| 编号: | 200156 |
| 中文名称: | Hirudin (54-65) (desulfated) |
| 英文名: | Hirudin (54-65) (desulfated) |
| CAS号: | 113274-56-9 |
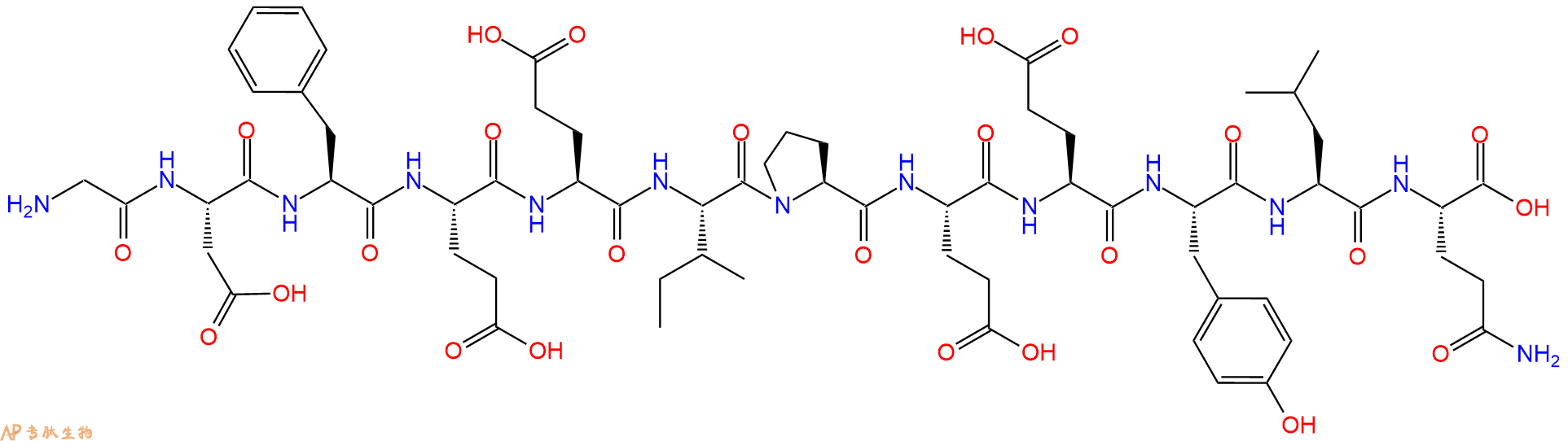
| 单字母: | H2N-GDFEEIPEEYLQ-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Gly甘氨酸 -Asp天冬氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Ile异亮氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Tyr酪氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 12 |
| 分子式: | C66H93N13O25 |
| 平均分子量: | 1468.52 |
| 精确分子量: | 1467.64 |
| 等电点(PI): | 3.89 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | -3.02 |
| 平均亲水性: | 0.57 |
| 疏水性值: | -1.07 |
| 消光系数: | 1490 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 血液学 水蛭素(Hirudin) |
Definition
Hirudin is a thrombin-specific inhibitor isolated from the leech Hirudo medicinalis
Hirudin analogs
CX-397 is novel recombinant hirudin analog, composed of the N-terminal half of HV-1 (HV-11-36) combined with the C-terminal half of HV-3 (HV-337-66). Bivalirudin, a synthetic analog of the carboxy-terminus of hirudin, is a reversible thrombin inhibitor.
Structural Characteristics
The thrombin-specific inhibitor hirudin is a polypeptide of 65 or 66 amino acid residues isolated from the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Sequence analysis of different naturally occurring forms of hirudin revealed homologies 80%. The 6 cysteine residues of three disulfide bonds connecting Cys6with Cys14, Cys16 with Cys28, and Cys22 with Cys39 has also been detected. Hirudin consists of an amino-terminal compact domain (residues l-49) held together by the three disulfide linkages and a distorted carboxyl-terminal tail (residues 50- 65) which does not fold back on the rest of the protein. Hirudin reacts rapidly with a-thrombin forming tight, noncovalent 1. The specificity of the interaction of a-thrombin with macromolecular substrates is assumed to reside in interactions at three distinct regions: the primary binding pocket for the P1 residue, an apolar binding site adjacent to the catalytic site, and an anion-binding region which may be responsible for the specific interaction of thrombin with fibrinogen2.
Mode of Action
The hirudin acts as a potent anticoagulant by binding to thrombin with high specificity and affinity. Hirudin is distinguished from conventional protease inhibitors by two unique characteristics. (a) Unlike most protease inhibitors which contain a well-defined reactive site (P1 residue) that interacts with the active site of the target enzyme1. The structural element of hirudin which blocks the active site of thrombin is an extended hydrophobic site including the Hz-terminal residues (Val1, Val2, and Tyr3)3. (b) Unlike most serine protease inhibitors which are compact molecules, hirudin has a tadpole-like shape, consisting of a compact amino-terminal domain and a disordered carboxyl-terminal tail4.
Functions
CX-397, a novel recombinant hirudin analog - A study was conducted using four hirudin analogs in thrombin inhibition, which included CX-397, CX-397R, hirudin variants-1 (HV-11-36) and -3 (HV-337-366).Their anti-thrombin activity was determined by a fluorogenic enzyme assay and compared with that of recombinant HV-1 (rHV-1) and rHV-3. The order of the magnitude of dissociation constants (Ki) of these four hirudin analogs in thrombin inhibition was as follows: CX-397R (0.294 pM) > rHV-1 (0.148 pM) > rHV-3 (0.0593 pM) > CX-397 (0.0433 pM), indicating that CX-397 is the strongest inhibitor among them5.
Reduction of adhesion formation by intraperitoneal administration of a recombinant Hirudin analog - Adhesion formation is a major source of postoperative morbidity and mortality. Therefore, the reduction of postoperative adhesion formation would be of clinical benefit. Various modalities have been shown to reduce adhesion formation, including fibrinolytic enzymes, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and barriers that reduce the apposition of sites of potential adhesion formation. A study was conducted to examine the ability of an inhibitor of thrombin, a recombinant hirudin analog (recHirudin), to reduce the formation of intraperitoneal adhesions in two rabbit models of adhesion formation. In the sidewall and double uterine horn models, recHirudin was administered via Alzet miniosmotic pump for the entire postoperative interval. In both of these models, there was a dose-dependent reduction in adhesion formation as measured by (1) the area of the sidewall injury that was involved in adhesions to the cecum and the bowel or (2) the involvement of the uterine horns to themselves or other peritoneal organs. This implies that postoperative administration of recHirudin to the site of injury reduced the formation of postoperative adhesions in two animal models6.
Influence of bivalirudin on tissue factor-triggered coagulation - Bivalirudin, a synthetic analog of the carboxy-terminus of hirudin, is a reversible thrombin inhibitor. A study was conducted using three in-vitro models (numerical simulations, synthetic coagulation proteome and whole blood) of contact pathway-independent blood coagulation triggered with tissue factor. It was found that increasing concentrations of bivalirudin prolong the initiation phase of thrombin generation in a concentration-dependent manner. At subpharmacologic bivalirudin concentrations (0.5-2 micromol/l), total thrombin generation was significantly increased. At a pharmacologic concentration (5 micromol/l), bivalirudin suppressed thrombin generation in the synthetic coagulation proteome; in numerical simulations and contact pathway-inhibited whole blood, no thrombin generation was detected over 1200-2000 s and platelet activation was inhibited by 80%. The addition of a pharmacologic concentration (9 micromol/l) of a naturally occurring protease inhibitor aprotinin in the presence of at least 0.5 micromol/l bivalirudin provided limited enhancement of the bivalirudin inhibitory effect. This implied that bivalirudin at pharmacologic concentrations is an efficient inhibitor of thrombin generation, platelet activation and clot formation, which acts not as a modulator but as an 'on-off' switch of blood coagulation7.
References
1. Dodt J, Seemüller U, Maschler R, Fritz H (1985). The complete covalent structure of hirudin: Localization of the disulfide bonds. Biol. Chem. Hoppe. Seyler., 366(4), 379-85.
2. John W. Fenton , Frederick A. Ofosu, Diane V. Brezniak, Houria I. Hassouna (1998).Thrombin and Antithrombotics. Semin. Thromb. Hemost., 24, 87-91.
3. TJ Rydel, KG Ravichandran, A Tulinsky, W Bode, R Huber, C Roitsch, and JW Fenton 2nd (1990). The structure of a complex of recombinant hirudin and human alpha-thrombin. Science., 249 (4966), 277-280.
4. Chang JY (1983).The functional domain of hirudin, a thrombin-specific inhibitor. FEBS Lett., 164(2), 307-13.
5. Komatsu Y, Misawa S, Sukesada A, Ohba Y, Hayashi H (1993). CX-397, a novel recombinant hirudin analog having a hybrid sequence of hirudin variants-1 and -3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 196(2), 773-9.
6. Rodgers KE, Girgis W, Campeau JD, diZerega GS (1996). Reduction of adhesion formation by intraperitoneal administration of a recombinant Hirudin analog. J. Invest. Surg ., (5), 385-91.
7. Butenas S, Orfeo T, Brummel-Ziedins KE, Mann KG. 2007 Influence of bivalirudin on tissue factor-triggered coagulation. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis., 18(5), 407-14.
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1074/jbc.M110257200 | Binding of exosite ligands to human thrombin. Re-evaluation of allosteric linkage between thrombin exosites I and II | 下载 |
| 10.1002/jms.3919 | Effects of acidic peptide size and sequence on trivalent praseodymium adduction and electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry | 下载 |
多肽H2N-Gly-Asp-Phe-Glu-Glu-Ile-Pro-Glu-Glu-Tyr-Leu-Gln-COOH的合成步骤:
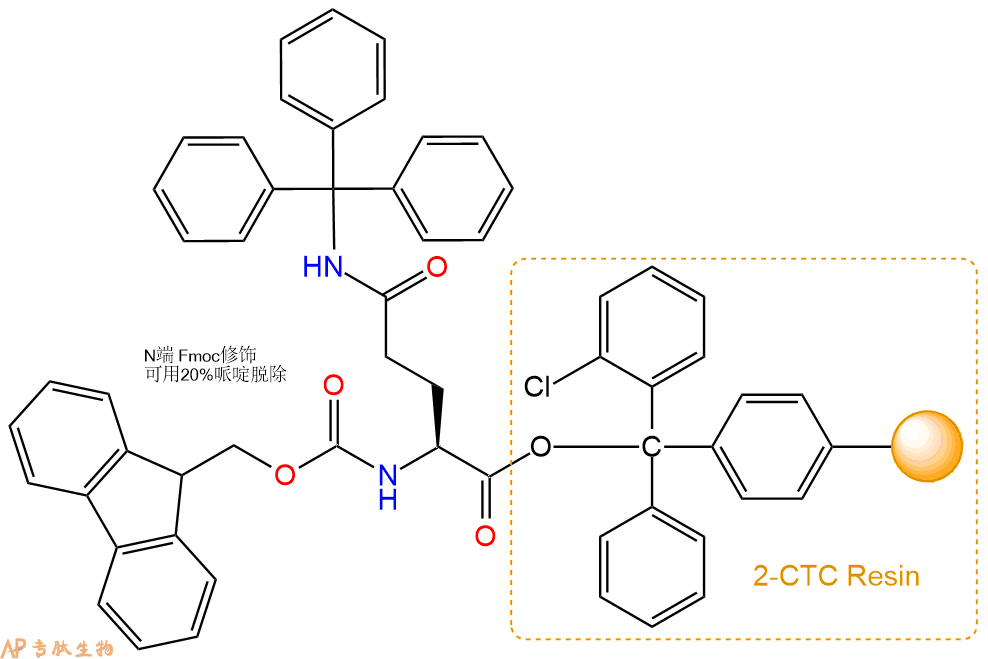
1、合成CTC树脂:称取0.41g CTC Resin(如初始取代度约为0.91mmol/g)和0.45mmol Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-OH于反应器中,加入适量DCM溶解氨基酸(需要注意,此时CTC树脂体积会增大好几倍,避免DCM溶液过少),再加入1.12mmol DIPEA(Mw:129.1,d:0.740g/ml),反应2-3小时后,可不抽滤溶液,直接加入1ml的HPLC级甲醇,封端半小时。依次用DMF洗涤2次,甲醇洗涤1次,DCM洗涤一次,甲醇洗涤一次,DCM洗涤一次,DMF洗涤2次(这里使用甲醇和DCM交替洗涤,是为了更好地去除其他溶质,有利于后续反应)。得到 Fmoc-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin。结构图如下:
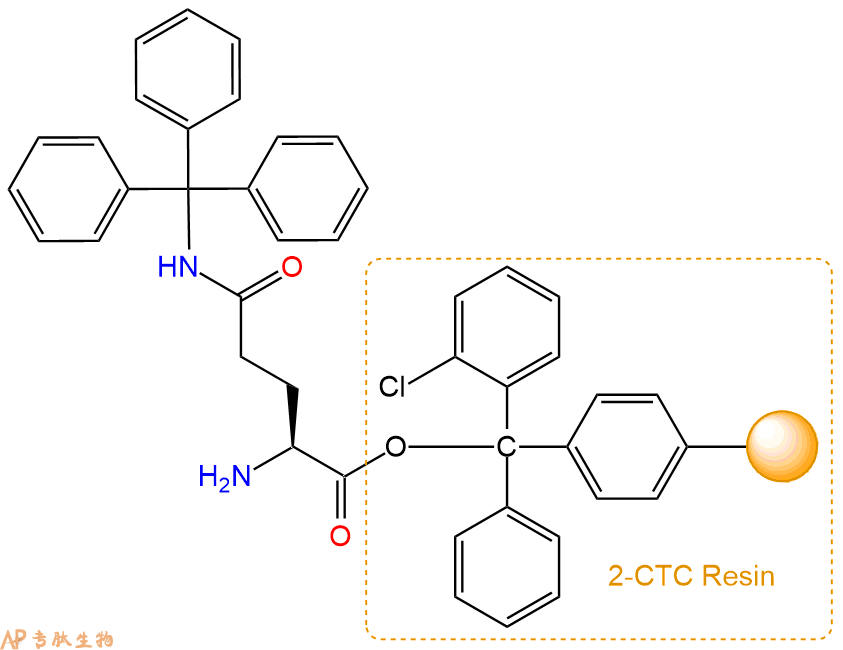
2、脱Fmoc:加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
3、缩合:取1.12mmol Fmoc-Leu-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入2.24mmol DIPEA,1.06mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
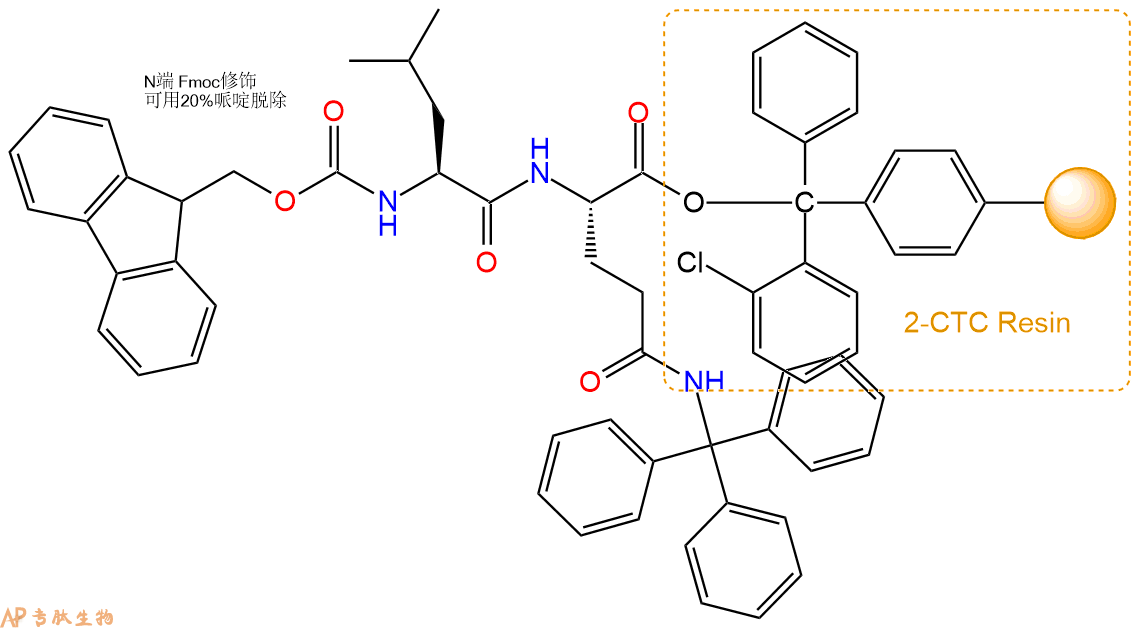
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Phe-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Phe-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Asp(OtBu)-Phe-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
H2N-Asp(OtBu)-Phe-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Asp(OtBu)-Phe-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Gly-Asp(OtBu)-Phe-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Ile-Pro-Glu(OtBu)-Glu(OtBu)-Tyr(tBu)-Leu-Gln(Trt)-CTC Resin,结构如下:
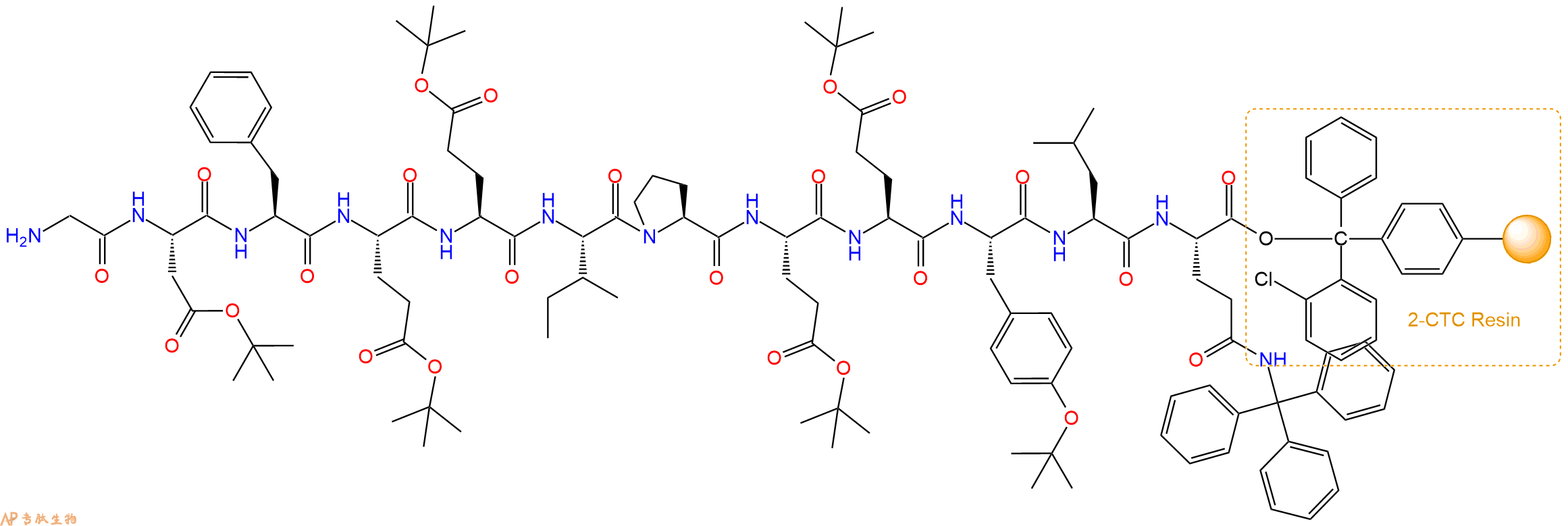
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Gly-Asp-Phe-Glu-Glu-Ile-Pro-Glu-Glu-Tyr-Leu-Gln-COOH。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽等。
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。