卫海燕教授课题组在ORGANOMETALLICS发表研究论文
Mechanism of Boron-Catalyzed N-Alkylation of Primary and Secondary Arylamines with Ketones Using Silanes under "Wet" Conditions
Chen, HC (Chen, Hongcai)[ 1 ] ; Yan, LN (Yan, Lina)[ 1 ] ; Wei, HY (Wei, Haiyan)[ 1 ]*(卫海燕)
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Jiangsu Prov Key Lab NSLSCS, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Key Lab Biofunct Mat, Nanjing 210097, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
ORGANOMETALLICS, 201811,37(21),3698-3707
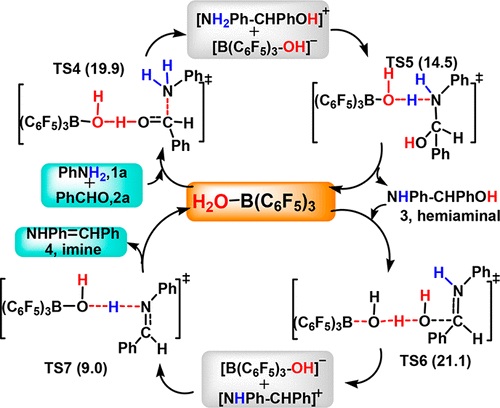
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been carried out to study the mechanism of N-alkylation of primary and secondary arylamines with aldehydes and ketones under the catalysis of the Lewis acid B(C6F5)(3) using silanes. The B(C6F5)(3)-mediated reduction of organic substrates is usually reported under anhydrous conditions. It is noteworthy that Ingleson and co-workers have established that B(C6F5)(3) could act as a water tolerant catalyst in N-alkylation of arylamines with aldehydes/ketones. Our DFT calculation results revealed that both Lewis acid B(C6F5)(3) and water play important roles in the condensation of amine and aldehyde to generate an imine intermediate and in the subsequent reduction of imine to yield an amine product. In the condensation reaction, Brensted acid B(C6F5)(3)-H2O acts as the effective catalyst to promote the proton transfer process. The activation free energy barrier is calculated to be 21.1 kcal/mol, which is 23.0 kcal/mol lower than that of the water-assisted condensation pathway. In the second stage of imine reduction, our DFT studies specifically show that a "one-pot" ionic outer-sphere S(N)2@Si transition state is the favorable pathway, featuring the imine hydrate nucleophilically attacking the eta(1)-silane boron adduct to activate silane, with an activation free energy barrier of 17.3 kcal/mol. With direct removal of silanol, a subsequent facile hydride transfer from the boronhydride anion [HB(C6F5)(3)](-) to the protonated iminium ion generates the alkylated amine product.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.organomet.8b00405
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com