400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
Endomorphin 1,一种高度选择性的高亲和力μ-opioid受体激动剂 , 对kappa3结合位点具有高亲和力 ,Ki为 20 到 30 nM 之间。
编号:118937
CAS号:189388-22-5
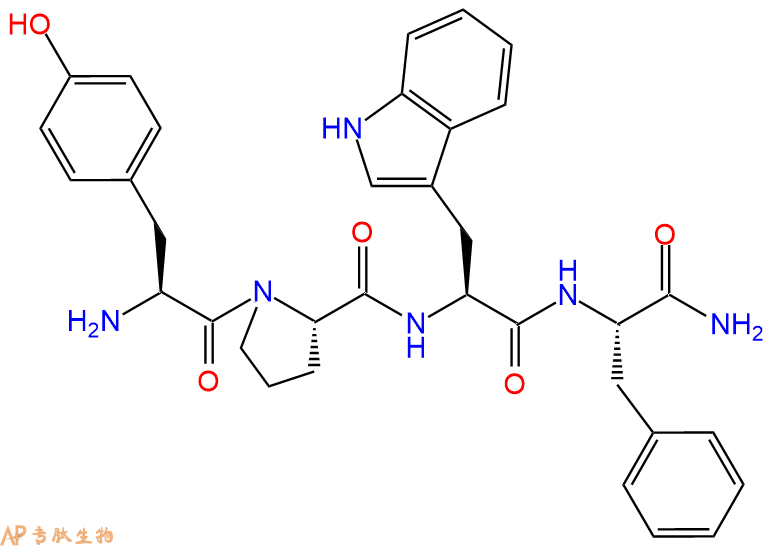
单字母:H2N-YPWF-CONH2
| 编号: | 118937 |
| 中文名称: | 内吗啡肽 1、Endomorphin 1 |
| 英文名: | Endomorphin 1 |
| CAS号: | 189388-22-5 |
| 单字母: | H2N-YPWF-CONH2 |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基:N-terminal amino group。在肽或多肽链中含有游离a-氨基的氨基酸一端。在表示氨基酸序列时,通常将N端放在肽链的左边。 -TyrL-酪氨酸:tyrosine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-3-(4-羟基苯基)丙酸。是编码氨基酸。符号:Y,Tyr。 -ProL-脯氨酸:proline。系统命名为吡咯烷-(2S)-羧酸。为亚氨基酸。是编码氨基酸。在肽链中有特殊作用,如易形成顺式的肽键等。符号:P,Pro。 -TrpL-色氨酸:tryptophan[e]。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-3-(3-吲哚基)丙酸。是编码氨基酸,哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:W,Trp。某些抗菌素中含有 D-色氨酸。 -PheL-苯丙氨酸:phenylalanine。系统命名为(2S)-氨基-3-苯基丙酸。是编码氨基酸。是哺乳动物的必需氨基酸。符号:F,Phe。 -CONH2C端酰胺化 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 4 |
| 分子式: | C34H38N6O5 |
| 平均分子量: | 610.7 |
| 精确分子量: | 610.29 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 1.97 |
| 平均亲水性: | -3.1 |
| 疏水性值: | -0.15 |
| 消光系数: | 6990 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 内吗啡肽(Endomorphin) |
| 参考文献(References): | J. Zadina et al, Nature, 386, 499, (1997) |
μ阿片类受体高度有效的选择性激动剂。
Endomorphin 1,一种高度选择性的高亲和力μ-opioid受体激动剂 , 对kappa3结合位点具有高亲和力 ,Ki为 20 到 30 nM 之间。
Endomorphin 1, a high affinity, highly selective agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, displays reasonable affinities for kappa3 binding sites, with Ki value between 20 and 30 nM.
阿片受体的强效和选择性内源性激动剂(Ki=360 pM;比δ和κ受体偏好4000和15000倍。)
Potent and selective endogenous agonist for the mo-opiate receptor (Ki = 360 pM; 4000- and 15000-fold preference over the delta and kappa receptors. )
背景
Endomorphins有两种内源性阿片肽。Endomorphin-1(Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2)和Endomorphin-2(Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2)是μ阿片类受体的已知最高亲和力和特异性的四肽。Endomorphin-1位于孤束核、室周的下丘脑和背内侧下丘脑处,在内神经元中发现Endomorphin-1,它可能具有调节镇静剂和冲动行为的作用[1]。假设Endomorphins是一个大的前体的分裂产物,但是这种多肽或蛋白质尚未确定。后下丘脑存在Perikarya表达类EM2免疫反应性,而在后下丘脑和孤束核(NTS)中都存在表达类EM1免疫反应性。类EM1免疫反应性比类EM2免疫反应性更广泛而密集的分布于整个大脑,而类EM2免疫反应性比类EM1免疫反应性更普遍的分布于脊髓。Endomorphins参与调节疼痛和自主神经系统的进程及对压力的反应能力。
参考文献:
1. Greco, MA; Fuller, PM; Jhou, TC; Martin-Schild, S; Zadina, JE; Hu, Z; Shiromani, P; Lu, J (2008). "Opioidergic projections to sleep-active neurons in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus". Brain Research 1245: 96–107.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)的定义
内吗啡肽(EM)-1和EM-2是位于中枢神经系统和免疫组织中的阿片样四肽,对μ-阿片受体1具有高度的选择性和亲和力【1】。
Endomorphin (EM)-1 and EM-2 are opioid tetrapeptides located in the central nervous system and immune tissues with high selectivity and affinity for the µ-opioid receptor 【1】.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)相关肽
阿片肽及其G蛋白偶联受体(δ、κ和μ受体)分布于中枢神经系统和外周组织。对阿片系统的研究旨在确定疼痛调节的内在机制,并开发出独特有效的疼痛控制物质,同时尽可能减少滥用潜力和副作用。存在两种类型的内源性阿片肽,一种含有色氨酸-甘氨酸-甘氨酸-苯丙氨酸(Trp-Gly-Gly-Phe)作为信息域(脑啡肽、内啡肽、强啡肽),另一种含有酪氨酸-脯氨酸-苯丙氨酸/色氨酸序列(内吗啡肽-1和-2)【2】。
Opioid peptides and their G-protein-coupled receptors (d, ? and µ) are located in the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. The opioid system has been studied to determine the intrinsic mechanism of modulation of pain and to develop uniquely effective pain-control substances with minimal abuse potential and side effects. Two types of endogenous opioid peptides exist, one containing Try-Gly-Gly-Phe as the message domain (enkephalins, endorphins, dynorphins) and the other containing the Tyr-Pro-Phe/Trp sequence (endomorphins-1 and -2) 【2】.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)的发现
1997年,Zadina等人从牛脑中分离出内吗啡肽1(EM1)和内吗啡肽2(EM2),并报道它们是迄今为止所描述的所有内源性物质中对μ受体具有最高特异性和亲和力的四肽【3】。
In 1997, Zadina et al., isolated Endomorphin 1 (EM1) and endomorphin 2 (EM2) from bovine brain, and reported them to be tetrapeptides having the highest specificity and affinity for the µ receptor of any endogenous substance so far described 【3】.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)的结构特征
含有内吗啡肽(EMs)信息域氨基酸序列Tyr-Pro-Phe/Trp的阿片样物质和阿片肽被发现具有独特的结合活性。内吗啡肽-1(Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2)和内吗啡肽-2(Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2)具有高度的μ受体亲和力和显著的选择性【2】。第三芳香环的正确空间取向和构象限制被认为是内吗啡肽与μ阿片受体(MOR)相互作用的关键【4】。
Opioidmimetics and opioid peptides containing the amino acid sequence of the message domain of endomorphins (EMs), Tyr-Pro-Phe/Trp, have been found to exhibit unique binding activity. Endomorphin-1 (Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) and endomorphin-2 (Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2) have high µ receptor affinity and remarkable selectivity 【2】. The proper spatial orientation and conformational restriction of the third aromatic ring is supposed to be crucial for the interaction of EMs with MOR (µ opioid receptor) 【4】.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)作用方式
在迄今为止描述的所有内源性物质中,内啡肽对µ受体的特异性和亲和力最高。在体外实验中,EM1比µ选择性类似物DAMGO更有效,且在小鼠体内产生强效且持久的镇痛作用。EM2(H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2)对µ受体也具有高亲和力和高选择性【2】。µ阿片受体是G蛋白偶联受体,在临床上使用的阿片受体激动剂的镇痛作用中发挥着关键作用。内啡肽诱导的镇痛作用是通过脊髓µ阿片受体介导的【5】。
The endomorphins have the highest specificity and affinity to the µ receptor among all endogenous substance so far described. EM1 is more effective than the µ- selective analogue DAMGO in vitro and produces potent and prolonged analgesia in mice. EM2 (H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2) also has a high affinity and selectivity to the µ receptor 【2】. The µ-opioid receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that play a pivotal role in the analgesic effects of opioid receptor agonists used clinically. Endomorphin-induced antinociception is mediated by spinal µ-opioid receptors 【5】.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)的功能
内吗啡肽(Endomorphins)与多种生理功能有关,包括镇痛、心血管、呼吸、消化、奖赏和内分泌反应【5】。内吗啡肽1(EM1)和内吗啡肽2(EM2)具有显著的纳洛酮敏感性和血管舒张活性【6】。它们能调节小胶质细胞的吞噬作用、趋化作用和超氧阴离子产生【7】。基于内吗啡肽设计的类似物可能具有治疗潜力【8】。
Endomorphins have been implicated in a broad range of physiological functions including antinociceptive, cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, rewarding, and endocrine responses 【5】 EM 1 and EM2 have significant naloxone-sensitive, vasodepressor activity 【6】. They modulate phagocytosis, chemotaxis and superoxide anion production by microglia 【7】. The analogues designed based on endomorphins may have therapeutic potential 【8】.
内吗啡肽(Endomorphin)的相关文献
1. Coventry TL, Jessop DS, Finn DP, Crabb MD, Kinoshita H, Harbuz MS (2001). Endomorphins and activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. J Endocrinol., 169(1):185-193.
2. Okada Y, Tsuda Y, Bryant SD, Lazarus LH (2002). Endomorphins and related opioid peptides. Vitam Horm., 65:257-279.
3. Zadina JE, Hackler L, Ge LJ, Kastin AJ (1997). A potent and selective endogenous agonist for the mu-opiate receptor. Nature, 386(6624):499–502
4. Yu Y, Shao X, Cui Y, Liu HM, Wang CL, Fan YZ, Liu J, Dong SL, Cui YX, Wang R (2007).Structure-activity study on the spatial arrangement of the third aromatic ring of endomorphins 1 and 2 using an atypical constrained C terminus. ChemMedChem., 2(3):309-317.
5. Xie H, Woods JH, Traynor JR, Ko MC (2008). The Spinal Antinociceptive Effects of Endomorphins in Rats: Behavioral and G Protein Functional Studies. Anesth Analg., 106(6):1873-1881.
6. Champion HC, Zadina JE, Kastin AJ, Hackler L, Ge LJ, Kadowitz PJ (1997).. The Endogenous Mu-Opioid Receptor Agonists Endomorphins 1 and 2 Have Novel Hypotensive Activity in the Rabbit. Biochemi Biophysl Res Commun., 235(3) 567-570
7. Azuma Y, Ohura K, Wang PL, Shinohara M (2001). Endomorphins 1 and 2 modulate chemotaxis, phagocytosis and superoxide anion production by microglia. J Neuroimmunol., 119(1):51-56.
8. Huo XF, Ren WH, Wu N, Wang R (1998).The design and synthesis of endomorphins and their analogues. Chinese Science Bulletin., 46(13):1096-1099.
Goldberg IE, et al. Pharmacological characterization of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2 in mouse brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Aug;286(2):1007-13. : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9694962
Goldberg IE, et al. Pharmacological characterization of endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2 in mouse brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Aug;286(2):1007-13. : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9694962
多肽H2N-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2的合成步骤:
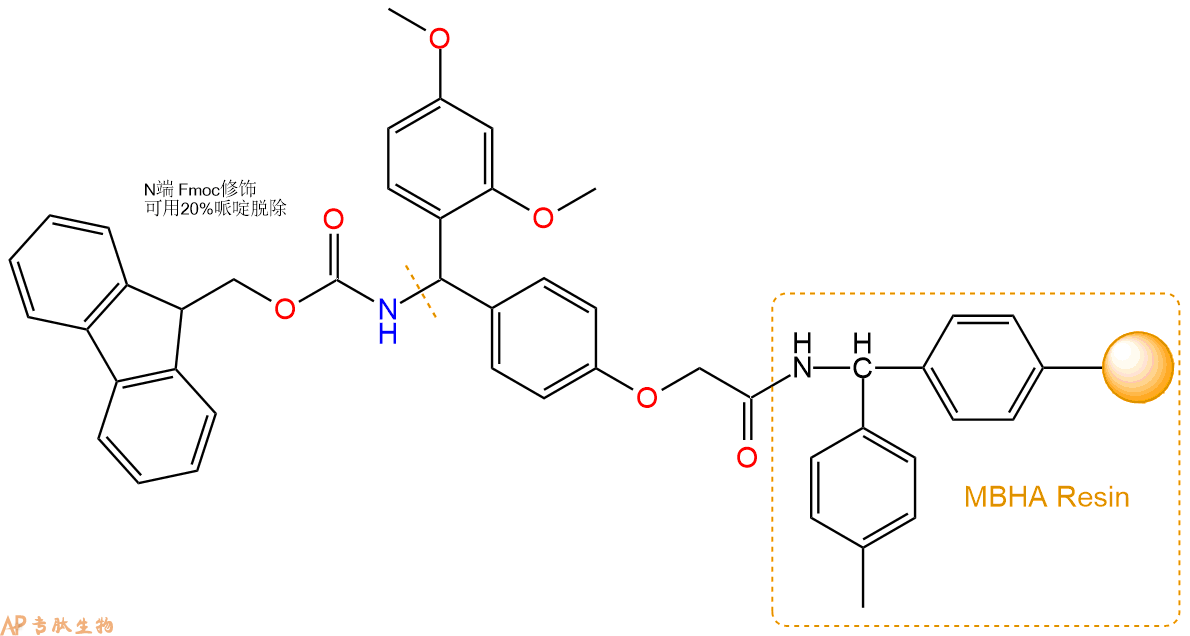
1、合成MBHA树脂:取若干克的MBHA树脂(如初始取代度为0.5mmol/g)和1倍树脂摩尔量的Fmoc-Linker-OH加入到反应器中,加入DMF,搅拌使氨基酸完全溶解。再加入树脂2倍量的DIEPA,搅拌混合均匀。再加入树脂0.95倍量的HBTU,搅拌混合均匀。反应3-4小时后,用DMF洗涤3次。用2倍树脂体积的10%乙酸酐/DMF 进行封端30分钟。然后再用DMF洗涤3次,甲醇洗涤2次,DCM洗涤2次,再用甲醇洗涤2次。真空干燥12小时以上,得到干燥的树脂{Fmoc-Linker-MHBA Resin},测定取代度。这里测得取代度为 0.3mmol/g。结构如下图:
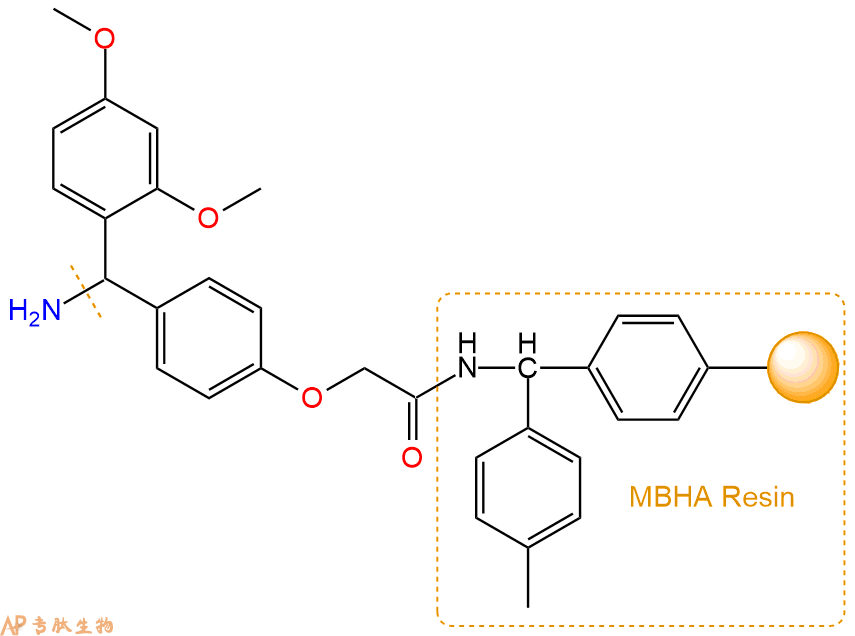
2、脱Fmoc:取2.94g的上述树脂,用DCM或DMF溶胀20分钟。用DMF洗涤2遍。加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Linker-MBHA Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
3、缩合:取2.65mmol Fmoc-Phe-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入5.29mmol DIPEA,2.51mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
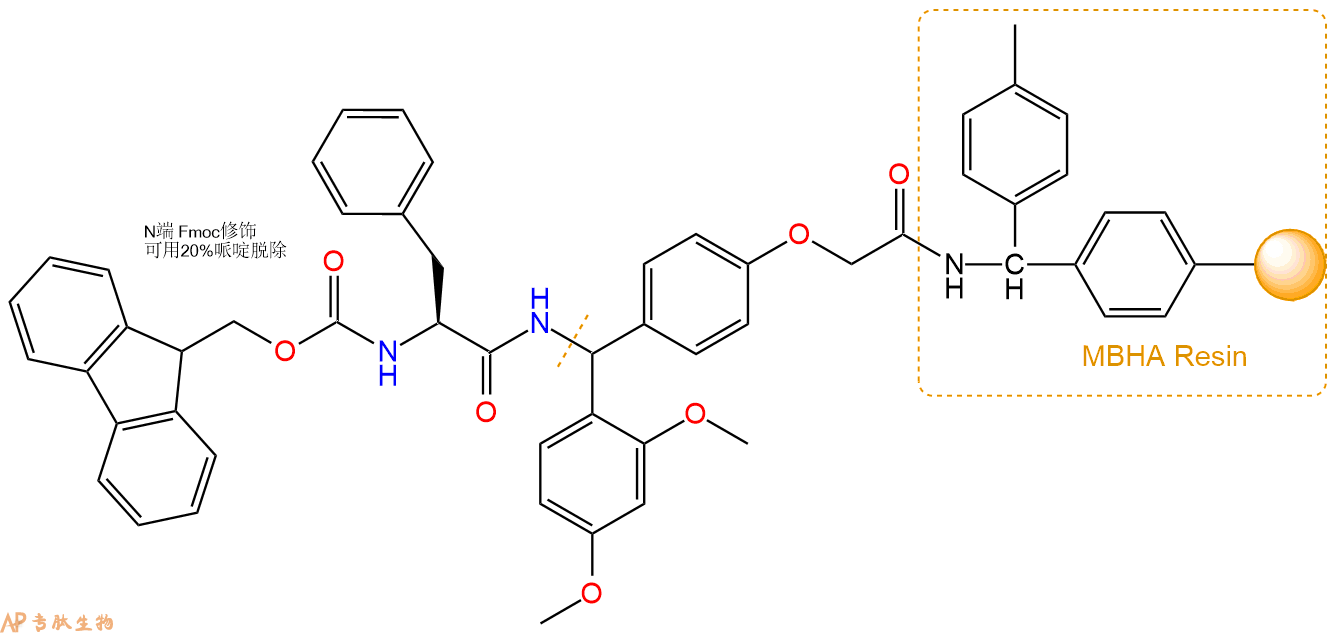
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Trp(Boc)-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Trp(Boc)-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Trp(Boc)-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Pro-Trp(Boc)-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-Pro-Trp(Boc)-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Tyr(tBu)-Pro-Trp(Boc)-Phe-Linker-MBHA Resin,结构如下:
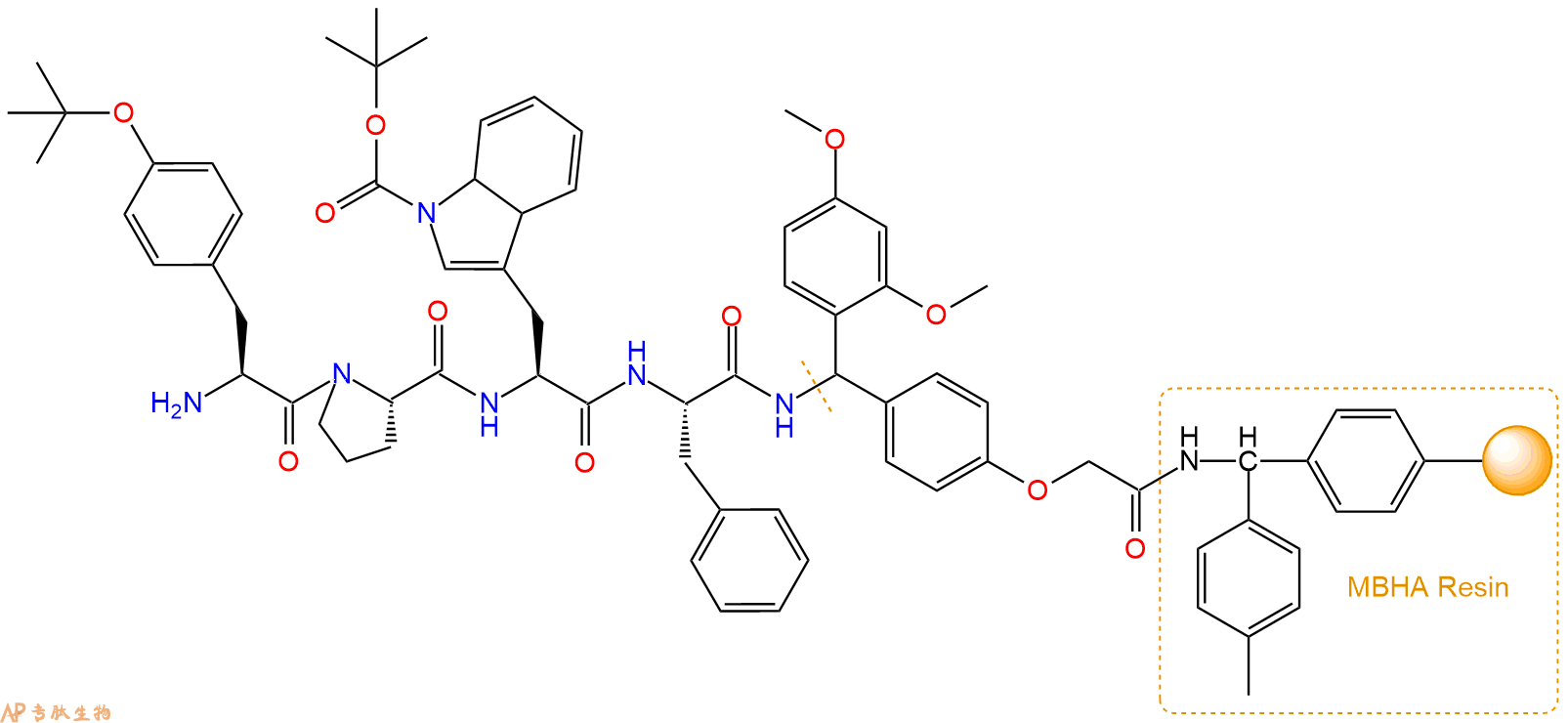
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。