191338-86-0 * | 半胱天冬酶8 | 可逆的 | -- | -- |
| mFluor™450-VAD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶1,2,3,6,8,9,10 | 不可逆的 | 406 | 445 |
| mFluor™510-VAD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶1,2,3,6,8,9,10 | 不可逆的 | 412 | 505 |
| FITC-C6-DEVD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 不可逆的 | 491 | 516 |
| FITC-C6-DEVD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶3、7 | 不可逆的 | 491 | 516 |
| FITC-C6-LEHD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶9 | 不可逆的 | 491 | 516 |
| FITC-C6-LEHD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶9 | 不可逆的 | 491 | 516 |
| FAM-VAD-FMK | 半胱天冬酶1,2,3,6,8,9,10 | 不可逆的 | 493 | 517 |
| SRB-VAD-FMK [磺胺丁胺B-VAD-FMK] | 半胱天冬酶1,2,3,6,8,9,10 | 不可逆的 | 559 | 577 |
Definition
Neuropeptides with the Arg-Phe-amide motif at their C termini (RFamide peptides) were identified in the brains of several vertebrates, and shown to have important physiological roles in neuroendocrine, behavioral, sensory, and autonomic functions.
Discovery
Price DA, Greenberg MJ in 1977 studied the structure of a molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide. Neuropeptides with Arg-Phe-amide (RFamide) motif at their C termini, which were found in the ganglia of the venus clam, (FMRFamide), have been identified in the brains of several vertebrates and referred to as RFamide peptide(s). A chicken pentapeptide (LPLRFPamide) has also been isolated from its brain. Two pain modulatory neuropeptides [FF and AF], prolactin-releasing peptide (PrRP), gonadotropin- inhibitory hormone,and GH-releasing peptide are also RFamide peptides. To date, these RFamide-peptides have had important physiological roles in neuroendocrine, behavioral, sensory, and autonomic functions. Two PrRPs consisting of 31 amino acids (PrRP31) and 20 amino acids (PrRP20) from bovine hypothalamus extract were potent stimulators of prolactin (PRL) release as an endogenous ligand of an orphan G protein-coupled receptor (hGR3). Immunocytochemical studies showed that, in rat, PrRP cell bodies were located in the brain and hypothalamus, and that their nerve fibers projected into a wide range of areas in the brain 1,2,3.
Structural Characteristics
FMRF-amide-related peptides (FaRPs) are small peptides of 4–18 amino acids with RFamide (arg-phe-NH2) at the C terminus. Neuropeptides with the Arg-Phe-amide motif at their C termini (RFamide peptides) were identified in the brains of several vertebrates. Moriyama S et al., (2007) identified RFamide peptides, which are teleost prolactin-releasing peptide (PrRP) homologs, in the sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus and characterized their effect on the release of pituitary hormones in vitro. Two RFamide peptides (RFa-A and RFa-B) were isolated from an acid extract of sea lamprey brain, including hypothalamus by Sep-Pak C18 cartridge, affinity chromatography using anti-salmon PrRP serum, and reverse-phase HPLC on an ODS-120T column. Amino acid sequences and mass spectrometric analyses revealed that RFa-A and RFa-B consist of 25 and 20 aa, respectively, and have 75% sequence identity within the C-terminal 20 aa. The RFa-B cDNA encoding a preprohormone of 142 aa was cloned from the lamprey brain, and the deduced aa sequence from positions 48–67 was identical to the sequence of RFa-B 4.
Mode of Action
The potency (muscle force-generated) of a number of long-chain RFamide neuropeptides has been examined. Many of the heptapeptides, octapeptides and the decapeptide LMS were found to induce greater contraction than FMRFamide in both smooth muscles and in both species. RFamide neuropeptides interacted with the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in an additive way and RFamide-induced contractions were inhibited by the neuromodulator serotonin. Pre-treatment with a calcium-free saline completely abolished acetylcholine-induced responses but only partially inhibited RFamide responses in the muscles, suggesting that acetylcholine acts to cause influx of extracellular calcium for contraction. Result suggests that an additional involvement of a fast calcium channel is present in the RFamide responses. Force regulation in these muscles appears to result from a complex interaction of RFamide neuropeptides with the primary transmitter acetylcholine and the neuromodulator serotonin 5.
Unlike in mammals, a few RFamide peptide fibers were projected to the pituitary, and terminated close to PRL producing cells in the rostral pars distalis (RPD) and to the somatolactin somatolactin (SL)-producing cells in the pars intermedia (PI) in rainbow trout. On the basis of the localization of salmon RFamide peptide, compared its hypophysiotropic effects on the release of three evolutionarily related hormones, PRL and SL. Salmon RFamide peptide stimulated PRL release from the pituitary both in vivo and in vitro, as well as in tilapia. Salmon RFamide peptide also affected SL releases from the pituitary 6,7.
Functions
Regulation of PRL release, these results indicate that RFamide peptide is a major hypothalamic peptide involved in the regulation of PRL release and that this peptide may exist throughout vertebrate evolution 6.
RFamide during the development of a primary polyp, antisera to the sequence Arg-Phe-amide (RF-amide) have a high affinity to the nervous system of fixed hydroid polyps. Incubation of Hydractinia echinata gastrozooids with RFamide antisera visualizes an extremely dense plexus of neuronal processes in body and head regions. A ring of sensory cells around the mouth opening is the first group of neurons to show RFamide immunoreactivity during the development of a primary polyp 8.
Two RFamide peptides in lamprey were identified, which are structurally related to teleost PrRP, by peptide isolation and cDNA cloning from lamprey brain/hypothalamus. Evidence suggests that RFamide peptides are major hypothalamic and/or pituitary peptides that may be involved in inhibition of GH and MSH release in lamprey 4.
References
1. Price DA, Greenberg MJ (1977). Structure of a molluscan cardioexcitatory neuropeptide. Science, 197:670–671.
2. Dockray GJ, Reeve Jr JR, Shively J, Gayton RJ, Barnard CS (1983). A novel active pentapeptide from chicken brain identified by antibodies to FMRFamide. Nature, 305:328-330.
3. Yang HY, Fratta W, Majane EA, Costa E (1985). Isolation, sequencing, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of two brain neuropeptides that modulate the action of morphine. PNAS., 82:7757-77614.
4. Moriyama S, Kasahara M, Amiya N, Takahashi A, Amano M, Sower SA, Yamamori K, Kawauchi H (2007). RFamide peptides inhibit the expression of melanotropin and growth hormone genes in the pituitary of an Agnathan, the sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus. Endocrinology, 148(8):3740-3749.
5. Moulis A, Huddart H (2004). RFamide neuropeptide actions on molluscan proboscis smooth muscle: interactions with primary neurotransmitters J Comp Physiol B., 174(5):363-370.
6. Moriyama S, Ito T, Takahashi A, Amano M, Sower SA, Hirano T, Yamamori K, Kawauchi H (2002). A homolog of mammalian PRL-releasing peptide (fish arginyl-phenylalanyl-amide peptide) is a major hypothalamic peptide of PRL release in teleost fish. Endocrinology, 143:2071-2079.
7. Sakamoto T, Agustsson T, Moriyama S, Itoh T, Takahashi A, Kawauchi H, Björnsson BT, Ando M (2003). Intra-arterial injection of prolactin-releasing peptide elevates prolactin gene expression and plasma prolactin levels in rainbow trout. J Comp Physiol., 173:333-337.
8. Grimmelikhuijzen CJP (1985). Antisera to the sequence Arg-Phe-amide visualize neuronal centralization in hydroid polyps. Cell and Tissue Research., 241(1):171-182.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02716 | Salt Taste Enhancing l-Arginyl Dipeptides from Casein and Lysozyme Released by Peptidases of Basidiomycota | 下载 |