400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
源于流感病毒 (Influenza A/PR/8/35) 核蛋白的 H2-Db 限制性表位。
编号:200780
CAS号:132326-73-9
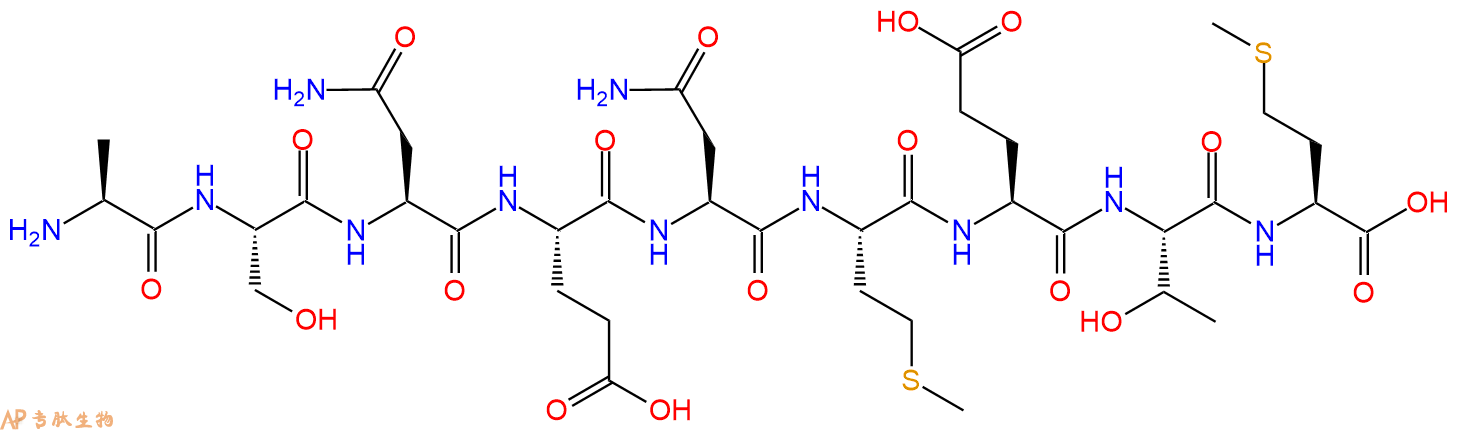
单字母:H2N-ASNENMETM-OH
Influenza A NP(366-374) Strain A/PR/8/35 是源于流感病毒 (Influenza A/PR/8/35) 核蛋白的 H2-Db 限制性表位。
Influenza A NP(366-374) Strain A/PR/8/35 is an H2-Db-restricted epitope from Influenza A/PR/8/35 nucleoprotein[1].
Peptide H-ASNENMETM-OH is a Research Peptide with significant interest within the field academic and medical research. Recent citations using H-ASNENMETM-OH include the following: Distinct proteolytic processes generate the C and N termini of MHC class I-binding peptides XY Mo, P Cascio, K Lemerise - The Journal of , 1999 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/163/11/5851/44134 Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked Db does not induce an influenza-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response or recycle membrane-bound peptides UMA Motal, CL Sentman, X Zhou - European journal of , 1995 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.1830250441 Major histocompatibility complex class I-binding peptides are recycled to the cell surface after internalization UM Abdel Motal, X Zhou, A Joki - European journal of , 1993 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.1830231227 Major histocompatibility complex class I-presented antigenic peptides are degraded in cytosolic extracts primarily by thimet oligopeptidase T Saric , J Beninga, CI Graef, TN Akopian - Journal of Biological , 2001 - ASBMBhttps://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(20)86725-8/abstract complex class I-restricted presentation of influenza virus nucleoprotein peptide by B lymphoma cells harboring an antibody gene antigenized with the virus peptide R Billetta, G Filaci, M Zanetti - European journal of immunology, 1995 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/eji.1830250323 Distinct Proteolytic Processes Generate the C and N Termini of MHC Class I-binding Peptides M XY, P Cascio, K Lemerise, AL Goldberg - JOURNAL OF , 1999 - iris.unito.ithttps://iris.unito.it/handle/2318/3854 Db-binding peptides from influenza virus: effect of non-anchor residues on stability and immunodominance LJ Sigal , P Goebel, DE Wylie - Molecular immunology, 1995 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0161589095000319 Role of non-anchor residues of Db-restricted peptides in class I binding and TCR triggering LJ Sigal , DE Wylie - Molecular immunology, 1996 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0161589096000995 Enhanced delivery of exogenous peptides into the class I antigen processing and presentation pathway L De Haan, AR Hearn, AJ Rivett, TR Hirst - Infection and immunity, 2002 - Am Soc Microbiolhttps://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/iai.70.6.3249-3258.2002 Low-avidity self-specific T cells display a pronounced expansion defect that can be overcome by altered peptide ligands KE de Visser , TA Cordaro, HWHG Kessels - The Journal of , 2001 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/167/7/3818/83530 Identification of naturally processed viral nonapeptides allows their quantification in infected cells and suggests an allele-specific T cell epitope forecast. K Falk, O Rötzschke , K Deres, J Metzger - The Journal of , 1991 - rupress.orghttps://rupress.org/jem/article-abstract/174/2/425/58121 MHC/peptide binding studies indicate hierarchy of anchor residues K Deres, W Beck, S Faath, G Jung, HG Rammensee - Cellular immunology, 1993 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0008874983712281 TAP1-dependent peptide translocation in vitro is ATP dependent and peptide selective JC Shepherd, TNM Schumacher , PG Ashton-Rickardt - Cell, 1993 - cell.comhttps://www.cell.com/cell/pdf/0092-8674(93)80058-M.pdf Peptide amino acid sequence analysis using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and fourier transform mass spectrometry JA Castoro, CL Wilkins, AS Woods - Journal of mass , 1995 - Wiley Online Libraryhttps://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jms.1190300115 Fine Specificity of Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Primed In Vivo Either with Virus or Synthetic Lipopeptide Vaccine or Primed In Vitro with Peptide By Hansj6rg Schild, Maria HG Rammensee - ncbi.nlm.nih.govhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2119046/ Fine specificity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes primed in vivo either with virus or synthetic lipopeptide vaccine or primed in vitro with peptide. H Schild, M Norda, K Deres, K Falk - The Journal of , 1991 - rupress.orghttps://rupress.org/jem/article-abstract/174/6/1665/58168 Binding of longer peptides to the H-2Kb heterodimer is restricted to peptides extended at their C terminus: refinement of the inherent MHC class I peptide binding H HoÃ\x8cË\x86rig, A Young, NJ Papadopoulos - The Journal of , 1999 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/163/8/4434/32397 A Previously Unrecognized H-2Db-Restricted Peptide Prominent in the Primary Influenza A Virus-Specific CD8+T-Cell Response Is Much Less Apparent following GT Belz , W Xie, JD Altman , PC Doherty - Journal of virology, 2000 - Am Soc Microbiolhttps://journals.asm.org/doi/abs/10.1128/jvi.74.8.3486-3493.2000 The three-dimensional structure of an H-2Ld-peptide complex explains the unique interaction of Ld with beta-2 microglobulin and peptide GK Balendiran, JC Solheim - Proceedings of the , 1997 - National Acad Scienceshttps://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.94.13.6880 Thimet oligopeptidase biochemical and biological significances: past, present, and future directions ES Ferro , MCF Gewehr, A Navon - Biomolecules, 2020 - mdpi.comhttps://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/9/1229 Anti-Peptide Antibody Blocks Peptide E Reticulum - J Immunol, 2001 - researchgate.nethttps://www.researchgate.net/profile/Craig-Hilton/publication/12092680_Anti-Peptide_Antibody_Blocks_Peptide_Binding_to_MHC_Class_I_Molecules_in_the_Endoplasmic_Reticulum/links/5de01809a6fdcc2837f3d244/Anti-Peptide-Antibody-Blocks-Peptide-Binding-to-MHC-Class-I-Molecules-in-the-Endoplasmic-Reticulum.pdf A mechanistic model for predicting cell surface presentation of competing peptides by MHC class I molecules DSM Boulanger, RC Eccleston , A Phillips - Frontiers in , 2018 - frontiersin.orghttps://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01538 Tapasin-mediated editing of the MHC I immunopeptidome is epitope specific and dependent on peptide off-rate, abundance, and level of tapasin expression DSM Boulanger, LR Douglas, PJ Duriez - Frontiers in , 2022 - frontiersin.orghttps://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.956603/full Variant antigenic peptide promotes cytotoxic T lymphocyte adhesion to target cells without cytotoxicity DM Shotton , A Attaran - Proceedings of the National , 1998 - National Acad Scienceshttps://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.95.26.15571 complex class I H-2Db molecules is controlled by dominant negative elements at peptide non-anchor residues: implications for peptide selection and presentation D Hudrisier , H Mazarguil, MBA Oldstone - Journal of Biological , 1996 - ASBMBhttps://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(19)86989-2/abstract Anti-peptide antibody blocks peptide binding to MHC class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum CJ Hilton , AM Dahl, KL Rock - The Journal of Immunology, 2001 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/166/6/3952/70418 Anti-Peptide Antibody Blocks Peptide CJ Hilton , AM Dahl, KL Rock - scholar.archive.orghttps://scholar.archive.org/work/c72ogauyunfuhgex7k36gpd7w4/access/wayback/http://www.umassmed.edu/uploadedFiles/otm2/Ready_to_sign/00-32%20Ref.pdf MedChemComm C Mayorga , D Andreu , J Rojo - core.ac.ukhttps://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/36213374.pdf Plant-produced potato virus X chimeric particles displaying an influenza virus-derived peptide activate specific CD8+ T cells in mice C Lico , C Mancini, P Italiani , C Betti , D Boraschi - Vaccine, 2009 - Elsevierhttps://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264410X09009189 Dominance of a single peptide bound to the class I (B) molecule, Qa-1b. A DeCloux, AS Woods , RJ Cotter - (Baltimore, Md.: 1950 , 1997 - journals.aai.orghttps://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article-abstract/158/5/2183/30399
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1128/AAC.01098-15 | The Flavonoid Isoliquiritigenin Reduces Lung Inflammation and Mouse Morbidity during Influenza Virus Infection | 下载 |