周宁琳教授课题组在COLLOIDS AND SURFACES B-BIOINTERFACES 发表研究论文
Novel controlled drug release system engineered with inclusion complexes based on carboxylic graphene
Xiao, Yinghong[ 1 ]; Zhang, Ming[ 1 ]; Fan, Yunting[ 1 ]; Zhang, Qicheng[ 1 ]; Wang, Yuli[ 1 ]; Yuan, Wenwen[ 1 ]; Zhou, Ninglin*[ 1 ](周宁琳); Che, Jianfei[ 2 ]*
[ 1 ] Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Biomedical Functional Materials, School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, 210023, China
[ 2 ]School of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210094, China
COLLOIDS AND SURFACES B-BIOINTERFACES ,201903,175,18-25
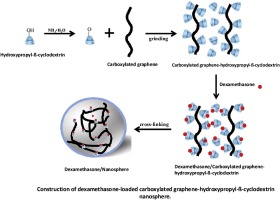
A novel drug carrier is constructed by compositing hydrophilic hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrins (HP-beta-CD) and carboxylated graphene nanomaterial (GO-COOH). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirms that the two materials are successfully combined via chemical bonds. Further, a crosslinking agent of glutaraldehyde is applied to fabricate composite GO-COO-HP-beta-CD nanospheres, as demonstrated by an atomic force microscope. Dexamethasone (DEX) is selected as the model drug, and the drug loading efficiency and water solubility of the nanospheres greatly increased. Additionally, the achieved DEX/nanosphere inclusion complex exhibits better heat resistance compared with pure DEX, which is a desired property for drug processing. More importantly, different models are applied to different releasing durations to investigate in detail the release profile of DEX. The best fitting release kinetics model is given to reveal the release mechanism of the drug delivery system. The highest hemolysis rate of the DEX/nanosphere inclusion is 0.44%, far lower than the standard of 5% delivered by the American Society for Testing and Materials, ensuring its safety in practical applications. Meanwhile, recalcification tests indicate that DEX/nanosphere retains the normal blood coagulation function. In vitro cytotoxicity tests of the inclusion demonstrate that the nanospheres have no toxicity and are qualified for intravenous applications with good blood compatibility. Finally, the bioactivity of DEX after release from the carriers is investigated. Results corroborate that the drug anti-inflammation efficacy is not affected and that the biomedical function can be well retained. The engineered controlled drug release system represents a promising formulation platform for a broad range of therapeutic medicine in pharmaceutical technology.
文章链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776518308403?via%3Dihub
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com