邱晓雨博士、唐亚文教授课题组在ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA发表研究论文
Construction of ultrasensitive ammonia sensor using ultrafine Ir decorated hollow graphene nanospheres
Zhang, HF (Zhang, Huaifang)[ 1,2 ] ; Wang, Y (Wang, Yao)[ 1,2 ] ; Zhang, BB (Zhang, Binbin)[ 1,2 ] ; Yan, YW (Yan, Yawei)[ 1,2 ] ; Xia, J (Xia, Jie)[ 1,2 ] ; Liu, XJ (Liu, Xuejiang)[ 1,2 ] ; Qiu, XY (Qiu, Xiaoyu)[ 1,2 ]*(邱晓雨); Tang, YW (Tang, Yawen)[ 1,2 ]*(唐亚文)
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Jiangsu Key Lab New Power Batteries, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Nanjing KaiYan Chem Co Ltd, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
ELECTROCHIMICA ACTA,201905,304,109-117
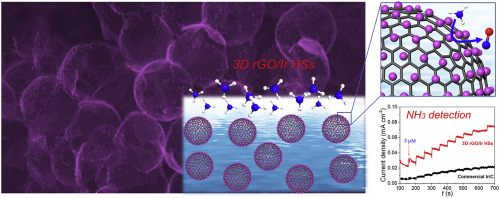
The study on electrochemical behavior of ammonia is a far-reaching topic, not only for its electro-oxidation elimination from effluent treatments, but also for detection of ammonia concentration by employing electrochemical sensors. Herein, we report a simple electro-chemical ammonia detector with high sensitivity/selectivity, superfast response, and long-time stability, using ultrafine Ir nanoparticles decorated 3D graphene hollow spheres. Morphological and structural analysis reveals that the inner ultrathin graphene shell effectively maximize the specific surface area and outer tiny Ir nanoparticles are optimal for offering active adsorption sites of NH3. Because of the well-defined morphology and 3D interconnected architecture, the rGO/Ir HSs modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) exhibits superior activity for the electro-oxidation of NH3 performed in neutral medium, which is 4 times higher than that of commercial Ir/C catalyst. The amperometry technique is served to investigate the ammonia-detected performance of the rGO/Ir HSs-modified GCE, demonstrating high sensitivity and quick response from wide linear range of 0.015-75mM (R-2 = 0.998) with a detection limit of 6.5 mu M. This work offers a new type of graphene-based nanohybrids to enhance the electro-oxidation and gas sensing abilities toward ammonia, leading to the development of manufacturing high-performance electro-analytical sensors.
文章链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013468619303743?via%3Dihub
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com