万密密副教授课题组在ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES发表研究论文
Erythrocyte Membrane-Wrapped Magnetic Nanotherapeutic Agents for Reduction and Removal of Blood Cr(VI)
Wang, M (Wang, Meng)[ 1 ] ; Yan, WQ (Yan, Wenqiang)[ 2 ] ; Chu, ML (Chu, Meilin)[ 1 ] ; Li, T (Li, Ting)[ 1 ] ; Liu, ZY (Liu, Zhiyong)[ 1 ] ; Yu, YQ (Yu, Yueqi)[ 1 ] ; Huang, YY (Huang, Yangyang)[ 1 ] ; Zhu, TY (Zhu, Tianyu)[ 1 ] ; Wan, MM (Wan, Mimi)[ 1 ]*(万密密); Mao, C (Mao, Chun)[ 1 ] ; Shi, DQ (Shi, Dongquan)[ 2 ]*
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Natl & Local Joint Engn Res Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Nanjing 210023, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Nanjing Univ, Nanjing Drum Tower Hosp, Affiliated Hosp, Med Sch,Dept Sports Med & Adult Reconstruct Surg, Nanjing 210008, Peoples R China
ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES,202006,12(25),28014-28023
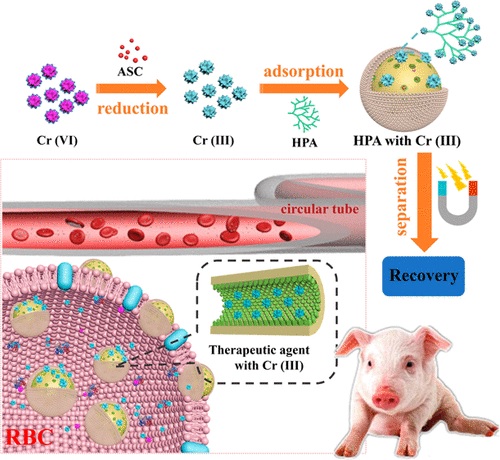
The hazard of hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) from environmental pollution and medical implanted metal has been recognized widely. However, removal of trace amount of Cr(VI) in the blood circumstance faces tremendous difficulties for that most of Cr(VI) located in erythrocytes, thus there is almost no literature to report the removal of Cr(VI) in blood. Herein, a removal strategy, named as reduction-adsorption-separation, is proposed to realize the removal of Cr(VI) in blood. First, magnetic core-shell mesoporous nanocomposite is fabricated by using Fe3O4 nanoparticles as magnetic core and mesoporous silica (MS) as shell, hyperbranched polyamide (HPA) as mesoporous channel modifier and ascorbic acid (ASC) as the reductant drug loaded in the mesoporous channels, which is also denoted as Fe/MS/HPA/ASC. Then, on the basis of the bionic idea, the erythrocyte membrane (EM)-wrapped Fe/MS/HPA/ASC to protect ASC from deactivation is obtained and named as the therapeutic agent (Fe/MS/HPA/ASC@EM). During removal process, the therapeutic agent can enter in erythrocytes to use ASC to reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III) and HPA in mesoporous channels to adsorb Cr(III) and can then be recollected from blood by magnetic separation. Finally, an animal model of blood Cr(VI) poisoning is constructed and used to test the removal ability of Cr(VI) from pig blood in vivo, verifying the effectiveness of this blood Cr(VI) removal strategy, providing a possible way to design more efficient and biosafe therapeutic agents for blood purification.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.0c06437
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com