杨朕副教授、杨维本教授课题组在SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGY发表研究论文
Flocculation of different types of combined contaminants of antibiotics and heavy metals by thermo-responsive flocculants with various architectures
Hou, TY (Hou, Tianyang)[ 1 ] ; Du, HW (Du, Hongwei)[ 1 ] ; Yang, Z (Yang, Zhen)[ 1 ]*(杨朕); Tian, ZQ (Tian, Ziqi)[ 2 ] ; Shen, SC (Shen, Shichao)[ 1 ] ; Shi, YX (Shi, Yaxuan)[ 1 ] ; Yang, WB (Yang, Weiben)[ 1 ]*(杨维本); Zhang, LM (Zhang, Limin)[ 1 ]
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Jiangsu Prov Key Lab Mat Cycling & Pollut Control, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Chinese Acad Sci, Ningbo Inst Mat Technol & Engn, Ningbo 315000, Zhejiang, Peoples R China
SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGY,201909,223,123-132
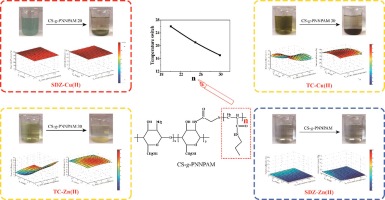
Combined contaminants of antibiotics and heavy metals in wastewater have caused global concern. Reusable flocculant CS-g-PNNPAM with different lengths of grafted thermo-responsive branches were synthesized for the removal of different types of combined contaminants (tetracycline-Cu(II), tetracycline-Zn(II), sulfadiazine-Cu (II), and sulfadiazine-Zn(II)) from wastewater. Response surface methodology was employed to study interactive effects among wastewater temperature (X-1), flocculant stock solution temperature (X-2) and flocculant dosage (X-3). The flocculation difficulty for different types of combined contaminants went with the sequence of sulfadiazine-Cu(II) < tetracycline-Cu(II) < tetracycline-Zn(II) < sulfadiazine-Zn(II), which was the opposite order of binding energies of antibiotic-heavy metals. This indicated combined contaminants with stronger binding interactions had the nature to be flocculated more easily. The optimal average length of grafted branches in the flocculant was obtained for each type of wastewater; Meantime, since it is not appropriate to manually adjust wastewater temperature (X-1) considering energy consumption aspects, operation strategies, by adjusting stock solution temperature (X-2) and flocculant dosage (X-3) to reach highest removal efficiencies of antibiotics and heavy metals, were respectively optimized for several fixed X-1 values, using statistical analysis of the results from jar tests. Finally, via a two-step method, antibiotics and heavy metals were sequentially recovered from flocs, and CS-g-PNNPAM was regenerated for further use, which follows the concepts of resource reutilization.
文章链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1383586619305611?via%3Dihub
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com