李亚飞教授课题组在JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY发表研究论文
PtTe Monolayer: Two-Dimensional Electrocatalyst with High Basal Plane Activity toward Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Wang, Y (Wang, Yu)[ 1 ] ; Li, YF (Li, Yafei)[ 1 ] *(李亚飞); Heine, T (Heine, Thomas)[ 2,3 ]*
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Key Lab New Power Batteries, Jiangsu Collaborat Innovat Ctr Biomed Funct Mat, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Tech Univ Dresden, Sch Sci, Theoret Chem, Bergstr 66c, D-01062 Dresden, Germany
[ 3 ] Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf, Inst Resource Ecol, Permoserstr 15, D-04318 Leipzig, Germany
JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY,201810,140(40),12732-12735
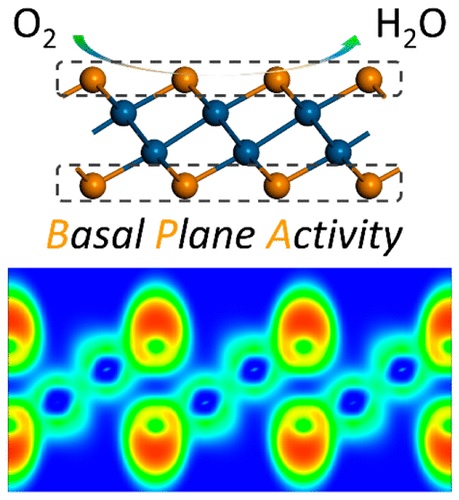
PtTe is a layered bulk material that was discovered in 1897. According to first-principles calculations, it is one of the few layered materials that maintains structure and metallic character when thinned down to the monolayer. Interlayer energy is small enough to allow for chemical exfoliation techniques. Our calculations show that monolayer PtTe is a candidate to substitute Pt electrodes, and we computationally studied its catalytic performance in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Remarkably, the basal plane of a PtTe monolayer exhibits excellent catalytic activity toward ORR, with a positive half-wave potential (similar to 0.90 V) and a high four-electron reduction pathway selectivity. These characteristics suggest that it outperforms Pt electrodes as catalyst, has a reduced Pt content, high Pt utilization, and a high surface area, and is a promising candidate for fuel cell components.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.8b08682
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com