李亚飞教授课题组在ACS SUSTAINABLE CHEMISTRY & ENGINEERING发表研究论文
Two-Dimensional Metal Hexahydroxybenzene Frameworks as Promising Electrocatalysts for an
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Zhang, J (Zhang, Juan)[ 2 ] ; Zhou, ZP (Zhou, Zhenpei)[ 2 ] ; Wang, F (Wang, Fei)[ 2 ] ;
Li, YF (Li, Yafei)[ 1 ]*(李亚飞); Jing, Y (Jing, Yu)[ 2 ]*
[ 1 ]Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct
Mat, Jiangsu Key Lab New Power Batteries, Nanjing 210023, Peoples R China
[ 2 ]Nanjing Forestry Univ, Coll Chem Engn, Jiangsu Coinnovat Ctr Efficient Proc & Utilizat
F, Nanjing 210037, Peoples R China
ACS SUSTAINABLE CHEMISTRY & ENGINEERING,202005,8(19),7472-7479
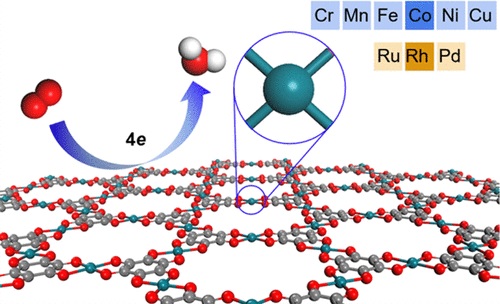
Exploring efficient and inexpensive electrocatalysts for a cathode oxygen reduction
reaction (ORR) is essential to the large-scale commercialization of fuel cells. Via first
principles calculations, we systematically investigated the electrocatalytic performance of
two-dimensional (2D) metal-hexahydroxybenzene frameworks (M-3(C6O6 )(2), where M denotes
Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Ru, Rh, and Pd) for ORR. Owing to the sufficient Jr-electron
conjugation and effective interaction between the metal and the organic linkers, the
studied 2D M-3(C6O6)(2) are all metallic with good conductivity for electron transfer.
Interestingly, the catalytic activity of M-3(C6O6)(2) turns out to be dependent on the
interaction strength between the ORR intermediates and the metal complex (MO4) and can be
modified by changing the metal atoms with different d-electron occupations. Remarkably,
while 2D Mn-3(C6O6)(2), Fe-3(C6O6)(2), and Rh-3(C6O6)(2) show a rather good ORR activity
rivaling that of Pt, 2D Co-3(C6O6)(2) presents a much higher onset potential than that of
Pt. Our investigations provide important insights into designing and screening efficient
ORR catalysts.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01908
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com