Aβ 25-35 的反向序列用作非活动控制。
编号:200051
CAS号:1802078-24-5
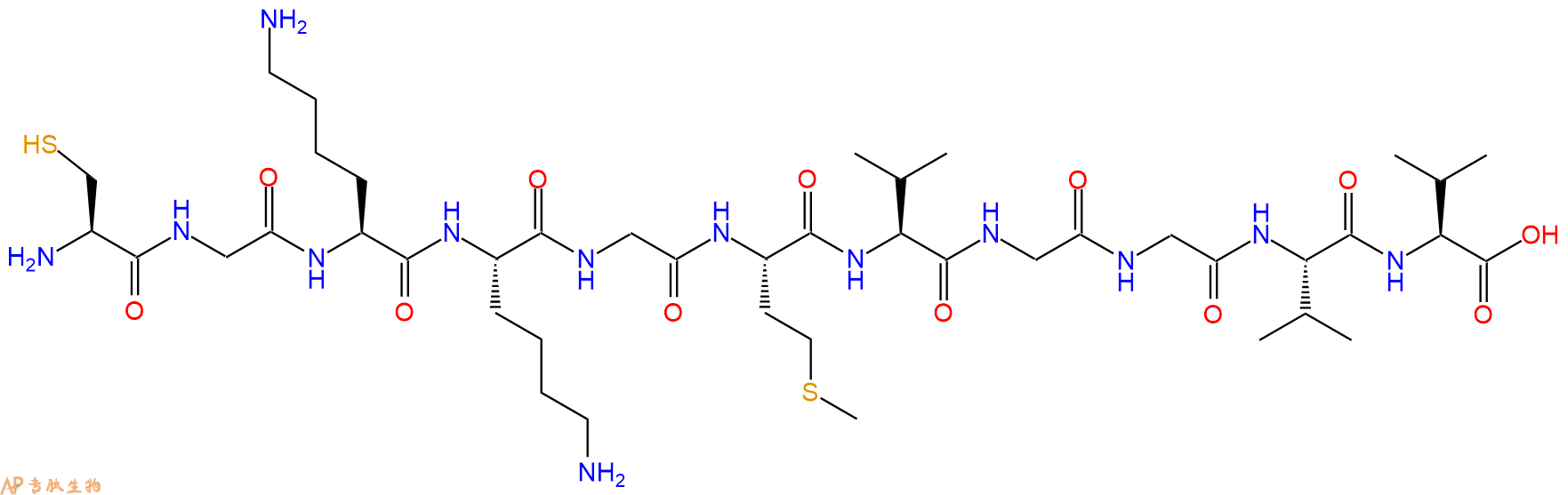
单字母:H2N-CGKKGMVGGVV-OH
| 编号: | 200051 |
| 中文名称: | 淀粉肽Cys-Gly-Lys-Lys-Gly-Amyloid β-Protein (35-40) t |
| CAS号: | 1802078-24-5 |
| 单字母: | H2N-CGKKGMVGGVV-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Cys半胱氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Lys赖氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 11 |
| 分子式: | C43H79N13O12S2 |
| 平均分子量: | 1034.3 |
| 精确分子量: | 1033.54 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 3.94 |
| 平均亲水性: | -0.11428571428571 |
| 疏水性值: | 0.69 |
| 消光系数: | - |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 淀粉样肽(Amyloid Peptides) 阿尔兹海默症 |
The reverse sequence of Aβ 25-35 is used as inactive control.
淀粉肽背景:β淀粉样蛋白(Aβ或Abeta)是从淀粉样前体蛋白加工而成的含有36–43个氨基酸的多肽。Aβ是与阿尔兹海默病相关的淀粉样蛋白斑的成分。已有证据表明,Aβ是一个多功能肽,具有显著的非病理性活性。Aβ是阿尔兹海默病患者脑中发现的沉积物的主要成分。在散发性阿尔兹海默病患者的脑中,Aβ的水平升高,造成脑血管病变和神经毒性。Aβ蛋白是由β和γ分泌酶的连续作用而产生的。γ分泌酶产生Aβ肽的C末端,在APP的转膜结构域切割,可以产生许多36-43个氨基酸残基长度的异构体,最常见的异构体是Aβ40和Aβ42。更长形式的Aβ在内质网中切割产生,而更短形式的Aβ在反面高尔基网中产生。
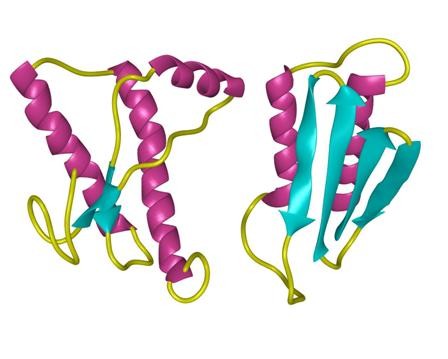
structure of Amyloid β-Peptide (1-40) (human)
淀粉样蛋白肽的 定义淀粉样蛋白 是丝状蛋白质沉积物,大小从纳米到微米不等,并且由肽β链的平行或反平行排列形成的聚集的肽β折叠构成。
结构特征:使用固态NMR(SSNMR),与计算能量最小化过程结合,Tycko和合作者已经提出从淀粉状蛋白肽SS(Aß1-40)的40个残基的形式形成的淀粉样蛋白原纤维的结构在pH 7.4和24 o C在静止条件下。在这种结构中,每个Aß1-40分子在原纤维的核心区域贡献一对ß链,大约跨越残基12-24和30-40。这些由回路25-29连接的链不是同一张ß-sheet的一部分,但参与同一原丝内两个不同的ß-sheets的形成。不同的Aß分子2、3至少从第9到39位残基以平行排列和对齐的方式相互堆叠。通过调用其他实验约束,例如使用透射电子显微镜(TEM)观察到的原丝直径和单位质量通过扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)1、2测得的长度表明,单个原丝是由四个ß片组成的,它们之间的距离约为10Å。
作用模式:阿尔茨海默氏病(AD)是淀粉样蛋白丝状沉积物的结果,淀粉状蛋白沉积物在分子水平上定义该疾病,发生在神经周膜,轴突,树突和神经元末端,如神经原纤维缠结(NFT),在细胞外神经纤维中淀粉样斑块(APC),以及周围的血管称为淀粉样嗜血性血管病(ACA)。淀粉样蛋白沉积物显然发生在发展NFT的神经元末端区域。已经表明,APC和ACA的主要成分已被证明是4.5kDa的淀粉样蛋白,最初被称为“β-蛋白”或“淀粉样蛋白A4”,我们现在将其称为“βA4”。
功能:钙失调和膜破坏是可溶性淀粉样蛋白低聚物普遍存在的神经毒性机制:进行了一项研究,以研究Ca 2+信号转导可能参与淀粉样蛋白诱导的细胞毒性,疾病相关淀粉样蛋白(β,病毒,胰岛淀粉样蛋白)的均质制剂制备了处于各种聚集状态的多肽,聚谷氨酰胺和溶菌酶),并测试了它们对加载fluo-3的SH-SY5Y细胞的作用。寡聚形式的所有淀粉样蛋白的应用(0.6-6 µg / ml)迅速(约5 s)使细胞内Ca 2+升高,而等量的单体和原纤维则没有。细胞内Ca 2+耗尽后,Abeta42低聚物引起的Ca 2+信号持续存在店,和小信号仍留在钙2 + -游离介质,指示从细胞外和细胞内Ca贡献2+源。膜对Ca 2+的渗透性增加不能归因于内源性Ca 2+通道的活化,因为反应不受强力的Ca 2 +-通道阻滞剂钴的影响。取而代之的是,观察到Abeta42和其他低聚物引起阴离子荧光染料的快速细胞泄漏,这表明膜通透性普遍提高。导致的离子和分子通量失调可能为许多淀粉样变性疾病中Ca 2+失调提供了由低聚物介导的毒性的常见机制。离子起着至关重要的作用,因为它们的跨膜浓度梯度很强,并且参与了细胞功能障碍和死亡。
2型糖尿病中的胰岛淀粉样蛋白和毒性低聚物假说: 2型糖尿病(T2DM)的特征是胰岛素抵抗,胰岛素分泌缺陷,β细胞量减少,β细胞凋亡增加和胰岛淀粉样蛋白。胰岛淀粉样蛋白源自胰岛淀粉样蛋白多肽(IAPP,胰岛淀粉样多肽),该蛋白是通过胰β细胞与胰岛素共表达和共分泌的蛋白。与其他淀粉样蛋白一样,IAPP具有形成膜渗透性毒性低聚物的倾向。越来越多的证据表明,这些有毒的寡聚体而不是这些蛋白质的细胞外淀粉样蛋白形式,是导致神经退行性疾病中神经元丢失的原因。有人提出,胞内IAPP寡聚物的形成可能会导致T2DM 6中的β细胞丢失。
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-01-00010.2002 | Rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of neuronal proteins including tau and focal adhesion kinase in response to amyloid-beta peptide exposure: involvement of Src family protein kinases | 下载 |
| 10.1046/j.0022-3042.2001.00681.x | Beta-amyloid inhibits integrated mitochondrial respiration and key enzyme activities | 下载 |
| 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02072-7 | Abeta(25-35) and Abeta(1-40) act on different calcium channels in CA1 hippocampal neurons | 下载 |
| 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0516 | Beta-amyloid fragment 25-35 causes mitochondrial dysfunction in primary cortical neurons | 下载 |
| 10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00097-9 | Differential toxicity of nitric oxide, aluminum, and amyloid beta-peptide in SN56 cholinergic cells from mouse septum | 下载 |
| 10.1023/a:1022389503105 | Discussion of the role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-phospholipase A2 pathway in production of reactive oxygen species in Alzheimer's disease | 下载 |
| 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02546.x | Involvement of calcineurin in the neurotoxic effects induced by amyloid-beta and prion peptides | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.brainres.2003.11.021 | Effects of amyloid-beta on cholinergic and acetylcholinesterase-positive cells in cultured basal forebrain neurons of embryonic rat brain | 下载 |
| 10.1002/jnr.20135 | Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release through ryanodine and inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptors in the neurotoxic effects induced by the amyloid-beta peptide | 下载 |
| 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1170-04.2004 | Involvement of the intracellular ion channel CLIC1 in microglia-mediated beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.bbalip.2004.09.006 | Amyloid beta(1-42) and its beta(25-35) fragment induce activation and membrane translocation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in bovine retina capillary pericytes | 下载 |
| 10.1007/s00221-005-0069-z | Modelling of amyloid beta-peptide induced lesions using roller-drum incubation of hippocampal slice cultures from neonatal rats | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.01.010 | Dose-dependent and sequence-sensitive effects of amyloid-beta peptide on neurosteroidogenesis in human neuroblastoma cells | 下载 |
| 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00685.x | Membrane cholesterol content plays a key role in the neurotoxicity of β-amyloid: implications for Alzheimer's disease | 下载 |
| 10.2220/biomedres.32.67 | Effects of Hericium erinaceus on amyloid β(25-35) peptide-induced learning and memory deficits in mice | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.gene.2011.06.004 | The Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) binds a specific DNA Aβ-interacting domain (AβID) in the APP, BACE1, and APOE promoters in a sequence-specific manner: characterizing a new regulatory motif | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.gene.2011.06.017 | Functional activity of the novel Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide interacting domain (AβID) in the APP and BACE1 promoter sequences and implications in activating apoptotic genes and in amyloidogenesis | 下载 |
| 10.1074/jbc.M111.276550 | Sublethal doses of β-amyloid peptide abrogate DNA-dependent protein kinase activity | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.07.004 | Na+ and K+ ion imbalances in Alzheimer's disease | 下载 |
| 10.1021/cn200127e | Neuropeptide Y protects rat cortical neurons against β-amyloid toxicity and re-establishes synthesis and release of nerve growth factor | 下载 |
| 10.3233/JAD-131715 | Mitochondrial DNA copy numbers in pyramidal neurons are decreased and mitochondrial biogenesis transcriptome signaling is disrupted in Alzheimer's disease hippocampi | 下载 |
| 10.1007/s12017-014-8315-9 | The Aβ peptides-activated calcium-sensing receptor stimulates the production and secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor-A by normoxic adult human cortical astrocytes | 下载 |
| 10.1186/s40478-014-0145-3 | β-amyloid induces a dying-back process and remote trans-synaptic alterations in a microfluidic-based reconstructed neuronal network | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.neuint.2015.01.007 | Acetylation and phosphorylation of STAT3 are involved in the responsiveness of microglia to beta amyloid | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.07.051 | Lentiviral-mediated overexpression of nerve growth factor (NGF) prevents beta-amyloid [25-35]-induced long term potentiation (LTP) decline in the rat hippocampus | 下载 |
| 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64354-4 | CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, is expressed on microglia in Alzheimer's disease brains and can mediate production of reactive oxygen species in response to beta-amyloid fibrils | 下载 |
| 10.1002/jnr.10127 | Inhibition by R(+) or S(-) pramipexole of caspase activation and cell death induced by methylpyridinium ion or beta amyloid peptide in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma | 下载 |
| 10.1002/glia.20005 | Astrocyte modulation of in vitro beta-amyloid neurotoxicity | 下载 |
| 10.3892/etm.2014.2033 | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor exerts neuroprotective actions against amyloid β-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells | 下载 |