刘犇教授课题组在CHEMICAL SCIENCE发表研究论文
Mesoporous gold nanospheres via thiolate-Au(I) intermediates
Lv, H (Lv, Hao)[ 1 ] ; Xu, DD (Xu, Dongdong)[ 1 ] ; Henzie, J (Henzie, Joel)[ 2,3 ] ; Feng, J (Feng, Ji)[ 4 ] ; Lopes, A (Lopes, Aaron)[ 5 ] ; Yamauchi, Y (Yamauchi, Yusuke)[ 2,6,7,8 ]*; Liu, B (Liu, Ben)[ 1 ]*(刘犇)
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Jiangsu Key Lab New Power Batteries, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Qingdao Univ Sci & Technol, Coll Chem & Mol Engn, Key Lab Ecochem Engn, Qingdao 266042, Shandong, Peoples R China
[ 3 ] NIMS, Int Ctr Mat Nanoarchitecton WPI MANA, 1-1 Namiki, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3050044, Japan
[ 4 ] Univ Calif Riverside, Dept Chem, Riverside, CA 92521 USA
[ 5 ] MIT, Dept Chem Engn, Cambridge, MA 02139 USA
[ 6 ] Univ Queensland, Sch Chem Engn, Brisbane, Qld 4072, Australia
[ 7 ] Univ Queensland, AIBN, Brisbane, Qld 4072, Australia
[ 8 ] Kyung Hee Univ, Dept Plant & Environm New Resources, 1732 Deogyeong Daero, Yongin 446701, Gyeonggi Do, South Korea
CHEMICAL SCIENCE,201907,10(26),6423-6430
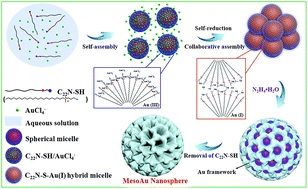
Mesoporous gold (mesoAu) nanospheres support enhanced (electro)catalytic performance owing to their three-dimensional (3D) interior mesochannels that expose abundant active sites and facilitate electron/mass transfers. Although various porous Nanostructured Au has been fabricated by electrochemical reduction, alloying-dealloying and hard/soft templating methods, successful synthesis of mesoAu nanospheres with tailorable sizes and porosities remains a big challenge. Here we describe a novel surfactant-directed synthetic route to fabricate mesoAu nanospheres with 3D interconnected mesochannels by using the amphiphilic surfactant of C22H45N+(CH3)(2)-C3H6-SH (Cl-) (C22N-SH) as the mesopore directing agent. C22N-SH can not only self-reduce trivalent Au(III)Cl-4(-) to monovalent Au(I), but also form polymeric C22N-S-Au(I) intermediates via covalent bonds. These C22N-S-Au(I) intermediates facilitate the self-assembly into spherical micelles and inhibit the mobility of Au precursors, enabling the crystallization nucleation and growth of the mesoAu nanospheres via in situ chemical reduction. The synthetic strategy can be further extended to tailor the sizes/porosities and surface optical properties of the mesoAu nanospheres. The mesoAu nanospheres exhibit remarkably enhanced mass/specific activity and improved stability in methanol electrooxidation, demonstrating far better performance than non-porous Au nanoparticles and previously reported Au nanocatalysts. The synthetic route differs markedly from other long-established soft-templating approaches, providing a new avenue to grow metal nanocrystals with desirable nanostructures and functions.
文章链接:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/SC/C9SC01728C#!divAbstract
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com