许冬冬副教授、刘犇教授课题组在GREEN CHEMISTRY发表研究论文
One-pot aqueous synthesis of ultrathin trimetallic PdPtCu nanosheets for the electrooxidation of alcohols
Lv, H (Lv, Hao)[ 1 ] ; Sun, LZ (Sun, Lizhi)[ 1 ] ; Xu, DD (Xu, Dongdong)[ 1 ]*(许冬冬); Suib, SL (Suib, Steven L.)[ 2,3 ] ; Liu, B (Liu, Ben)[ 1 ]*(刘犇)
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Jiangsu Key Lab New Power Batteries, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Univ Connecticut, Dept Chem, Storrs, CT 06269 USA
[ 3 ] Univ Connecticut, Inst Mat Sci, Storrs, CT 06269 USA
GREEN CHEMISTRY,201905,21(9),2367-2374
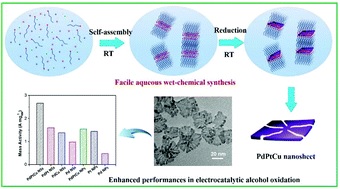
Due to their synergistic structural and compositional advantages, ultrathin multimetallic nanosheets are widely recognized as highly efficient electrocatalysts for alcohol electrooxidation. However, despite significant efforts, current synthetic strategies for the preparation of multimetallic nanosheets mainly focus on the reduction of metal precursors in organic solvents or in the presence of toxic CO. In this study, a one-pot aqueous synthesis method based on the self-assembly of the novel surfactant docosyltrimethyl-ammonium chloride was employed to produce ultrathin free-standing trimetallic PdPtCu nanosheets under ambient and eco-friendly conditions. No toxic chemicals or organic solvents were employed in this synthesis. The obtained PdPtCu nanosheets were ultrathin with a dendrite-like nanostructure (with an average thickness of similar to 3.5 nm) and alloyed crystalline features. The proposed synthetic strategy is also universally applicable for tuning the elemental ratios and compositions of ultrathin multimetallic nanosheets. Due to the multiple advantages of unique ultrathin dendrite nanostructures and multimetallic elemental compositions, the PdPtCu nanosheets exhibited remarkably enhanced performance in the electrooxidation of alcohols (methanol, ethanol, glycerol and glucose). The proposed one-pot eco-friendly synthetic concept could be used to build more multimetallic nanostructures with synergetic enhancement effects for a range of electrocatalytic applications.
文章链接:
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/GC/C9GC00741E#!divAbstract
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com