400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
LL-37, human 是一种由37 个氨基酸残基组成的两亲性组织蛋白酶衍生的抗菌肽,具有广泛的抗菌活性。
编号:125937
CAS号:154947-66-7
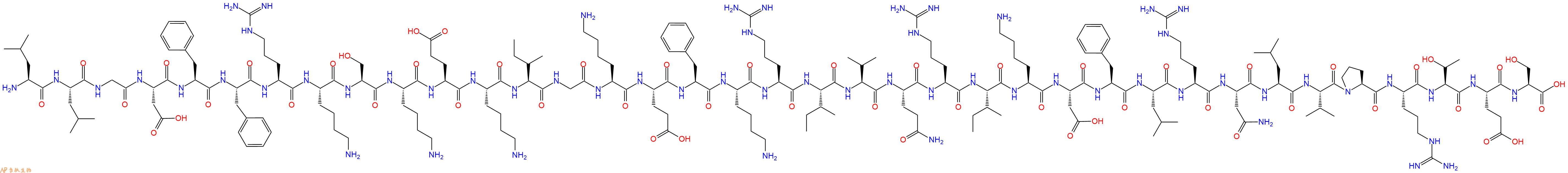
单字母:H2N-LLGDFFRKSKEKIGKEFKRIVQRIKDFLRNLVPRTES-OH
LL-37, human 是一种由37 个氨基酸残基组成的两亲性组织蛋白酶衍生的抗菌肽,具有广泛的抗菌活性。它有助于保护角膜免受感染,对于伤口愈合有着良好的促进作用,同时对多种革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性病原体具有抗菌和抗生物膜活性。
LL-37, human is a 37-residue, amphipathic, cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide, which exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. LL-37, human could help protect the cornea from infection and modulates wound healing.
LL-37是一种具有血管生成活性的抗菌肽。它对应于人组织蛋白酶抗菌蛋白hCAP18/LL-37的C末端序列(134-170),并通过蛋白水解过程从hCAP18/LL-37细胞外释放。hCAP18/LL-37是先天免疫系统的效应器,在白细胞和上皮细胞中表达,与炎症和损伤相关上调。可以证明hCAP18/LL-37在一系列乳腺癌中的过表达。LL-37被认为部分通过甲酰肽受体样1(FPRL1)刺激上皮细胞增殖,因为用百日咳毒素阻断受体会使LL-37的增殖作用降低约50%。
LL-37 is an antimicrobial peptide with angiogenic activity. It corresponds to the C-terminal sequence (134-170) of the human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein hCAP18/LL-37 and is extracellularly released from hCAP18/LL-37 by proteolytic processing. hCAP18/LL-37 is an effector of the innate immune system and is expressed in leukocytes and epithelial cells where it is upregulated in association with inflammation and injury. An overexpression of hCAP18/LL-37 in a series of breast carcinomas could be demonstrated. LL-37 has been suggested to stimulate epithelial cell proliferation partially through formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) since blocking the receptor with pertussis toxin decreased the proliferative effect of LL-37 by approximately 50 %.
LL-37是由嗜中性粒细胞和其他白细胞产生的37个氨基酸的肽。该肽已被证明具有抗炎特性,这可能是由于其结合和激活G蛋白偶联受体(GPCR)甲酰肽受体样1(FPRL1)的能力,导致抑制炎症介质如IL-8的产生。LL-37还与离子通道结合,这可能导致膜去极化,从而阻止钙流入细胞。已显示LL-37通过抑制T细胞受体信号传导和减少细胞因子产生来抑制T细胞的活化。\nLL-37对B细胞和巨噬细胞上的抗体结合位点也具有高亲和力,并且可以以高特异性结合肥大细胞上的IgE,从而抑制肥大细胞脱粒。LL-37与这些受体的结合导致组织炎症减轻,这可能
LL-37 is a 37 amino acid peptide that is produced by neutrophils and other leukocytes. This peptide has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may be due to its ability to bind and activate the G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1), leading to inhibition of the production of inflammatory mediators such as IL-8. LL-37 also binds to ion channels, which may lead to membrane depolarization, thereby blocking calcium influx into the cell. LL-37 has been shown to inhibit the activation of T cells by inhibiting T cell receptor signaling and reducing cytokine production.\nLL-37 also has a high affinity for antibody binding sites on B cells and macrophages and can bind with high specificity to IgE on mast cells, leading to inhibition of mast cell degranulation. The binding of LL-37 with these receptors leads to reduced inflammation in tissues, which may
LL-37是一种有效的抗菌肽,已被证明对癌细胞有效,目前正在作为潜在的抗肿瘤药物进行研究。LL-37与白细胞受体结合,导致趋化性,p53表达增加和细胞凋亡。LL-37还在体外和体内诱导上皮组织中的凋亡细胞死亡。该肽已被证明可诱导癌细胞死亡,以及其他类型细胞的细胞死亡。
LL-37 is a potent antimicrobial peptide that has been shown to be effective against cancer cells and is currently being investigated as a potential antineoplastic agent. LL-37 binds to the leukocyte receptor, which leads to chemotaxis, increased expression of p53 and apoptosis. LL-37 also induces apoptotic cell death in epithelial tissues, both in vitro and in vivo. This peptide has been shown to induce death in cancer cells, as well as cell death in other types of cells.
LL-37是一种具有血管生成活性的抗菌肽。它对应于人cathelicidin抗菌蛋白hCAP18/LL-37的C端序列(134-170),并通过蛋白水解加工从hCAP18/LL-37细胞外释放。hCAP18/LL-37是先天免疫系统的效应物,在白细胞和上皮细胞中表达,并与炎症和损伤相关上调。可以证明hCAP18/LL-37在一系列乳腺癌中过表达。已经提出LL-37部分通过甲酰肽受体样1(FPRL1)刺激上皮细胞增殖,因为用百日咳毒素阻断受体会使LL-37的增殖作用降低约50%。
LL-37 is an antimicrobial peptide with angiogenic activity. It corresponds to the C-terminal sequence (134-170) of the human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein hCAP18/LL-37 and is extracellularly released from hCAP18/LL-37 by proteolytic processing. hCAP18/LL-37 is an effector of the innate immune system and is expressed in leukocytes and epithelial cells where it is upregulated in association with inflammation and injury. An overexpression of hCAP18/LL-37 in a series of breast carcinomas could be demonstated. LL-37 has been suggested to stimulate epithelial cell proliferation partially through formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) since blocking the receptor with pertussis toxin decreased the proliferative effect of LL-37 by approximately 50 %.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.03.030 | LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides | 下载 |
| 10.1167/iovs.05-1649 | Multifunctional roles of human cathelicidin (LL-37) at the ocular surface | 下载 |
| 10.1371/journal.pone.0124706 | Antiviral Activity of the Human Cathelicidin, LL-37, and Derived Peptides on Seasonal and Pandemic Influenza A Viruses | 下载 |
| 10.1371/journal.pone.0133454 | Identifying the Critical Domain of LL-37 Involved in Mediating Neutrophil Activation in the Presence of Influenza Virus: Functional and Structural Analysis | 下载 |
| 10.1172/JCI17545 | An angiogenic role for the human peptide antibiotic LL-37/hCAP-18 | 下载 |
| 10.1002/ijc.20795 | Antimicrobial protein hCAP18/LL-37 is highly expressed in breast cancer and is a putative growth factor for epithelial cells | 下载 |
| 10.1152/ajplung.00286.2004 | Human endogenous antibiotic LL-37 stimulates airway epithelial cell proliferation and wound closure | 下载 |
| 10_1002cplu_202200240 | Self-Assembly of Linear, Natural Antimicrobial Peptides: An Evolutionary Perspective | 下载 |