400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
该糖原合酶肽-2被糖原合酶激酶-3特异性磷酸化。(GSK-3)。GSK-3的活性可以通过从GS肽2的磷酸化活性中减去GS肽1的磷酸化活性来计算。
编号:413496
CAS号:851366-97-7
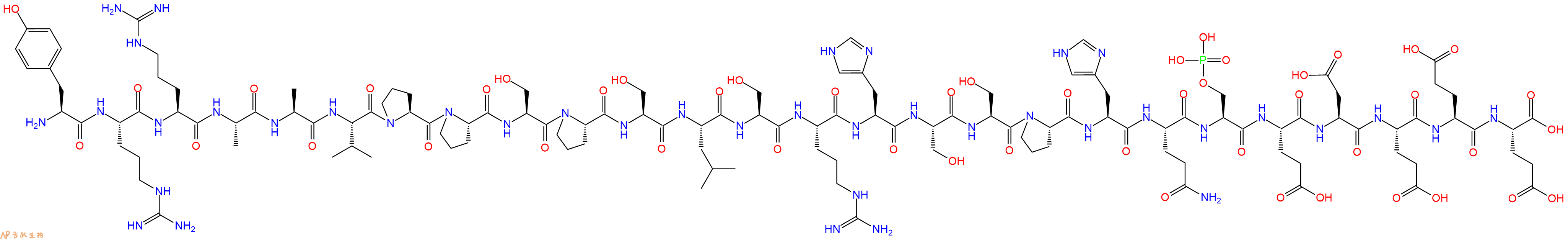
单字母:H2N-YRRAAVPPSPSLSRHSSPHQ-pSer-EDEEE-OH
| 参考文献(References): | Tanji, C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 36955 (2002) Eldar-Finkelman, H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 987 (1995). |
该糖原合酶肽-2被糖原合酶激酶-3特异性磷酸化。(GSK-3)。GSK-3的活性可以通过从GS肽2的磷酸化活性中减去GS肽1的磷酸化活性来计算。
This glycogen synthase peptide-2 is specifically phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase-3. (GSK-3). The activity of GSK-3 can be calculated by subtracting the activity of phosphorylation of GS peptide 1 from that of phosphorylation of GS peptide 2.
磷酸肽的合成
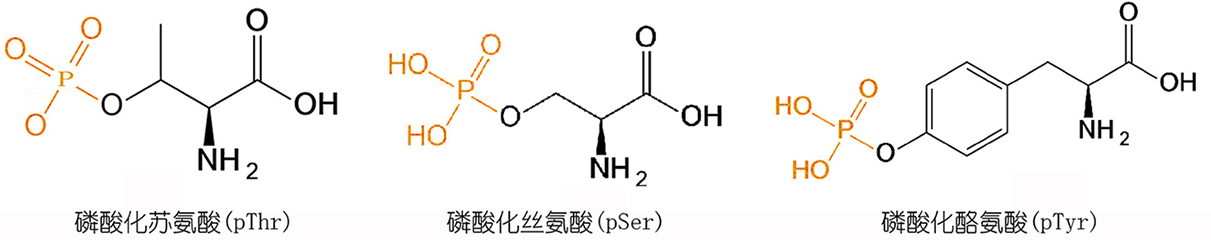
在生命过程中发挥重要作用,磷酸化的位置在多肽上的Tyr、Ser,Thr,。目前磷酸肽合成一般都采用磷酸化氨基酸,目前使用的都是单苄基磷酸化氨基酸。磷酸化氨基酸的连接一般采用HBTU/HOBt/DIEA方法,但是目前采用该方法合成磷酸化多肽也有缺点,特别是在合成多磷酸化多肽或氨基酸较长的多肽的时候,连接效率低,最后产品纯度很低,对于这种磷酸化多肽,我们考虑采用后磷酸化方法,其合成过程就是在多肽合成结束后,选择性脱去要标记的氨基酸的侧链保护基,对于Tyr,Thr可以直接使用侧链不保护的氨基酸进行反应,而Ser可以采用Fmoc-Ser(trt),在1% TFA/DCM条件下可以定量的脱除。后磷酸化,采用双苄基亚磷酰胺,四氮唑生成亚磷酰胺四唑活性中间体,连接到羟基上,随后在过氧酸下氧化生成磷酰基,完成反应。
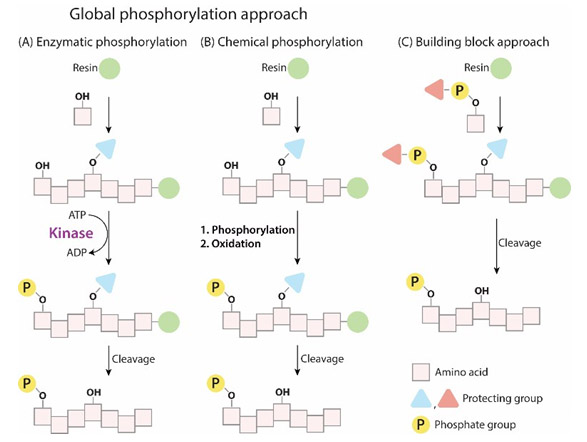
目前,多肽的磷酸化修饰方法主要有两种:
(1)将适当保护的磷酸化氨基酸直接引入到多肽序列中;
(2)多肽序列在树脂上合成完后,再对其中的Ser、Tyr或Thr的侧链羟基进行磷酸化。
1)将适当保护的磷酸化氨基酸直接引入到多肽序列中:
即事先将需要磷酸化的氨基酸(Thr,Ser或Tyr)磷酸化并适当保护,然后按照正常SPPS 合成流程将磷酸化单体缩合到多肽指定位点。这种方法操作简便,已经成为多肽单位点 磷酸化修饰的主要方法。
2)多肽序列在树脂上合成完后,再对其中的Ser、Tyr或Thr的侧链羟基进行磷酸化:
采用将磷酸化单体缩合到多肽中的方法进行磷酸化修饰时,磷酸化的氨基酸由于侧链修 饰的较大基团产生的位阻而导致难以与肽链缩合,并且之后的氨基酸引入都会比较困难, 尤其在含有多个磷酸化位点修饰时,合成将变得异常困难,并且最终产物成分复杂,难 以分离,产率极低。
因此,当肽链中多个位点进行磷酸化时,可以考虑采用将多肽序列 在树脂上合成完后,再对其中的Ser、Tyr或Thr的侧链羟基进行磷酸化:其合成过程主要 就是在多肽合成结束之后,选择性的脱去要标记氨基酸的侧链保护基,对于Tyr,Thr可 以直接使用侧链不保护的氨基酸进行反应。
侧链保护基在1%TFA/DCM条件下可以定量的脱 除。采用这种方法时,可以采用双苄基亚磷酰胺,四氮唑生成亚磷酰胺四唑活性中间体, 连接到羟基上,然后在过氧酸条件下氧化生成磷酰基,完成反应。
磷酸肽的的介绍
在所有的PTM中,磷酸化是最丰富和最重要的修饰之一。磷酸基团是一个高度带负电的分子,在磷原子周围有一个四面体结构。磷酸化多肽主要指肽链中的Ser、Tyr和Thr 残基的侧链羟基被修饰成酸式磷酸酯多肽。许多激素均是通过提高丝氨酸(Ser)或苏氨酸(Thr)残基的磷酸化状态来调节特异性酶的活性。磷酸化与人类疾病高度相关。例如,tau、α-synuclein和huntingtin的过度/多重磷酸化与人类疾病高度相关,聚集磷酸化也爆发神经退行性疾病的主要原因之一,例如阿尔茨海默氏病、帕金森氏病和亨廷顿氏病。目前,对磷酸化氨基酸的主要研究集中在羟基磷酸单酯型磷酸化氨基酸(O-磷酸化氨基酸),即磷酸化丝氨酸,磷酸化苏氨酸,磷酸化酪氨酸。
专肽生物生物为客户提供pSer、pTyr、pThr和D-pSer、D-pTyr、D-pThr的磷酸化修饰服务,也可以进行二、三、四、五个磷酸化位点修饰的高质量多肽的合成。
Definition
Protein kinases are transferase that catalyze the phosphorylation of proteins by covalently attaching phosphate groups to them, using ATP as a phosphate donor. Reversible protein phosphorylation-dephosphorylation has a principal role in the regulation of essentially all cellular functions. Kinase/phosphatase substrates can be found grouped according to their kinase families. A single substrate can have a many number of modifications.
Discovery
Phoebus AL at the Rockefeller Institute identified phosphate in the protein Vitellin (phosvitin) in 1906 1 and by 1933 Fritz Lipmann had detected phosphoserine in Casein 2. In 1954 Eugene P. Kennedy described the first ‘enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins’ in a variety of normal and malignant tissues, he showed that the phosphorus of the phosphoprotein fraction undergoes a high rate of turnover, as measured by incorporation of 32P 3 .
Structural Characteristics
There are thousands of different kinds of proteins in any particular cell that are substrate for different kinases and phosphatases. Phosphorylation of any site on a given protein can change the structure, function or localization of that protein. Within a protein, phosphorylation can occur on several amino acids. Phosphorylation on serine is the most common, followed by threonine. Tyrosine phosphorylation is relatively rare. However, since tyrosine phosphorylated proteins are relatively easy to purify using antibodies, tyrosine phosphorylation sites are relatively well understood. Histidine and aspartate phosphorylation occurs in prokaryotes as part of two-component signaling and in some cases in eukaryotes in some signal transduction pathways 4. Phosphorylation of seryl or threonyl (and occasionally tyrosyl) residues triggers small conformational changes in these proteins that alter their biological properties.
Mode of Action
Phosphatase removes a phosphate group from its substrate by hydrolysing phosphoric acid monoesters into a phosphate ion and a molecule with a free hydroxyl group. Protein kinases are the effectors of phosphorylation and catalyse the transfer of a y-phosphate from ATP to specific amino acids on proteins. The addition of a phosphate (PO4) molecule to a polar R group of an amino acid residue can turn a hydrophobic portion of a protein into a polar and extremely hydrophilic portion of molecule. In this way it can introduce a conformational change in the structure of the protein via interaction with other hydrophobic and hydrophilic residues in the protein. Several protein kinases are important in cellular control (e.g. glycogen synthase kinase-3, acetyl CoA carboxylase kinase, tyrosine hydroxylase kinase and casein kinase-2), which are themselves controlled by allosteric effectors, phosphorylation, insulin and other growth factors, or by regulators. Protein phosphatase catalytic units are responsible for dephosphorylating many regulated proteins in the cytoplasm that are phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues. Some protein phosphatases are controlled by second messengers. PP-1(Protein phosphatase-1) is regulated by cyclic AMP in several ways that vary with the form of the enzyme and the tissue. It is inhibited by cyclic AMP through the phosphorylation of inhibitor-1 and its isoforms through the phosphorylation of targeting proteins such as the glycogen-binding subunit, and through allosteric inhibition by phosphorylase a. PP-2B (Protein phosphatase-2B) is activated by Ca2+ through the interaction of this second messenger with an integral Ca2+ -binding subunit, as well as calmodulin itself. Protein phosphorylation-dephosphorylation is the basis of a network of interlocking systems that allow hormones and other extracellular signals, acting through just a few second messengers, to coordinate biochemical functions 5.
Functions
Reversible phosphorylation of proteins is an important regulatory mechanism that occurs in living cells 6. Reversible phosphorylation results in a change in conformation the structure in many enzymes and receptors, causing them to become activated or deactivated.
Regulatory roles, the p53 protein is heavily regulated through phosphorylation sites, it has 18 different phosphorylation sites. Activation and phosphorylation of p53 can lead to cell cycle arrest, which can be reversed under some circumstances, or apoptotic cell death 7. In energy-requiring reactions, phosphorylation of Na+/K+-ATPase during the transport of sodium (Na+) and potassium(K+) ions across the cell membrane in osmoregulation to maintain homeostasis.
Enzyme regulation, phosphorylation of the enzyme GSK-3 by AKT (Protein kinase B) is a important regulation in insulin signaling pathway.
Protein-protein interaction, phosphorylation of the cytosolic components of NADPH oxidase, a large membrane-bound, multi-protein enzyme plays an important role in the regulation of protein-protein interactions of the enzyme.
Protein degradation, phosphorylation of some proteins causes them to be degraded by the ATP-dependent ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. These proteins become substrates for particular E3 ubiquitin ligases only when they are phosphorylated 8.
References
1. Levene PA, Alsberg CL (1906). The cleavage products of vitellin. J. Biol. Chem., 2(1): 127-133.
2. Lipmann FA, Levene PA (1932). Serinephosphoric acid obtained on hydrolysis of vitellinic acid. J. Biol. Chem., 98 (1):109-114.
3. Burnett G, Kennedy EP (1954). The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 211(2):969–980.
4. Aumailley M, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Carter WG, Deutzmann R, Edgar D, Ekblom P, Engel J, Engvall E, Hohenester E, Jones JC, Kleinman HK, Marinkovich MP, Martin GR, Mayer U, Meneguzzi G, Miner JH, Miyazaki K, Patarroyo M, Paulsson M, Quaranta V, Sanes JR, Sasaki T, Sekiguchi K, Sorokin LM, Talts JF, Tryggvason K, Uitto J, Virtanen I, von der Mark K, Wewer UM, Yamada Y, Yurchenco PD (2005). A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol., 24(5):326-332.
5. Cohen P (1988). Protein Phosphorylation and Hormone Action. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Biological Sciences, 234(1275):115-144.
6. Barford D, Das AK, Egloff MP (1998). The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct., 27:133–164.
7. Ashcroft M, Kubbutat MH, Vousden KH (1999). Regulation of p53 function and stability by phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol., 19(3):1751–1758.
8. Babior BM (1999). NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood, 93(5):1464–1476.
多肽H2N-Tyr-Arg-Arg-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser-Pro-Ser-Leu-Ser-Arg-His-Ser-Ser-Pro-His-Gln-Ser(PO3H2)-Glu-Asp-Glu-Glu-Glu-COOH的合成步骤:
1、合成CTC树脂:称取2.37g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为0.9mmol/g)和2.56mmol Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入6.4mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
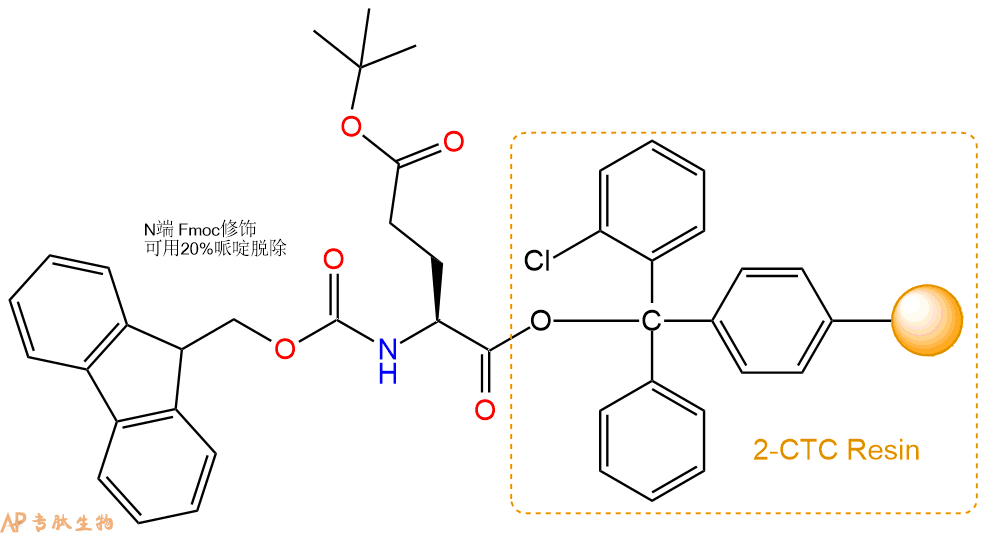
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
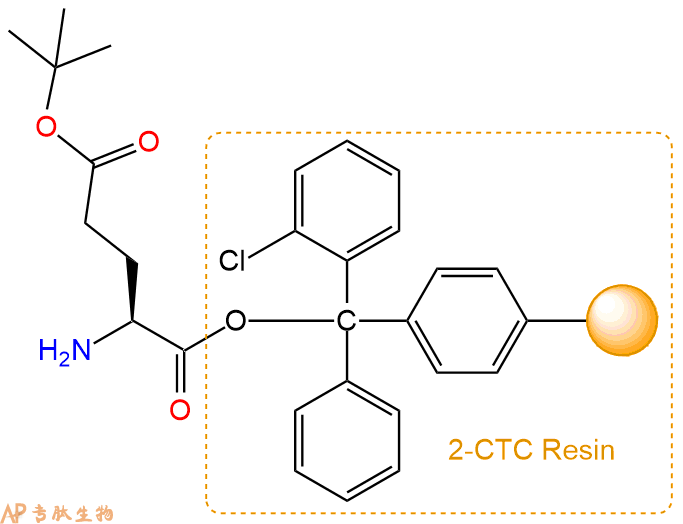
3、缩合:取6.4mmol Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入12.8mmol DIPEA,6.08mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
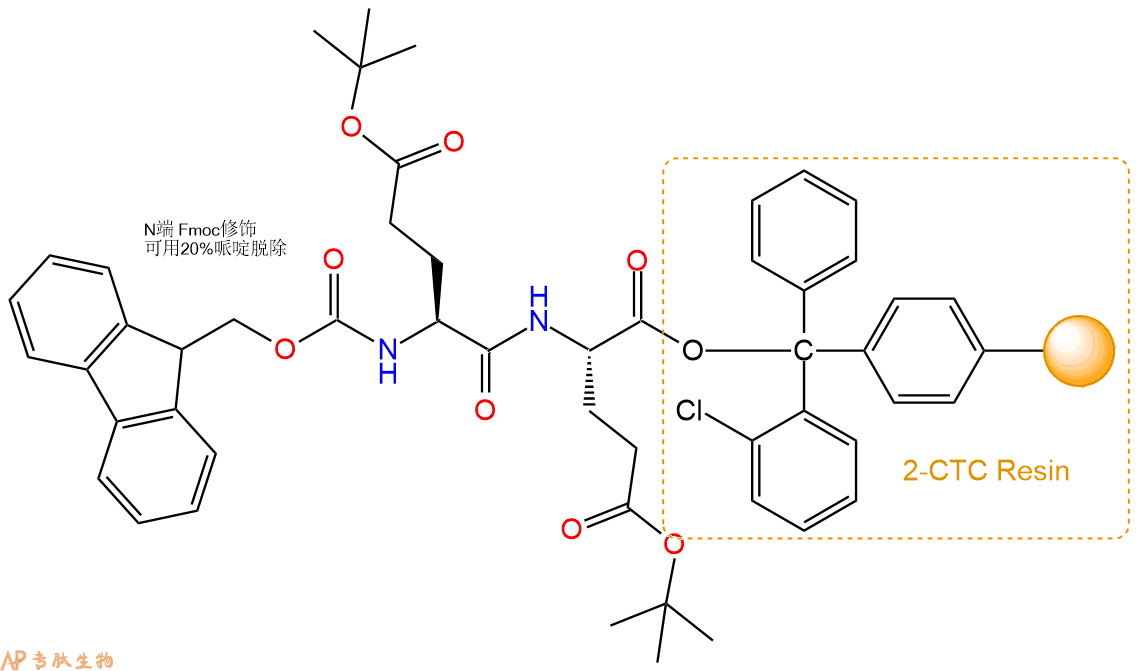
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Arg(Pbf)-Arg(Pbf)-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
H2N-Arg(Pbf)-Arg(Pbf)-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-Arg(Pbf)-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Tyr(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-Arg(Pbf)-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Pro-Ser(tBu)-Leu-Ser(tBu)-Arg(Pbf)-His(Trt)-Ser(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Pro-His(Trt)-Gln(Trt)-Ser(HPO3Bzl)-Glu(OtBu)-Asp(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-CTC Resin,结构如下:
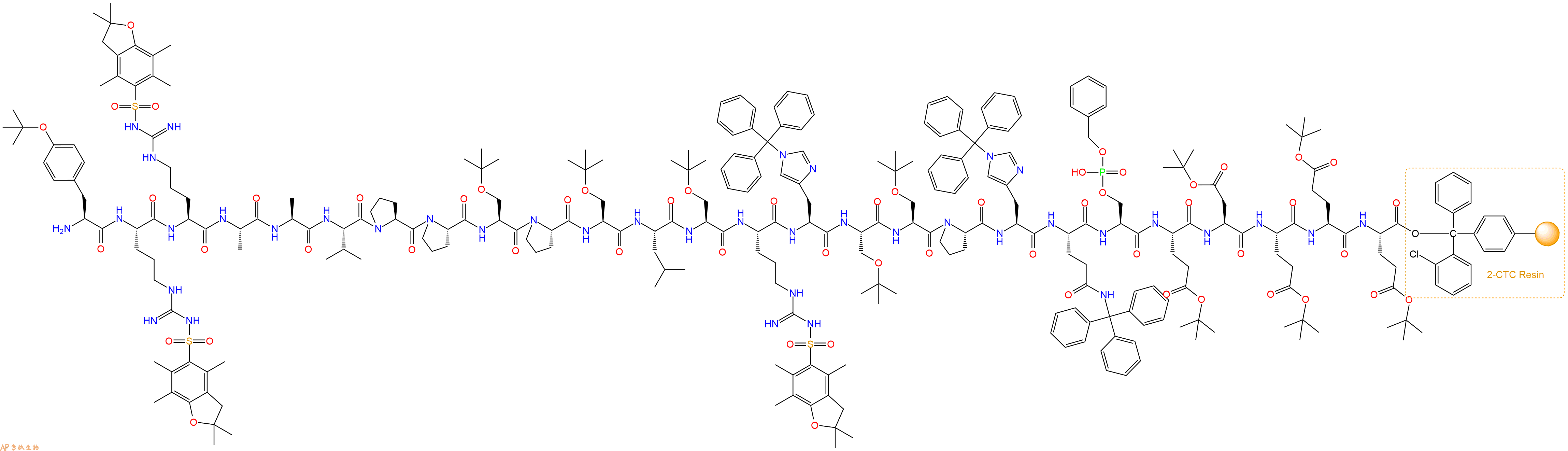
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Tyr-Arg-Arg-Ala-Ala-Val-Pro-Pro-Ser-Pro-Ser-Leu-Ser-Arg-His-Ser-Ser-Pro-His-Gln-Ser(PO3H2)-Glu-Asp-Glu-Glu-Glu-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽等。
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。