LL-37, human 是一种由37 个氨基酸残基组成的两亲性组织蛋白酶衍生的抗菌肽,具有广泛的抗菌活性。
编号:125937
CAS号:154947-66-7
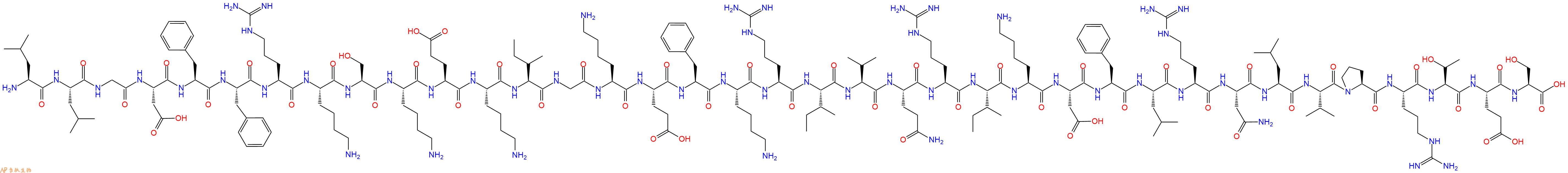
单字母:H2N-LLGDFFRKSKEKIGKEFKRIVQRIKDFLRNLVPRTES-OH
| 编号: | 125937 |
| 中文名称: | 抗菌肽LL-37, Antimicrobial Peptide , human |
| 英文名: | LL-37 (Cathelicidin) |
| 英文同义词: | LL37 |
| CAS号: | 154947-66-7 |
| 单字母: | H2N-LLGDFFRKSKEKIGKEFKRIVQRIKDFLRNLVPRTES-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Leu亮氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Arg精氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Leu亮氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Thr苏氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 37 |
| 分子式: | C205H340N60O53 |
| 平均分子量: | 4493.26 |
| 精确分子量: | 4490.58 |
| 等电点(PI): | 11.7 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 6.98 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.67647058823529 |
| 疏水性值: | -0.72 |
| 消光系数: | - |
| 标签: | 抗菌肽(Antimicrobial Peptides AMPs) 现货多肽 炎症研究 |
LL-37, Human TFA 是一种具有 37 个残基的两亲性组织蛋白酶衍生的抗菌肽,具有广泛的抗菌活性。LL-37, Human TFA 有助于保护角膜免受感染,调节伤口愈合。
LL-37, human is a 37-residue, amphipathic, cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide, which exhibits a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity.
LL-37, human could help protect the cornea from infection and modulates wound healing[2]
LL-37, human 是一种由37 个氨基酸残基组成的两亲性组织蛋白酶衍生的抗菌肽,具有广泛的抗菌活性。它有助于保护角膜免受感染,对于伤口愈合有着良好的促进作用,同时对多种革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性病原体具有抗菌和抗生物膜活性。
AMPs是由相对较小的分子组成的异质基团,通常含有不到100个氨基酸。 它们最初是在20世纪60年代由Zeya和Spitznagel 在多形核白细胞溶酶体中描述的。 迄今为止,已在数据库(如数据库)中 确定和登记了2600多个AMP。 它们是由几乎所有的生物群产生的,包括细菌、真菌、植物和动物。 许多脊椎动物AMPs是由上皮表面分泌的,如 哺乳动物的气管、舌、肠粘膜或两栖动物的皮肤。 有些在中性粒细胞、单核 细胞和巨噬细胞中表达。 AMPs参与动物和植物的免疫防御系统。 构成表达或诱导它们在抵御微生物入侵者 的第一道防线中起着关键作用。
结构/分类 AMPs可以根据其氨基酸组成和结构进行分类。 可以区分两大类AMP。
第一类由线性分子组成,它们要么倾向于采用α螺旋结构,要么富含精氨酸、甘氨 酸、组氨酸、脯氨酸和色氨酸等某些氨 基酸。
第二类由含半胱氨酸的肽组成, 可分为单一或多个二硫结构。 在许多情 况下,抗菌活性需要存在二硫桥。 大多数AMPs是阳离子肽,但也有阴离子肽,如真皮素,一种富含天冬氨酸 的人肽和两栖动物的最大蛋白H5皮肤。 其他非阳离子AMPs包括神经肽前体分子的片段,如原啡肽A, 芳香二肽主要从二翅目幼虫中分离出来,或从节肢动物或茴香物种的氧结合 蛋白中提取的肽。
专肽生物可定制合成各类序列的抗菌肽,可标记FITC/FAM/TAMRA等常见荧光素。
Definition
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are as widespread as bacterial inactivator molecules in the innate immune systems of insects, fungi, plants, and mammals. These peptides are also known as host defense peptides (HDPs) as they have other immuno-modulatory functions besides the direct antimicrobial actions and are even capable of killing cancerous cells 1,2.
Classification
Three broad categories of HDPs have been identified: 1) the linear peptides with helical structures, 2) the cysteine stabilized peptides with beta-sheet, and 3) a group of linear peptides rich in proline and arginine that primarily have been identified in non-mammalian species.
Structural characteristics
In mammals, cathelicidins and defensins are the two principal AMP families. Cathelicidins are peptides with a conserved proregion and a variable C-terminal antimicrobial domain. Defensins are the best-characterized AMPs, they have six invariant cysteines, forming three intramolecular cystine-disulfide bonds.
Mode of action
The mode of action of AMPs elucidated to date include inhibition of cell wall formation, formation of pores in the cell membrane resulting in the disruption of membrane potential with eventual lysis of the cell. These peptides also inhibit nuclease activity of both RNase and DNase.
Functions
They have a broad ability to kill microbes. AMPs form an important means of host defense in eukaryotes. Large AMPs (>100 amino acids), are often lytic, nutrient-binding proteins or specifically target microbial macromolecules. Small AMPs act by disrupting the structure of microbial cell membranes. It plays an active role in wound repair and regulation of the adaptive immune system. They have multiple roles as mediators of inflammation with impact on epithelial and inflammatory cells, influencing diverse processes such as cell proliferation, wound healing, cytokine release, chemotaxis and immune induction 3.
References
1. Gottlieb CT, Thomsen LE, Ingmer H, Mygind PH, Kristensen HH, Gram L(2008). Antimicrobial peptides effectively kill a broad spectrum of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus strains independently of origin, sub-type, or virulence factor expression. BMC Microbiol., 8:205.
2. Yeaman MR and Yount NY (2003). Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Peptide Action and Resistance. Pharmocological Reviews, 55(1).
3. Hanna Galkowska H and Olszewski WL (2003). Antimicrobial peptides – their role in immunity and therapeutic potential. Centr Eur J Immunol., 28 (3):138–141.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.03.030 | LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides | 下载 |
| 10.1167/iovs.05-1649 | Multifunctional roles of human cathelicidin (LL-37) at the ocular surface | 下载 |
| 10.1371/journal.pone.0124706 | Antiviral Activity of the Human Cathelicidin, LL-37, and Derived Peptides on Seasonal and Pandemic Influenza A Viruses | 下载 |
| 10.1371/journal.pone.0133454 | Identifying the Critical Domain of LL-37 Involved in Mediating Neutrophil Activation in the Presence of Influenza Virus: Functional and Structural Analysis | 下载 |
| 10_1002cplu_202200240 | Self-Assembly of Linear, Natural Antimicrobial Peptides: An Evolutionary Perspective | 下载 |