细胞因子,调节白细胞。白细胞介素-2(IL-2)属于白细胞介素家族,是免疫系统的细胞因子信号分子,参与调节免疫系统白细胞的活性。
编号:167160
CAS号:
单字母:H2N-ILNGINNYKNPKL-OH
| 编号: | 167160 |
| 中文名称: | β-白细胞介素II(44-56)、β-Interleukin II (44-56) |
| 英文名: | β-Interleukin II (44-56) |
| 单字母: | H2N-ILNGINNYKNPKL-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Gly甘氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Tyr酪氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Pro脯氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 13 |
| 分子式: | C68H113N19O19 |
| 平均分子量: | 1500.74 |
| 精确分子量: | 1499.85 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 3.97 |
| 酸性基团个数: | 2 |
| 碱性基团个数: | 疏水 |
| 平均亲水性: | -0.34545454545455 |
| 疏水性值: | -0.62 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 闪点: | 1280 M-1cm-1 |
| 消光系数: | 1490 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 白细胞介素(Interleukin) |
背景
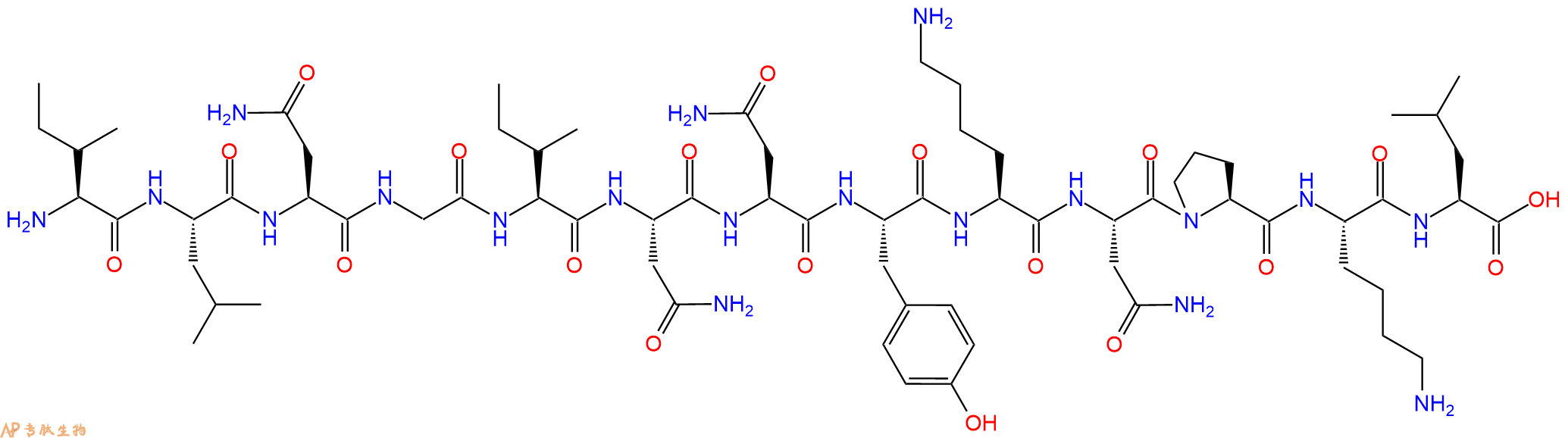
β-白细胞介素II(44-56),分子式为C68H113N19O19,序列为NH2-ILE-LEU-ASN-GLY-ILE-ASN-ASN-TYR-LYS-ASN-PRO-LYS-LEU-COOH,分子量为1500.7。白细胞介素-2(IL-2)属于白细胞介素家族,是免疫系统的细胞因子信号分子,参与调节免疫系统白细胞的活性。IL-2是免疫系统的可溶性激素样调节剂,是鉴定到的第一个白介素分子,参与T细胞的生长、增殖和分化,促进T细胞形成“效应子”T细胞。IL-2是在免疫应答过程中由T细胞产生的,对于T细胞免疫记忆的发展是必须的,这取决于抗原选择性T细胞数目和功能的扩展。在胸腺的T细胞的发育中,IL-2对于T细胞的成熟是必须的,又被称为调节性T细胞。
参考文献:
1. Cantrell DA, Smith KA (June 1984). "The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model". Science 224 (4655): 1312–6.
2. Smith KA (May 1988). "Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications". Science 240 (4856): 1169–76.
3. Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M (August 1995). "Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases". J. Immunol. 155 (3): 1151–64.
4. ThorntonAM, Shevach EM (July 1998). "CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production". J. Exp. Med. 188 (2): 287–96.
Definition
The polypeptide hormone interleukin-1 (IL-1) is one of the key mediators of host's response to microbial invasion, inflammation, tissue injury, or immunological reactions. IL-1 is a prominent member of a group of polypeptide mediators now called cytokines.
Related Peptides
The IL-1 gene family is composed of IL-1a, IL-1b, and IL-1Ra. Each member is first synthesized as a precursor protein; the precursors for IL-1 (prolL-1a and prolL-1b) each have a molecular mass of 31 kDa. The prolL-1a and mature 17 kDa lL-1a are both biologically active. In contrast, prolL-1b is relatively inactive and requires cleavage to a 17-kDa peptide for optimal biological activity. The IL-1Ra precursor has a leader sequence, is cleaved to its mature form, and is secreted like most proteins1.
Structural Characteristics
IL-1 ligands (IL-1a and IL-1b, collectively referred to as IL-1) are pluripotent, proinflammatory cytokines. These two IL l’s share only small stretches of amino acid homology (26% in the case of human IL 1). Each IL 1 is coded by a separate gene, both genes are located on chromosome 2, and each gene contains seven exons. mRNA coding for IL-1b predominates over that coding for IL-1a and this prevalence of IL-1b has been observed in the proportion of the two IL 1 forms measured in the circulation and other body fluids. Both forms of IL 1 are unique in that they are initially translated as precursor polypeptides (31,000 kDa), and despite the fact that IL 1 is found in the extracellular compartment, neither form contains a signal cleavage sequence. The generation of the NH2 terminus of the mature peptide (17,500 kDa) and smaller peptides occurs by the action of senine proteases. Of particular interest is the a/b homologous region termed C-D, which is coded entirely by the sixth exon. It has been suggest that this region may contain the minimal recognition site for IL 1 receptors. Receptors for IL 1 equally recognize the b and a forms, both forms possess the same spectrum of biological properties, and molecular modeling studies reveal that the two IL l’s are composed of b - folded sheets2,3.
Mode of Action
IL 1 specifically binds to a variety of cells. Studies with T lymphocytes and fibroblasts suggest the existence of a single class of high-affinity receptor with a dissociation constant (KD) that varies from 5 to 50 pM with 100-4000 binding sites per cell. The high-affinity receptors are rapidly internalized and bind to nuclear structures, and responsiveness to IL 1 is down-regulated. The rapid down-regulation of IL 1 receptor is specific and may account, in part, for modulating IL1 effects in several cells4. In cells stimulated with IL1, cytosolic calcium increases, sodium/potassium ion fluxes occur, and protein kinase activity increases4.
Functions
Interleukin-1: Regulator of Neuroinflammation - Interleukins 1a and 1b (IL-1) are very potent signaling molecules that are expressed normally at low levels, but are induced rapidly in response to local or peripheral insults. IL-1 coordinates systemic host defense responses to pathogens and to injury within the central nervous system (CNS). Numerous reports have correlated the presence of IL-1 in the injured or diseased brain, and its effects on neurons and nonneuronal cells in the CNS, it has been recently shown that the importance of IL-1 signaling. Further it has been demonstrate that IL-1 is at or near the top of the hierarchical cytokine signaling cascade in the CNS that results in the activation of endogenous microglia and vascular endothelial cells to recruit peripheral leukocytes (i.e., neuroinflammation). The IL-1 system thus provides an attractive target for therapeutic intervention to ameliorate the destructive consequences of neuroinflammation5.
Role of interleukin-1 in stress responses - Stress responses have been characterized as central neurohormonal changes, as well as behavioral and physiological changes. Administration of IL-1 has been shown to induce effects comparable to stress-induced changes. IL-1 acts on the brain, especially the hypothalamus, to enhance release of monoamines, such as norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin, as well as secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). IL-1-induced activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in vivo depends on secretion of CRH, an intact pituitary, and the ventral noradrenergic bundle that innervates the CRH-containing neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Recent studies have shown that IL-1 is present within neurons in the brain, suggesting that IL-1 functions in neuronal transmission. It has been shown that IL-1 in the brain is involved in the stress response, and that stress-induced activation of monoamine release and the HPA axis were inhibited by IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) administration directly into the rat hypothalamus. IL-1Ra has been known to exert a blocking effect on IL-1 by competitively inhibiting the binding of IL-1 to IL-1 receptors6.
References
1. Dinarello CA (1994). The interleukin-1 family. 10 years of discovery. FASEBJ, 8(15):1314-25.
2. Auron PE, Warner SJ, Webb AC, Cannon JG, Bernheim HA, McAdam KJ, Rosenwasser LJ, LoPreste G, Mucci SF, Dinarello CA (1987). Studies on the molecular nature of human interleukin-1. J. Immunol, 138(5):1447-1456.
3. Dinarello C A (1988). Biology of interleukin 1. FASEBJ, 2: 108-115.
4. Mizel S B, Kilian P L, Lewis J C, Paganelli KA, Chizzonite RA (1987). The interleukin 1 receptor. Dynamics of interleukin 1 binding and internalization in T cells and fibroblasts. J. Immunol., 138: 2906-2912.
5. Basu A, Krady JK, Levison SW(2004). Interleukin-1: A Master Regulator of Neuroinflammation. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 78:151–156.
6. Shintani F, Nakaki T, Kanba S, Kato R, Asai M(1995). Role of interleukin-1 in stress responses - A putative neurotransmitter. Molecular Neurobiology, 10: 47-71.
多肽H2N-Ile-Leu-Asn-Gly-Ile-Asn-Asn-Tyr-Lys-Asn-Pro-Lys-Leu-COOH的合成步骤:
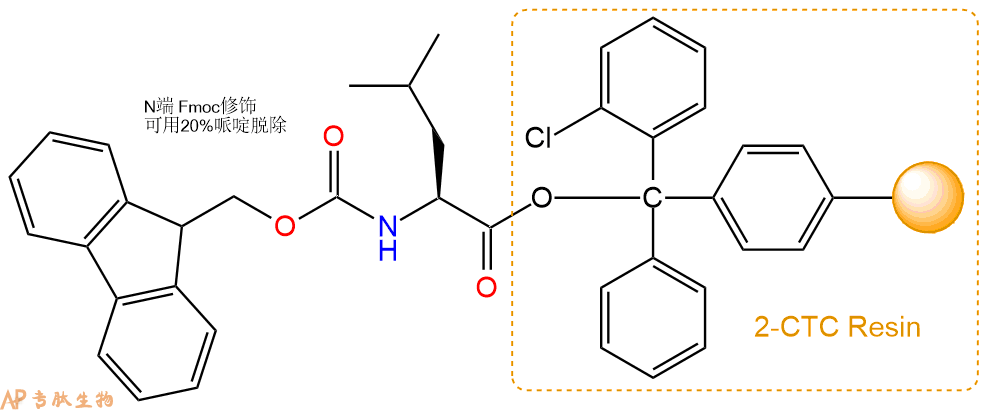
1、合成CTC树脂:称取2.41g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为0.76mmol/g)和2.2mmol Fmoc-Leu-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入5.49mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Leu-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
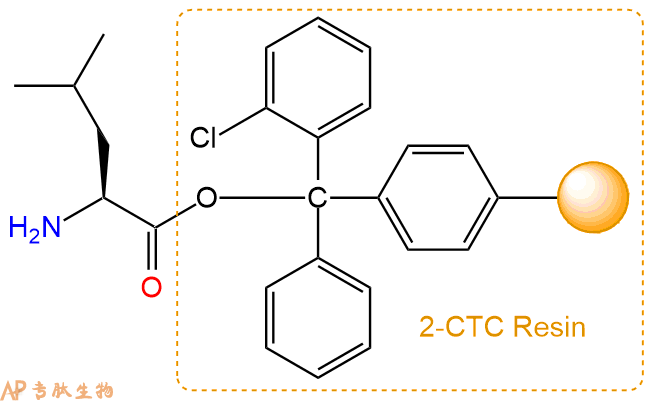
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Leu-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
3、缩合:取5.49mmol Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入10.99mmol DIPEA,5.22mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:

4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Asn(Trt)-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Leu-Asn(Trt)-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
H2N-Leu-Asn(Trt)-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ile-Leu-Asn(Trt)-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Ile-Leu-Asn(Trt)-Gly-Ile-Asn(Trt)-Asn(Trt)-Tyr(tBu)-Lys(Boc)-Asn(Trt)-Pro-Lys(Boc)-Leu-CTC Resin,结构如下:
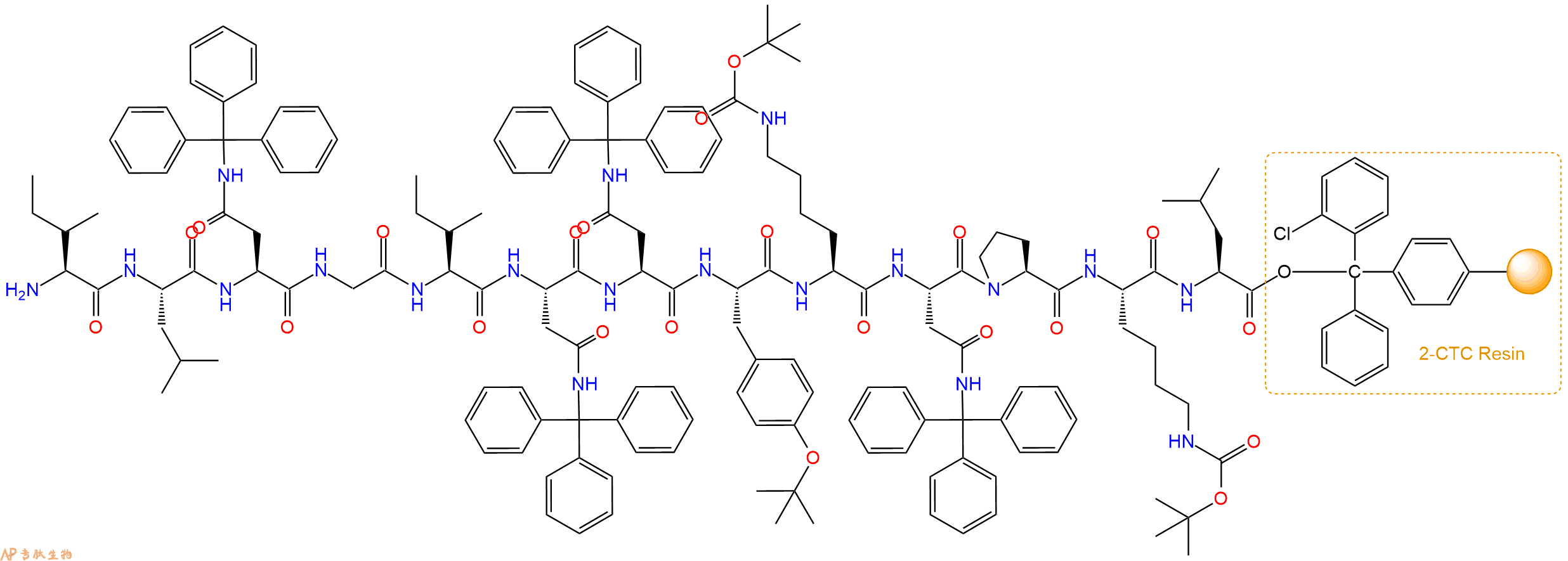
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Ile-Leu-Asn-Gly-Ile-Asn-Asn-Tyr-Lys-Asn-Pro-Lys-Leu-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽等。
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。