一种未消化的麦醇溶蛋白肽,可诱导肠道内的先天性免疫反应并干扰内吞运输。Gliadin p31-43 TFA 可用于乳糜泻的研究。
编号:200640
CAS号:
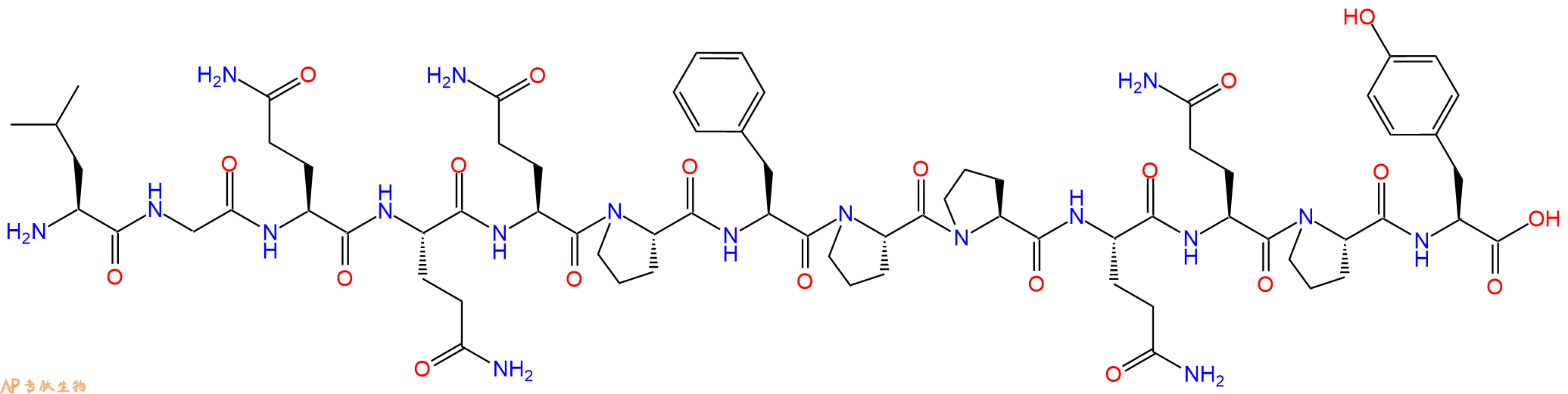
单字母:H2N-LGQQQPFPPQQPY-OH
| 编号: | 200640 |
| 中文名称: | Gliadin p31-43 |
| 单字母: | H2N-LGQQQPFPPQQPY-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Leu亮氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Pro脯氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Pro脯氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Pro脯氨酸 -Tyr酪氨酸 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 13 |
| 分子式: | C71H102N18O20 |
| 平均分子量: | 1527.68 |
| 精确分子量: | 1526.75 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 1.97 |
| 平均亲水性: | -0.8375 |
| 疏水性值: | -1.43 |
| 消光系数: | 1490 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 防御素(Defensins) |
Gliadin p31-43 TFA 是一种未消化的麦醇溶蛋白肽,可诱导肠道内的先天性免疫反应并干扰内吞运输。Gliadin p31-43 TFA 可用于乳糜泻的研究。
Gliadin p31-43 TFA is an undigested gliadin peptide. Gliadin p31-43 TFA induces an innate immune response in the intestine and interferes with endocytic trafficking. Gliadin p31-43 TFA can be used for celiac disease research[1][2].
定义
防御素是具有广泛抗菌活性的小型抗菌肽(AMP)。它在宿主防御感染,炎症,伤口修复和获得性免疫中起重要作用
发现
在1960年代研究兔和豚鼠白细胞裂解物的抗菌活性时,发现了防御素。所谓的富含精氨酸的阳离子肽是由其高阴极电泳活性迁移率定义的,并因其分离和详细的化学表征而引起了人们的关注1。
分类
哺乳动物防御素可根据其结构上的差异被细分为三个主要类别:所述一个防御素,b防御素和q防御素。一个防御素具有广泛的 抗革兰氏阴性菌和革兰氏阳性抗菌活性 细菌,真菌和包膜病毒。b-防御素 主要对革兰氏阴性细菌和酵母具有活性。q-防御素是一种 在猕猴白细胞中发现的含有18个氨基酸和3个二硫键的环状肽2。三种防御素(人类嗜中性粒细胞防御素[HNP] -1,HNP-2和HNP-3)构成人类多形核嗜中性粒细胞(PMN)3的嗜铁粒颗粒中总蛋白质的30-50%。
结构特征
防御素是小的半胱氨酸富含阳离子的蛋白质与18-45个氨基酸,并用3.4〜4.5 kDa的分子量。所有防御素共有一个特征性的三个二硫键基序。这些半胱氨酸二硫键对于防御素的生物活性至关重要。
行动方式
抗菌 活性的具体机制涉及细菌膜的透化作用。它 已经假定各个单体低聚以形成 通过阴离子膜的孔径,虽然证据仅仅是 间接4。
防御素的杀微生物活性是通过阴离子脂质双层的透化作用和随后 细胞内含物的释放而实现的。防御素和 细菌膜之间的相互作用主要受静电力控制。透化的一种机理被认为涉及 细菌膜中离子孔的形成。第二种模型也称为地毯模型,它假定防御素被认为聚集成带正电荷的贴剂 ,该贴剂可 在肽周围的较大区域中和膜的阴离子脂质头基。这种中和破坏 了脂质双层的完整性,导致 出现瞬时间隙并允许离子渗透到膜4中。
功能
防御素是免疫细胞响应细菌感染而产生的抗菌肽。它还在阻止人类宿主细胞对HIV 5的侵袭中起作用,并在小鼠6中诱导针对肿瘤的细胞介导的免疫反应。各种防御素对单核细胞,T细胞和树突状细胞具有趋化活性。 细胞在先天宿主防御过程中产生的防御素可作为 启动,动员和增强适应性免疫宿主防御的信号。
参考
1. Ganz.T (2003). Defensins: Antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nature, 3,710-720.
2. Schneider JJ, Unholzer A, Schaller M, Schäfer-Korting M, Korting HC (2005). Human defensins. J Mol Med, 83(8), 587-595.
3. R I Lehrer, A Barton, K A Daher, S S Harwig, T Ganz, and M E Selsted (1989). Interaction of human defensins with Escherichia coli. Mechanism of bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest, 84(2), 553–561.
4. Hoover DM, Rajashankar KR, Blumenthal R, Puri A, Oppenheim JJ, Chertov O, Lubkowski J (2000). The structure of human beta-defensin-2 shows evidence of higher order oligomerization. J Biol Chem, 275(42), 32911-32918.
5. Zhang L, Yu W, He T, Yu J, Caffrey RE, Dalmasso EA, Fu S, Pham T, Mei J, Ho JJ, Zhang W, Lopez P, Ho DD (2002). Contribution of human alpha-defensin 1, 2, and 3 to the anti-HIV-1 activity of CD8 antiviral factor. Science, 303 (5657), 467.
6. Biragyn A, Ruffini PA, Leifer CA, Klyushnenkova E, Shakhov A, Chertov O, Shirakawa AK, Farber JM, Segal DM, Oppenheim JJ, Kwak LW. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by beta-defensin 2. Science, 298(5595), 1025-1029.
Definition
Defensins are small antimicrobial peptide (AMP) with a broad spectrum of antibacterial activity. It plays an important role in host defenses against infections, inflammation, wound repair and acquired immunity
Discovery
Defensins were discovered when the antimicrobial activity of rabbit and guinea-pig leukocyte lysates were studied in the 1960’s. The so-called arginine- rich cationic peptides were defined by their high cathodal electrophorectic activity mobility and attracted attention because of their isolation and detailed chemical characterization1.
Classification
The mammalian defensins can be subdivided into three main classes according to their structural differences: the a-defensins, b-defensins and q-defensins. a-Defensins have broad antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, fungi, and enveloped viruses. b-Defensins are mainly active against Gram-negative bacteria and yeast. q-Defensin is a cyclic peptide containing 18 amino acids with three disulfides discovered in macaque leukocytes2. Three defensins (human neutrophil peptide defensin [HNP]-1, HNP-2, and HNP-3) constitute between 30-50% of the total protein in azurophil granules of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN)3.
Structural Characteristics
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins with 18-45 amino acids and with a molecular weight of 3.4 to 4.5 kDa. All defensins share a characteristic three disulfide bond motif. These cysteine disulfide bonds are essential for the biological activities of defensins.
Mode of action
The specific mechanism of antimicrobial activity involves permeabilization of bacterial membranes. It has been postulated that individual monomers oligomerize to form a pore through anionic membranes, although the evidence is only indirect4.
The microbicidal activity of defensins is brought about by permeabilization of anionic lipid bilayers and the subsequent release of cellular contents. Interactions between defensins and bacterial membranes are governed mainly by electrostatic forces. One mechanism of permeabilization is thought to involve the formation of ion pores in bacterial membranes. The second model also known as carpet model assumes that the defensins are thought to aggregate into positively charged patches that neutralize anionic lipid head groups of the membrane over a wide area around the peptides. This neutralization disrupts the integrity of the lipid bilayer, causing transient gaps to arise and allowing ions to permeate the membrane4.
Functions
Defensins are antimicrobial peptides produced by immune cells in response to bacterial infection. It also functions in blocking of human host cell invasion against HIV5 and the induction of cell-mediated immune responses against tumors in mice6. Various defensins have chemotactic activity for monocytes, T cells and dendritic cells. Defensins produced by cells in the course of innate host defense serve as signals which initiate, mobilize, and amplify adaptive immune host defenses.
References
1. Ganz.T (2003). Defensins: Antimicrobial peptides of innate immunity. Nature, 3,710-720.
2. Schneider JJ, Unholzer A, Schaller M, Schäfer-Korting M, Korting HC (2005). Human defensins. J Mol Med, 83(8), 587-595.
3. R I Lehrer, A Barton, K A Daher, S S Harwig, T Ganz, and M E Selsted (1989). Interaction of human defensins with Escherichia coli. Mechanism of bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest, 84(2), 553–561.
4. Hoover DM, Rajashankar KR, Blumenthal R, Puri A, Oppenheim JJ, Chertov O, Lubkowski J (2000). The structure of human beta-defensin-2 shows evidence of higher order oligomerization. J Biol Chem, 275(42), 32911-32918.
5. Zhang L, Yu W, He T, Yu J, Caffrey RE, Dalmasso EA, Fu S, Pham T, Mei J, Ho JJ, Zhang W, Lopez P, Ho DD (2002). Contribution of human alpha-defensin 1, 2, and 3 to the anti-HIV-1 activity of CD8 antiviral factor. Science, 303 (5657), 467.
6. Biragyn A, Ruffini PA, Leifer CA, Klyushnenkova E, Shakhov A, Chertov O, Shirakawa AK, Farber JM, Segal DM, Oppenheim JJ, Kwak LW. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by beta-defensin 2. Science, 298(5595), 1025-1029.
Merlin Nanayakkara, et al. P31-43, an undigested gliadin peptide, mimics and enhances the innate immune response to viruses and interferes with endocytic trafficking: a role in celiac disease. Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 17;8(1):10821. : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30018339
María Florencia Gómez Castro, et al. p31-43 Gliadin Peptide Forms Oligomers and Induces NLRP3 Inflammasome/Caspase 1- Dependent Mucosal Damage in Small Intestine. Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 30;10:31. : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30761127/