杨朕副教授和杨维本教授课题组在ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES发表研究论文
Norfloxacin and Bisphenol-A Removal Using Temperature-Switchable Graphene Oxide
Yao, N (Yao, Na)[ 1 ] ; Zhang, XT (Zhang, Xuntong)[ 1 ] ; Yang, Z (Yang, Zhen)[ 1,2 ]*(杨朕) ; Yang, WB (Yang, Weiben)[ 1 ] *(杨维本); Tian, ZQ (Tian, Ziqi)[ 3 ] ; Zhang, LM (Zhang, Limin)[ 1 ]
[ 1 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Sch Chem & Mat Sci, Jiangsu Prov Key Lab Mat Cycling & Pollut Control, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, Peoples R China
[ 2 ] Nanjing Normal Univ, Changzhou Inst Innovat & Dev, Changzhou 213022, Peoples R China
[ 3 ] Chinese Acad Sci, Ningbo Inst Mat Technol & Engn, Ningbo 315201, Zhejiang, Peoples R China
ACS APPLIED MATERIALS & INTERFACES,201808,10(34),29083-29091
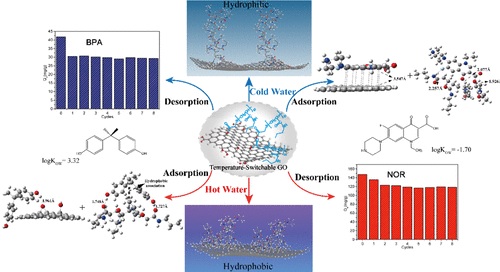
Graphene oxide (GO) is a competitive candidate used for adsorption of emerging organic contaminants (EOCs) from water. To overcome GO's spontaneous aggregation tendency in adsorption and to ease contaminant desorption from the adsorbent for adsorbent regeneration, a modified GO (P-GO), with temperature-switchable hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity, obtained by grafting temperature-responsive poly( N-n-propylacrylamide) was proposed. Two model EOCs, norfloxacin (NOR) and bisphenol A (BPA), with distinct hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity were employed. P-GO showed significant temperature-responsive adsorption behaviors: P-GO was more hydrophilic at a lower temperature and was beneficial for the adsorption of hydrophilic NOR, whereas it turned more hydrophobic at a higher temperature and was preferred for the adsorption of hydrophobic BPA. Compared with GO, P-GO under corresponding optimal conditions had comparable large adsorption amounts for NOR because of an "adsorption site replacement" strategy and notably enhanced adsorption for BPA because of strengthened hydrophobic association. Main interfacial binding interactions were pi-pi electron donor-acceptor effect and H-bonding for NOR adsorption and hydrophobic association and H-bonding for BPA uptake. On the basis of the temperature-responsive adsorption behaviors and studied interfacial interactions, regeneration of the adsorbent at designed temperatures using water (without additional chemicals) as an eluent is realized. This achievement is important for reducing risks of secondary environmental pollution during regeneration and easing further recovery of organic contaminants if needed.
文章链接:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.8b07233
版权与免责声明:本网页的内容由收集互联网上公开发布的信息整理获得。目的在于传递信息及分享,并不意味着赞同其观点或证实其真实性,也不构成其他建议。仅提供交流平台,不为其版权负责。如涉及侵权,请联系我们及时修改或删除。邮箱:sales@allpeptide.com