NocII 由17个氨基酸组成,它作为一种孤儿神经肽,可刺激小鼠运动。
编号:200720
CAS号:
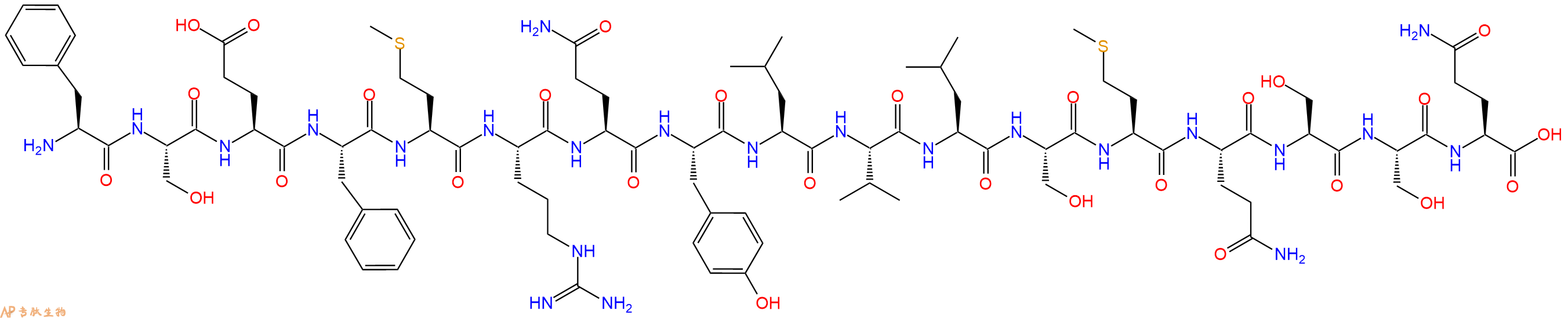
单字母:H2N-FSEFMRQYLVLSMQSSQ-OH
| 编号: | 200720 |
| 中文名称: | 孤儿神经肽NocII, Orphanin FQ2, (OFQ2, NOCII) |
| 英文名: | NocII , Orphanin FQ2, (OFQ2, NOCII) |
| 单字母: | H2N-FSEFMRQYLVLSMQSSQ-OH |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Glu谷氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Arg精氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Tyr酪氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Val缬氨酸 -Leu亮氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Met甲硫氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -Ser丝氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Gln谷氨酰胺 -OHC端羧基 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 17 |
| 分子式: | C92H141N23O28S2 |
| 平均分子量: | 2081.37 |
| 精确分子量: | 2079.98 |
| 等电点(PI): | 11.31 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 1.98 |
| 平均亲水性: | -0.48823529411765 |
| 疏水性值: | -0.08 |
| 消光系数: | 1490 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 神经肽及相关肽 脑啡肽(Enkephalins) |
NocII 由17个氨基酸组成,它作为一种孤儿神经肽,可刺激小鼠运动。
定义
神经肽的长度为3-40个氨基酸,可作为神经递质。它们广泛分布于中枢神经系统和周围神经系统。
发现
神经肽是由约翰·休斯博士和科斯特里茨博士于1975年发现的。它们是内啡肽,内在产生的吗啡样物质,会在体内产生一系列类似药物的作用。可以从序列信息1中鉴定神经肽前体mRNA序列,并且得到的翻译蛋白序列包括信号肽序列和一个或多个神经肽。广泛而复杂的一系列酶处理步骤,包括被激素或前蛋白转化酶切割以及其他翻译后修饰,在创建活性神经肽之前就发生在翻译后的蛋白质序列上 2,3。
结构特征
通过核磁共振(NMR)光谱研究了几种来自软体动物的类似神经肽的构象性质。肽的N末端可变区中的氨基酸取代对溶液中反向转化的种群具有显着影响。通过使用两个独立的NMR参数测得的转弯数,发现使用Helix aspersa的受体膜制剂与IC50值高度相关(r2 = 0.93和0.82)。这些结果表明,构象集合降低了特定肽相对于特定受体4,5的有效浓度。
神经肽Y与人肽相同,并且与禽胰多肽高度同源。神经肽Y和禽胰多肽之间的同源性保留了维持三级结构必不可少的所有残基。结果表明,神经肽保留了紧凑的三级结构,其特征是在N末端的聚脯氨酸II类螺旋和C末端的a螺旋 6之间广泛的疏水相互作用。
已经通过许多孤儿受体之一发现了一些肽,这些受体是内源性配体未知的受体,例如“类阿片受体样1”(ORL1)。随后,已阐明该ORL1受体的内源性激动剂的结构,一种称为孤儿蛋白FQ或伤害感受蛋白的17个氨基酸的肽7。
行动方式
神经肽是由神经元作为细胞间信使释放的肽。一些神经肽充当神经递质,而另一些充当激素。神经肽既可以为我们提供支持,也可以为我们提供帮助。抗炎神经肽可帮助我们减少皮肤发炎。神经肽是自然产生的,可以在非常有限的时间内与靶细胞膜受体在明确的作用位点相互作用。因此,大多数这些内源性化合物的特征在于低的生物屏障渗透性和非常高的酶促降解敏感性。脑室内或全身注射神经肽Y(NPY)可使cast割的雌性大鼠血浆中的促黄体生成激素(LH)水平降低。6。
功能
生物功能,神经肽控制着我们的情绪,能量水平,痛苦和愉悦感,体重以及解决问题的能力;它们还会形成记忆,情感行为,食欲和发炎,修复疤痕和皱纹并调节我们的免疫系统。这些活跃的大脑小信使实际上打开了皮肤7的细胞功能。因此,今天,与神经肽系统相互作用的药物设计是后基因组药物化学研究最广泛的途径之一。
P物质已被确定为负责伤害性信号传递的主要神经肽。内源性阿片类药物是天然神经肽,负责伤害性信号的调节(通常是抑制)。
免疫系统,当它们被分泌时,它们会激活自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞),从而增强我们的免疫系统。
随着内啡肽的分泌越来越多,血管病变使收缩的血管恢复到正常状态,使血液以正常方式流动。大多数成人疾病都始于血管堵塞。内啡肽有助于改善血液循环。
内啡肽通过去除超氧化物具有抗衰老作用。从呼吸进入人体的氧气可以转变为超氧化物。这是造成人类疾病和衰老的最大敌人之一。
抗压力激素,应对压力的能力与我们体内的内啡肽水平成正比。
缓解疼痛的作用是,我们的神经系统在接收到疼痛信号时会分泌神经递质。一旦内啡肽在疼痛的那一刻被释放,内啡肽就会与神经元上的内啡肽受体结合,从而阻止第一种神经递质被分泌出来。
记忆力,神经肽可以改善记忆力,因为它们可以使脑细胞保持年轻健康。
参考
1. Hummon AB, Richmond TA, Verleyen P, Baggerman G, Huybrechts J, Ewing MA, Vierstraete E, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Liliane SL, Robinson GE (2006). From the genome to the proteome: uncovering peptides in the Apis brain. Science, 27(314):647-649.
2. Rockwell NC, Krysan DJ, Komiyama T, Fuller RS (2002). Precursor processing by Kex2/Furin Proteases. Chem. Rev., 102:4525–4548.
3. Von ER, Beck-Sickinger AG (2004). Biosynthesis of peptide hormones derived from precursor sequences. Curr. Med. Chem.,11:2651–2665.
4. Edison AS, Espinoza E, Zachariah C (1999). Conformational Ensembles: The Role of Neuropeptide Structures in Receptor Binding. The Journal of Neuroscience., 19(15):6318-6326.
5. Payza K, Greenberg MJ, Price DA (1989). Further characterization of Helix FMRFamide receptors: kinetics, tissue distribution, and interactions with the endogenous heptapeptides. Peptides, 10:657-661.
6. Allen J, Novotný J, Martin J, Heinrich G (1987). Molecular structure of mammalian neuropeptide Y: Analysis by molecular cloning and computer-aided comparison with crystal structure of avian homologue. PNAS., 84:2532-2536.
7. Guya J, Lia S, Pelletier G (1988). Studies on the physiological role and mechanism of action of neuropeptide Y in the regulation of luteinizing hormone secretion in the rat. Regulatory Peptides., 23(2):209-216.
脑啡肽和前脑啡肽
定义
脑啡肽是在大脑和内分泌组织中高水平发现的阿片类肽。新出现的含有脑啡肽的肽的主要种类似乎是完整的前体,前脑啡肽1。
相关肽
阿片肽构成了一大类小蛋白,它们与鸦片生物碱,吗啡和海洛因相似,能与细胞膜受体相互作用。阿片生物碱衍生物广泛用于镇痛和麻醉。最初的阿片肽家族是脑啡肽,强啡肽和内啡肽。在心脏中已经发现了来自这三个阿片肽家族的代表性肽。已克隆并测序了三种不同的阿片受体:mu(µ),delta(d)和kappa(?)2。
发现
Kosterlitz和Hughes在1975年发现了脑啡肽和内啡肽3。
结构特征
蛋氨酸-脑啡肽(Met-Enk)的氨基酸序列为酪氨酸-甘氨酸-甘氨酸-苯丙氨酸-蛋氨酸。前脑啡肽序列包含五肽Met-Enk的四个拷贝,leu-脑啡肽之一和Met- enk的两个扩展形式(Met- enk -arg 6 -phe 7和met- enk -arg 6 -gly 7 -leu 8)。成对的碱性氨基酸标记这些小肽从前体裂解。原脑啡肽由称为原激素转化酶的内蛋白水解酶加工,该酶在二元氨基酸位点识别并切割。最初的前脑啡肽处理开始于传输到高尔基体网络之前,并且过程很快。后续处理需要在高尔基体网络远端的酸性环境中进行。前脑啡肽对肽B具有快速裂解,而较慢的裂解产生其他中等大小的产物,其最终被裂解成五肽至八肽。在各种组织(肌肉,神经,内分泌)中发现的不同分子量的最终产物可能是由于切割序列的差异和加工所需的局部酶促条件2所致。
作用方式
肽Met-Enk和Leu-Enk(阿片受体的内源性配体)起神经调节剂或神经递质的作用。脑啡肽在哺乳动物脑中最显着的作用是神经元放电速率的降低,并且已经表明这些肽是抑制性递质。脑啡肽抑制或增强了中枢神经元对几种假定的递质的反应,表明突触后的作用。还显示脑啡肽抑制K +诱导的去甲肾上腺素,多巴胺和乙酰胆碱从大鼠脑片的释放,表明突触前的作用。脑啡肽抑制豚鼠回肠中的肌间神经元的发射。这种抑制可能是由于脑啡肽的直接突触后作用导致神经元膜超极化4。。为了实现其生物学功能,必须将脑啡肽从水相转运至其膜结合受体蛋白的富含脂质的环境。现已知道,Met-enk通过三种主要的亚型受体起作用,分别称为μ,d和β。-受体。虽然前两个受体亚型介导了Met-enk的经典阿片样物质作用,但据报道β受体参与了该肽的非阿片样物质作用,即对细胞生长的抑制作用5。
功能
前脑啡肽是神经肽的前体,在神经内分泌和神经系统中具有多种功能。激活后,发现T辅助淋巴细胞表达高水平的前脑啡肽mRNA,并分泌大量的Met-Enk神经肽,这可能表明了免疫系统和神经系统相互作用的轴6。脑啡肽引起抗伤害感受和增强的吗啡镇痛作用,但它们也阻碍了耐受性和身体依赖性的发展。除了其中枢和外周镇痛作用外,阿片类药物还可以调节免疫活性和细胞增殖。此外,众所周知,它们在不同的生理过程中具有重要作用,例如细胞分化和再生,炎症,癌症和血管生成以及镇痛作用5。
参考
1、Fleminger G, Lahm HW, Udenfriend S (1984).Changes in rat adrenal catecholamines and proenkephalin metabolism after denervation. PNAS., 81(11):3587-3590.
2、Barbara A. Barron. 2000. Cardiac Opioids. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 224:1-7.
2、Fratta W, Yang HY, Hong J, Costa E (1977). Stability of Met-enkephalin content in brain structures of morphine-dependent or foot shock-stressed rats. Nature, 268(5619):452-453.
4、Wouters W, Den Bercken JV (1979). Hyperpolarisation and depression of slow synaptic inhibition by enkephalin in frog sympathetic ganglion. Nature, 277:53-54.
5、Tsanova A, Dacheva D, Penchev V, Georgiev G, Pajpanova T, Golovinski E, Lalchev Z (2009). Comparative study of the interaction between synthetic methionine-enkephalin and monolayers of zwitterionic and negatively 6、charged phospholipids. Biotechnol & Biotechnol., 23:463-466.
7、Rattner A, Korner M, Rosen H, Baeuerle PA, Citri Y (1991). Nuclear factor Kappa B activates proenkephalin transcription in T lymphocytes. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 11(2):1017-1022.
Enkephalins and Proenkephalins
Definition
Enkephalins are opioid peptides that are found at high levels in the brain and endocrine tissues. The major species of newly appearing enkephalin-containing peptide appears to be the intact precursor, proenkephalin 1.
Related Peptides
Opioid peptides constitute a large group of small proteins that interact with cell membrane receptors similarly to opiate alkaloids, morphine and heroin. Opiate alkaloid derivatives are extensively used for analgesia and anesthesia. The original opioid peptide families are enkephalins, dynorphins, and endorphins. Representative peptides from these three opioid peptide families have been found in the heart. Three different opiate receptors have been cloned and sequenced: mu (µ), delta (d), and kappa (?) 2.
Discovery
Kosterlitz and Hughes discovered enkephalins and endorphins in 1975 3.
Structural Characteristics
The amino acid sequence of methionine-enkephalin (Met-Enk) is tyrosine-glycine-glycine-phenylalanine-methionine. The proenkephalin sequence contains four copies of the pentapeptide Met-Enk, one of leu-enkephalin, and two extended forms of Met-enk (Met-enk-arg6-phe7 and met-enk-arg6-gly7-leu8). Pairs of basic amino acids mark these small peptides for cleavage from the precursor. Proenkephalin is processed by endoproteolytic enyzmes termed prohormone convertases, which recognize and cleave at dibasic amino acid sites. Initial proenkephalin processing starts before transport to the golgi network and are rapid. Later processing requires an acidic environment distal to the golgi network. Proenkephalin has a fast cleavage to peptide B, and slower cleavages yield other intermediate sized products that are cleaved ultimately to the penta to octapeptides. The different molecular-weight end products found in diverse tissues (muscle, neural, endocrine) may be due to variations in the cleavage sequence and local enzymatic conditions for processing 2.
Mode of Action
Pentapeptides Met-Enk and Leu-Enk, the endogenous ligands for the opiate receptor, function as neuromodulators or neurotransmitters. The most prominent action of enkephalins in the mammalian brain is depression of neuronal firing rate and it has been suggested that these peptides are inhibitory transmitters. The response of central neurones to several putative transmitter substances is depressed or enhanced by enkephalins, suggesting a postsynaptic action. It has also been shown that enkephalins suppress the K+-induced release of noradrenaline, dopamine and acetylcholine from rat brain slices, indicating a presynaptic effect. The firing of myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig ileum is inhibited by enkephalins. This inhibition is probably due to a direct postsynaptic action of the enkephalins resulting in a hyperpolarisation of the neuronal membrane 4. To achieve their biological function, enkephalins must be transported from an aqueous phase to the lipid-rich environment of their membrane bound receptor proteins. It is now known that Met-enk acts via three main subtypes of receptors referred to as µ, d and ? - receptors. While the first two receptor subtypes mediate the classic opioid effects of Met-enk, ?-receptors are reported to be involved in the non-opioid actions of the peptide, i.e. the inhibitory effect on the cell growth 5.
Functions
Proenkephalin is a precursor for neuropeptides with a variety of functions in the neuroendocrine and nervous systems. Upon activation, T-helper lymphocytes were found to express high levels of proenkephalin mRNA and to secrete large amounts of the Met-Enk neuropeptide, perhaps indicating an axis by which the immune and nervous systems interact 6. Enkephalins cause antinociception and potentiated morphine analgesia but they also block the development of tolerance and physical dependence. In addition to their central and peripheral antinociceptive function, opioids can modulate immune activity and cell proliferation. Moreover it is known that they have significant role in different physiological processes like cell differentiation and regeneration, inflammation, cancer and angiogenesis and analgesia effects 5.
References
Fleminger G, Lahm HW, Udenfriend S (1984).Changes in rat adrenal catecholamines and proenkephalin metabolism after denervation. PNAS., 81(11):3587-3590.
Barbara A. Barron. 2000. Cardiac Opioids. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 224:1-7.
Fratta W, Yang HY, Hong J, Costa E (1977). Stability of Met-enkephalin content in brain structures of morphine-dependent or foot shock-stressed rats. Nature, 268(5619):452-453.
Wouters W, Den Bercken JV (1979). Hyperpolarisation and depression of slow synaptic inhibition by enkephalin in frog sympathetic ganglion. Nature, 277:53-54.
Tsanova A, Dacheva D, Penchev V, Georgiev G, Pajpanova T, Golovinski E, Lalchev Z (2009). Comparative study of the interaction between synthetic methionine-enkephalin and monolayers of zwitterionic and negatively charged phospholipids. Biotechnol & Biotechnol., 23:463-466.
Rattner A, Korner M, Rosen H, Baeuerle PA, Citri Y (1991). Nuclear factor Kappa B activates proenkephalin transcription in T lymphocytes. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 11(2):1017-1022.
S Florin, et al. Orphan neuropeptide NocII, a putative pronociceptin maturation product, stimulates locomotion in mice. Neuroreport. 1997 Feb 10;8(3):705-7. : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9106751/