为肾上腺髓质素 (adrenomedullin receptor) 受体拮抗剂,同时在猫后肢血管床中,对降钙素基因相关肽 (CGRP) 受体也具有拮抗作用。
编号:192668
CAS号:159899-65-7
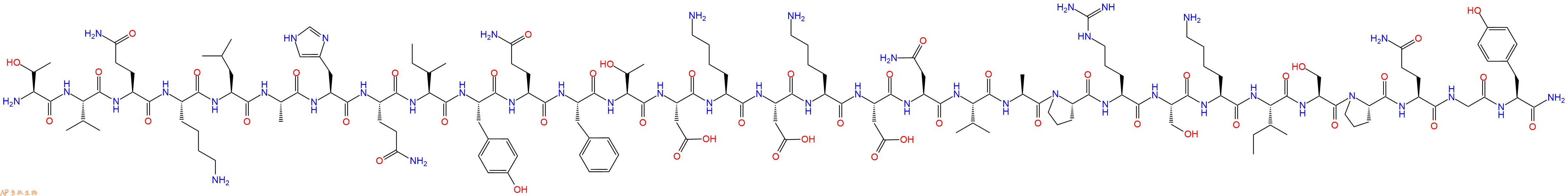
单字母:H2N-TVQKLAHQIYQFTDKDKDNVAPRSKISPQGY-NH2
| 编号: | 192668 |
| 中文名称: | 肾上腺髓质素Adrenomedullin(22-52), human |
| 英文名: | Adrenomedullin(22-52), human |
| 英文同义词: | 22-52-Adrenomedullin (human) (TFA) |
| CAS号: | 159899-65-7 |
| 单字母: | H2N-TVQKLAHQIYQFTDKDKDNVAPRSKISPQGY-NH2 |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Thr苏氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Lys赖氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Ala丙氨酸 -His组氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Tyr酪氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Thr苏氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Asn天冬酰胺 -Val缬氨酸 -Ala丙氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Gly甘氨酸 -Tyr酪氨酸 -NH2C端酰胺化 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 31 |
| 分子式: | C159H252N46O48 |
| 平均分子量: | 3575.98 |
| 精确分子量: | 3573.87 |
| 等电点(PI): | 10.91 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 5.21 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.2 |
| 疏水性值: | -1.04 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 消光系数: | 2980 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 肾上腺髓质素(Adrenomedullin) |
Adrenomedullin (AM) (22-52), human (22-52-Adrenomedullin human) (TFA),NH2 末端截短的 adrenomedullin 类似物,为肾上腺髓质素 (adrenomedullin receptor) 受体拮抗剂,同时在猫后肢血管床中,对降钙素基因相关肽 (CGRP) 受体也具有拮抗作用。
Adrenomedullin (AM) (22-52), human (22-52-Adrenomedullin human) TFA, an NH2 terminal truncated adrenomedullin analogue, is an adrenomedullin receptor antagonist. Adrenomedullin (AM) (22-52), human also antagonizes the calcitonin generelated peptide (CGRP) receptor in the hindlimb vascular bed of the cat[1].
肾上腺髓质素诱导的cAMP拮抗剂和在肾上腺髓质素和cgrp特异性受体方面比α-CGRP更有效的抑制剂。
Adrenomedullin-elicted cAMP antagonist and a more effective inhibitor than α-CGRP in terms of adrenomedullin- and CGRP-specific receptors.
Definition
Adrenomedullin (AM) is a pluripotent peptide and a hypotensive substance extracted from human adrenal tumour. Due to its origin of discovery, i.e. the medulla of the adrenal gland, the peptide is named adrenomedullin.
Discovery
AM was initially isolated from phaechromcytoma cells in 1993 by Kitmura K and his associates1.
Classification
AM is a member of the calcitonin family of peptides. In teleost fish, AM forms an independent subfamily consisting of five members viz. (AM1–AM5). This teleost AM family comprises three groups, AM1/AM4, AM2/AM3, and AM5 2,3.
Structural Characteristics
The peptide consists of 52 amino acids with a 6-member ring structure linked by a disulfide bond between amino acid 16 and 21 and amidated-COOH terminal4. It has 27 % homology with the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP).
Mechanism of action
AM peptides act through specific receptors in the plasma membrane to activate adenylate cyclase activity and modulate Ca2+ flux in the target cells. The intracellular free Ca2+ increases on the activation of phospholipase C and formation of inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate in the endothelial cells. The intracellular increase of Ca2+ activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase which leads to vascular relaxation5.
Function
AM is the most potent endogenous vasodilatory peptide found in the body6. They increase the tolerance of cells to oxidative stress, hypoxic injury and angiogenesis. It plays an important role in neurotransmission and ovarian function and in kidney, it acts as a diuretic and natriuretic7. AM is considered to play an important endocrine role in various tissues in maintaining electrolyte and fluid homeostasis8. It is used in the diagnosis and treatment of preeclampsia, type II diabetic patients and to promote fetal growth. They also play an important role in the regulation of insulin secretion and blood glucose metabolism.
References
1. Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H, Eto T (1993). Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun., 192 (2):553-560.
2. Ogoshi M, Nobata S, and Takei Y (2008). Potent osmoregulatory actions of homologous adrenomedullins administered peripherally and centrally in eels. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 295: 2075-2083.
3. Ogoshi M, Inoue K, Naruse K, Takei Y (2006). Evolutionary history of the calcitonin gene-related peptide family in vertebrates revealed by comparative genomic analyses. Peptides, 27 (12):3154-3164.
4. Cockcroft JR, Noon JP, Gardner-Medwin J, Bennett T (1997). Haemodynamic effects of adrenomedullin in human resistance and capacitance vessels. Br J Clin Pharmacol, 44(1):57-60.
5. Shimekake Y, Nagata K, Ohta S, Kambayashi Y, Teraoka H, Kitamura K, Eto T, Kangawa K, Matsuo H (1995). Adrenomedullin stimulates two signal transduction pathways, cAMP accumulation and Ca2+ mobilization, in bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem, 270: 4412-4417.
6. Yanagawa B, Nagaya N (2007). Adrenomedullin: molecular mechanisms and its role in cardiac disease. Amino Acids, 32 (1):157-164.
7. Vesely DL (2003). Natriuretic peptides and acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 285 (2):167-177.
8. Ruzicska E, Toth M, Tulassay Z, Somogyi A (2001). Adrenomedullin and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 17 (5):321-329.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1152/ajpregu.1997.272.1.R234 | Adrenomedullin-(22-52) antagonizes vasodilator responses to CGRP but not adrenomedullin in the cat | 下载 |