戴志晖教授课题组在SCIENCE CHINA-CHEMISTRY 发表研究论文
Component reconstitution-driven photoelectrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of Cu2+ based on advanced CuS/CdS p-n junction
Liu, J (Liu, Jing)[ 1 ] ; Liu, Y (Liu, Ying)[ 1 ] ; Wang, W (Wang, Wei)[ 1 ] ; Li, J (Li, Jing)[ 1 ] ; Yu, XY (Yu, Xinyuan)[ 1 ] ; Zhu, QS (Zhu, Qinshu)[ 1 ]*(朱钦舒) ; Dai, ZH (Dai, Zhihui)[ 1 ]*(戴志晖)
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
SCIENCE CHINA-CHEMISTRY,201910, DOI: 10.1007/s11426-019-9579-2
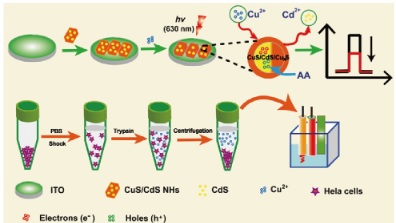
The rational design of robust photoactive material and artful sensing strategy are vital for the construction of an ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical (PEC) sensor. Although great progress has been made in PEC sensing, the resultant detection performances and adoptable sensing strategies are still limited. Herein, through the design of a subtle component reconstitution strategy, an ultrasensitive PEC sensor is developed for the detection of Cu2+ based on advanced CuS/CdS nanohybrids (NHs). This proposed sensor shows superior sensing performances with a low detection limit of 0.1 nM and a wide detection range from 0.2 nM to 60 mu M due to the formation of p-n junction between CuS and CdS and the component transformation of CdS to CuxS (x = 1,2). Moreover, such PEC sensor also displays goodish results for monitoring the Cu2+ released from apoptotic HeLa cells in vitro. This idea of component reconstitution provides a new paradigm for the design of advanced PEC sensors.
文章链接:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11426-019-9579-2
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com