| 编号: | 158093 |
| 中文名称: | 促胰酶素Cholecystokinin-33, porcine |
| 英文名: | Cholecystokinin-33, porcine |
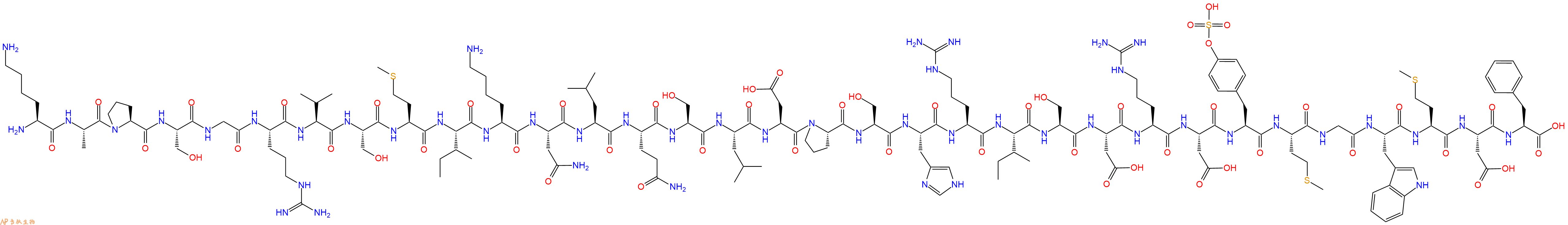
| 单字母: | H2N-KAPSGRVSMIKNLQSLDPSHRISDRD-sTyr-MGWMDF-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Lys赖氨酸 -Ala丙氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Leu亮氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Ser丝氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -His组氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Tyr(SO3H)磺酸化酪氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Trp色氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 33 |
| 分子式: | C166H261N49O53S4 |
| 平均分子量: | 3919.41 |
| 精确分子量: | 3916.81 |
| 等电点(PI): | 10.76 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 2.21 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.33571428571429 |
| 疏水性值: | -0.73 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 消光系数: | 5500 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 生成周期: | 2-3周 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 磺酸化修饰肽 胆囊收缩素(Cholecystokinin) |
Definition
Cholecystokinin (CCK), also called pancreozymin, is a peptide hormone in the small intestine that constitutes the classical gut hormone triad together with gastrin and secretin1. CCK is secreted into the blood following ingestion of a meal and plays a critical role in the ingestion, absorption, intestinal motility, satiety signaling, inhibition of gastric acid secretion and digestion of food1.
Discovery
CCK was discovered in 1928 because of its ability to induce gallbladder contraction2.
Classification
CCK is a neuropeptide. It is a family of hormones identified by the number of amino acids, for eg: CCK58 and CCK331.
Structural Characteristics
Prepro-CCK is a115 amino acid peptide that is first cleaved to pro-CCK which in turn results in CCK58, the major processed form of CCK3. CCK58 assumes a helix-turn-helix configuration3.
Mode of action
CCK binds to CCK receptors on the cell membrane that when activated increase the turnover of phosphatidyl inositol which results in the release of intracellular calcium4. The calcium released causes increased enzyme secretion either directly or through activation of protein kinase C4.
Functions
CCK induces the gall bladder to contract and eject bile into the intestine5. It stimulates the acinar cells of the pancreas to release water and ions and stimulates the secretion of a juice rich in pancreatic digestive enzymes5. It is known to induce growth of the exocrine pancreas and to stimulate insulin secretion5. CCK is the most abundant neuropeptide in the human brain where it induces panic attacks that are antagonized by a central cholecystokinin receptor antagonist6. ProCCK is expressed in certain neuroendocrine tumors and sarcomas, and the secretion of CCK is impaired in celiac disease and bulimia nervosa7.
References
1. Fink H, Rex A, Voits M, Voigt JP (1998). Major biological actions of CCK--a critical evaluation of research findings. Exp Brain Res., 123 (1-2), 77–83.
2. Hunt, J. N. (1948). A method for estimating peptic activity in gastric contents. Biochem. J., 42, 104-109.
3. Book: Neuropeptides By Fleur L. Strand, 387-389.
4. Dufresne M, Seva C, Fourmy D (2006). Cholecystokinin and gastrin receptors. Physiol. Rev., 86 (3), 805–47.
5. Chandra R, Liddle RA (2007). Cholecystokinin. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes., 14(1), 63-7.
6. Rehfeld JF, Friis-Hansen L, Goetze JP, Hansen TV (2007). The biology of cholecystokinin and gastrin peptides. Curr Top Med Chem, 7(12), 1154-65.
7. Rehfeld JF (2004). Clinical endocrinology and metabolism. Cholecystokinin. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab., 18(4), 569-86.