周宁琳教授课题组在CHEMISTRY OF MATERIALS发表研究论文
Multifunctional Nanocomposites for Targeted, Photothermal, and Chemotherapy
Zhang, M (Zhang, Ming)[ 1 ] ; Wu, F (Wu, Fan)[ 1 ] ; Wang, WT (Wang, Wentao)[ 1 ] ; Shen, J (Shen, Jian)[ 1 ] ; Zhou, NL (Zhou, Ninglin)[ 1 ]*(周宁琳); Wu, CZ (Wu, Changzhu)[ 2,3 ]*
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biol Funct Mat, Coll Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Key Lab Biofunct Mat, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Univ Southern Denmark, DIAS, DK-5230 Odense, Denmark
[ 3 ] Univ Southern Denmark, Dept Phys Chem & Pharm, DK-5230 Odense, Denmark
CHEMISTRY OF MATERIALS,201903,31(6), 1847-1859
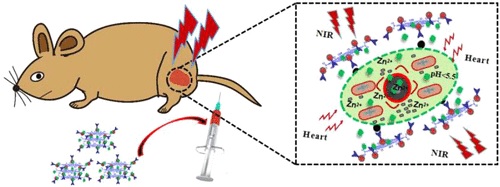
In the past decades, advances in nanoparticles (NPs) synthesis and engineering have greatly propelled the application of nanoscale agents for therapeutic and diagnostic functions, promoting an emerging field of "nanotheranostics". In particular, they are being increasingly exploited for cancer management, in which diagnosis and therapy are combined to address clinical challenges. In this work, core-shell-structured amorphous zinc oxide (a-ZnO) on gold NPs (Au-His@a-ZnO) was produced using histidine (His) to control the shell growth under hydrothermal conditions. Subsequently, Au-Hispa-ZnO NPs were integrated onto the planar structure of PEGylated graphene oxide (PEG-GO) via carbodiimide cross-linker chemistry. More importantly, strong absorption and near-infrared (NIR) emission in the range of 700 to 900 nm was observed with preferential uptake at tumors and high photothermal conversion efficiency (eta = 38%). Both in vitro and in vivo studies showed that the GO@Au-Hispa-ZnO NCs were biocompatible with low toxicity. Moreover, GO@Au-His@a-ZnO NCs were further conjugated with the antibody of epidermal growth factor receptor aptamer (anti-EGFR Apt) and doxorubicin (DOX), yielding Apt@GO@Au-His@a-ZnO@DOX NCs, which were then applied toward the synergetic treatment of lung cancer. The prepared Apt@GO@Au-Hispa-ZnO@DOX NCs showed a high loading capacity of DOX, as well as NIR/pH-sensitive drug release in which the metal-drug complex dissociated to release antitumor Zn2+ ions into the acidic endosome/lysosome. In addition, these materials also showed good biostability and anti-EGFR Apt-promoted binding specificity for lung cancer cells. The specific binding facilitated the cellular uptake into EGFR-mutated cancer sites, as compared with nontargeted controls. In particular, human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell (A549)-tumor bearing mice were selected as the animal model, and efficient targeted drug delivery and the high anticancer efficacy of Apt@GO@Au-Hispa-ZnO NCs in vivo were demonstrated. Taken together, our multifunctional NCs, Apt@GO@Au-His@a-ZnO@DOX NCs, have shown high efficacy in targeted, photothermal, and chemotherapy when applied to lung cancer. This proof-of-principle example suggests a fascinating perspective for these functional NCs for future clinical use.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org.ccindex.cn/doi/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00934
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com