400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
一种衍生自 Kassina 蛙的肽。Kassinin属于速激肽家族的神经肽。
编号:128268
CAS号:63968-82-1
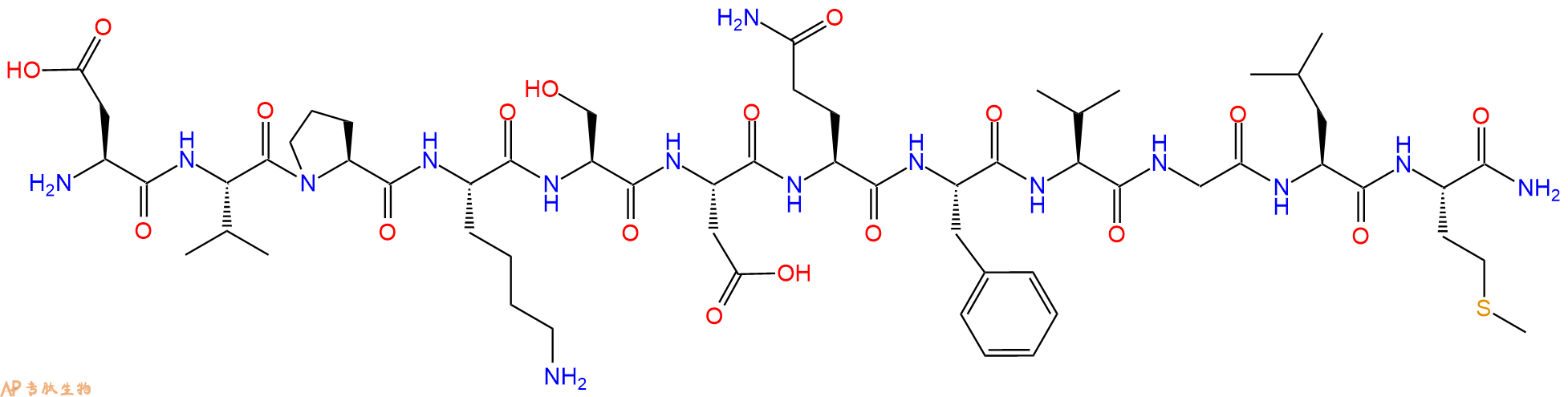
单字母:H2N-DVPKSDQFVGLM-CONH2
| 参考文献(References): | A. Anastasi et al., Experientia 33, 857 (1977) |
Kassinin 是一种衍生自 Kassina 蛙的肽。Kassinin属于速激肽家族的神经肽。Kassinin分泌作为防御信号,并参与神经肽信号传导。
Kassinin is a peptide derived from the Kassina frog. It belongs to tachykinin family of neuropeptides. It is secreted as a defense response, and is involved in neuropeptide signalling.
Kassinin acetate是一种来源于卡司纳蛙的速激肽,作为防御反应分泌,参与神经肽信号传导,并在哺乳动物中显示出对NK2比对NK1的选择性。
Kassinin acetate, a tachykinin peptide derived from the Kassina frog, is secreted as a defense response, and is involved in neuropeptide signaling and shows selectivity for NK2 over NK1 in mammals.
具有P物质样活性的速激肽,来源于非洲青蛙卡塞纳Senegalensis的皮肤。
Tachykinin peptide with substance P-like activity that is derived from the skin of the African frog, Kassina Senegalensis.
Definition
Dodecapeptide tachykinin that is kassinin is found in the central nervous system of the amphibian Kassina senegalensis. It is similar in structure and action to other tachykinins, but it is especially effective in contracting smooth muscle tissue and stimulating the micturition reflex.
Discovery
In 1964, Erspamer et al., first demonstrated the occurrence of bioactive peptide, kassinin in amphibian skin1. A biosynthetic precursor of kassinin cDNA encoding the novel kassinin analog (Thr2, Ile9)-kassinin was identified in skin secretion of amphibian2. In 1983, two new mammalian tachykinins, neurokinin A and neurokinin B, were discovered in the porcine spinal cord. Their pharmacological actions more closely resemble those of the amphibian tachykinin kassinin and the molluscan tachykinin eledoisin3.
Structural Characteristics
Tachykinins are among the most widely-studied families of regulatory peptides characterized by a highly-conserved C-terminal -Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met amide motif, which also constitutes the essential bioactive core. Both the aqueous and lipid-induced structure of kassinin, has been studied by Rani et al., (2001). Water kassinin prefers to be in an extended chain conformation, in the presence of perdeuterated dodecylphosphocholine (DPC) micelles, a membrane model system, helical conformation is induced in the central core and C-terminal region (K4-M12) of the peptide. N-terminus though less defined also displays some degree of order and a possible turn structure. The conformation adopted by kassinin in the presence of DPC micelles is consistent with the structural motif typical of neurokinin-1 selective agonists and with that reported for eledoisin in hydrophobic environment4.
Mode of Action
In frog skin, tachykinins stimulate the ion transport, by interacting with NK1-like receptors which can be estimated by measuring the short-circuit current (SCC) value. Kassinin (NK2 preferring in mammals) increases the SCC5. Kassinin also induces concentration-related contractions of the longitudinal muscle of the mouse distal colon. Contractile responses to the tachykinins result from a direct activation of smooth muscle cells. Kassinin evokes a contractile response in the absence of external Ca2+ and their myogenic activity was, to some extent, resistant to the inhibitory effect of nifedipine (a calcium channel blocker). So an additional process, probably the release of an intracellularly bound Ca2+ store, participates in the mechanism by which kassinin contracts the mouse distal colon. After desensitization of the mouse distal colon to Substance P (SP), the contractile activity provoked by SP was totally abolished whilst the responses evoked by kassinin were barely affected. These observations and other experimental findings indirectly support the assumption that the mouse distal colons possess different tachykinin-binding sites6.
Functions
Effect on rat urinary bladder - Synthetic replicates of kassinin are found to be active on rat urinary bladder smooth muscle at nanomolar concentrations2. Kassinin induces concentration-related contractions of the longitudinal muscle of the mouse distal colon.
Effect on endocrine pancreatic function - The effect of kassinin on endocrine pancreatic function was examined in the rat. Kassinin, injected intravenously in graded doses 10, 20, and 30 min before blood collection, significantly increased both plasma insulin and plasma glucagon in a dose-related fashion. The largest dose examined (10 µg) increased plasma insulin by 275% and plasma glucagon by 77% 7.
Synthetic kassinin affects splanchnic circulation - Effects of intravenously administered synthetic kassinin on splanchnic circulation and exocrine pancreatic secretion was examined in six anesthetized dogs. Kassinin caused dose-related increases in the blood flow in superior mesenteric artery and portal vein, and produced an initial increase followed by a decrease in pancreatic blood flow, but did not affect the exocrine pancreatic secretion. This study suggests that kassinin functions as a neuropeptide controlling the splanchnic circulation in mammalian species8.
References
1. Book : Handbook of chemical neuroanatomy. Chapter VI Neurokinin receptors in the CNS by Da-silva R, Mcleod AL, Krause JE.
2. Wang L, Zhou M, Lynch L, Chen T, Walker B, Shaw C (2009). Kassina senegalensis skin tachykinins: Molecular cloning of kassinin and (Thr2, Ile9)-kassinin biosynthetic precursor cDNAs and comparative bioactivity of mature tachykinins on the smooth muscle of rat urinary bladder. Biochimie, 91(5): 613-619.
3. Tan DP and Tsou K (1988). Differential Effects of Tachykinins Injected Intranigrally on Striatal Dopamine Metabolism. Journal of Neurochemistr, 51(5): 1333-1337.
4. Rani CR, Lynn AM, Cowsik SM (2001). Lipid Induced Conformation of the Tachykinin Peptide Kassinin. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 18 (4): 611-625.
5. Lippe C, Bellantuon V, Ardizzone C, Cassano G (2004). Eledoisin and Kassinin, but not Enterokassinin, stimulate ion transport in frog skin. Peptides, 25(11): 1971-1975.
6. Fontaine J and Lebrun P (1989). Contractile effects of substance P and other tachykinins on the mouse isolated distal colon. Br J Pharmacol, 96(3): 583–590.
7. Gullner HG, Yajimsa H, Harris V, Unger RH (1982). Kassinin: Stimulation of Insulin and Glucagon Secretion in the Rat. Endocrinology, 110 (4): 1246-1248.
8. Doi R, Inoue K, Kogire M, Sumi S, Takaori K, Yun M, Yajima H, Tobe T (1988). Effects of synthetic kassinin on splanchnic circulation and exocrine pancreas in dogs. Peptides, 9(5): 1055-1058.
定义
神经肽的长度为3-40个氨基酸,可作为神经递质。它们广泛分布于中枢神经系统和周围神经系统。
发现
神经肽是由约翰·休斯博士和科斯特里茨博士于1975年发现的。它们是内啡肽,内在产生的吗啡样物质,会在体内产生一系列类似药物的作用。可以从序列信息1中鉴定神经肽前体mRNA序列,并且得到的翻译蛋白序列包括信号肽序列和一个或多个神经肽。广泛而复杂的一系列酶处理步骤,包括被激素或前蛋白转化酶切割以及其他翻译后修饰,在创建活性神经肽之前就发生在翻译后的蛋白质序列上 2,3。
结构特征
通过核磁共振(NMR)光谱研究了几种来自软体动物的类似神经肽的构象性质。肽的N末端可变区中的氨基酸取代对溶液中反向转化的种群具有显着影响。通过使用两个独立的NMR参数测得的转弯数,发现使用Helix aspersa的受体膜制剂与IC50值高度相关(r2 = 0.93和0.82)。这些结果表明,构象集合降低了特定肽相对于特定受体4,5的有效浓度。
神经肽Y与人肽相同,并且与禽胰多肽高度同源。神经肽Y和禽胰多肽之间的同源性保留了维持三级结构必不可少的所有残基。结果表明,神经肽保留了紧凑的三级结构,其特征是在N末端的聚脯氨酸II类螺旋和C末端的a螺旋 6之间广泛的疏水相互作用。
已经通过许多孤儿受体之一发现了一些肽,这些受体是内源性配体未知的受体,例如“类阿片受体样1”(ORL1)。随后,已阐明该ORL1受体的内源性激动剂的结构,一种称为孤儿蛋白FQ或伤害感受蛋白的17个氨基酸的肽7。
行动方式
神经肽是由神经元作为细胞间信使释放的肽。一些神经肽充当神经递质,而另一些充当激素。神经肽既可以为我们提供支持,也可以为我们提供帮助。抗炎神经肽可帮助我们减少皮肤发炎。神经肽是自然产生的,可以在非常有限的时间内与靶细胞膜受体在明确的作用位点相互作用。因此,大多数这些内源性化合物的特征在于低的生物屏障渗透性和非常高的酶促降解敏感性。脑室内或全身注射神经肽Y(NPY)可使cast割的雌性大鼠血浆中的促黄体生成激素(LH)水平降低。6。
功能
生物功能,神经肽控制着我们的情绪,能量水平,痛苦和愉悦感,体重以及解决问题的能力;它们还会形成记忆,情感行为,食欲和发炎,修复疤痕和皱纹并调节我们的免疫系统。这些活跃的大脑小信使实际上打开了皮肤7的细胞功能。因此,今天,与神经肽系统相互作用的药物设计是后基因组药物化学研究最广泛的途径之一。
P物质已被确定为负责伤害性信号传递的主要神经肽。内源性阿片类药物是天然神经肽,负责伤害性信号的调节(通常是抑制)。
免疫系统,当它们被分泌时,它们会激活自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞),从而增强我们的免疫系统。
随着内啡肽的分泌越来越多,血管病变使收缩的血管恢复到正常状态,使血液以正常方式流动。大多数成人疾病都始于血管堵塞。内啡肽有助于改善血液循环。
内啡肽通过去除超氧化物具有抗衰老作用。从呼吸进入人体的氧气可以转变为超氧化物。这是造成人类疾病和衰老的最大敌人之一。
抗压力激素,应对压力的能力与我们体内的内啡肽水平成正比。
缓解疼痛的作用是,我们的神经系统在接收到疼痛信号时会分泌神经递质。一旦内啡肽在疼痛的那一刻被释放,内啡肽就会与神经元上的内啡肽受体结合,从而阻止第一种神经递质被分泌出来。
记忆力,神经肽可以改善记忆力,因为它们可以使脑细胞保持年轻健康。
参考
1. Hummon AB, Richmond TA, Verleyen P, Baggerman G, Huybrechts J, Ewing MA, Vierstraete E, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Liliane SL, Robinson GE (2006). From the genome to the proteome: uncovering peptides in the Apis brain. Science, 27(314):647-649.
2. Rockwell NC, Krysan DJ, Komiyama T, Fuller RS (2002). Precursor processing by Kex2/Furin Proteases. Chem. Rev., 102:4525–4548.
3. Von ER, Beck-Sickinger AG (2004). Biosynthesis of peptide hormones derived from precursor sequences. Curr. Med. Chem.,11:2651–2665.
4. Edison AS, Espinoza E, Zachariah C (1999). Conformational Ensembles: The Role of Neuropeptide Structures in Receptor Binding. The Journal of Neuroscience., 19(15):6318-6326.
5. Payza K, Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1989). Further characterization of Helix FMRFamide receptors: kinetics, tissue distribution, and interactions with the endogenous heptapeptides. Peptides, 10:657-661.
6. Allen J, Novotný J, Martin J, Heinrich G (1987). Molecular structure of mammalian neuropeptide Y: Analysis by molecular cloning and computer-aided comparison with crystal structure of avian homologue. PNAS., 84:2532-2536.
7. Guya J, Lia S, Pelletier G (1988). Studies on the physiological role and mechanism of action of neuropeptide Y in the regulation of luteinizing hormone secretion in the rat. Regulatory Peptides., 23(2):209-216.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1007/BF01951242 | Amino acid composition and sequence of kassinin, a tachykinin dodecapeptide from the skin of the African frog Kassina senegalensis | 下载 |