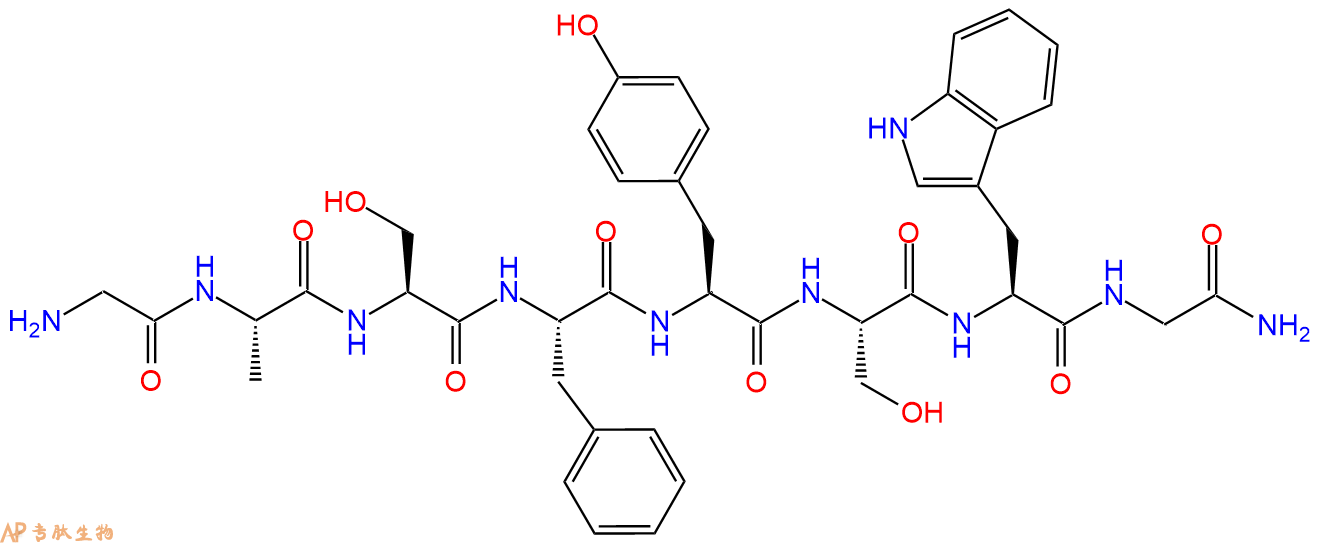
一种利尿八肽,从蟑螂头部提取物中得到。
编号:200827
CAS号:2703746-05-6/2703746-06-7
单字母:H2N-GASFYSWG-NH2
| 编号: | 200827 |
| 中文名称: | 白细胞激肽8、Leucokinin 8 |
| 英文名: | Leucokinin 8 |
| 英文同义词: | Leucokinin VIII |
| CAS号: | 2703746-05-6,free base 2703746-06-7,醋酸盐 |
| 单字母: | H2N-GASFYSWG-NH2 |
| 三字母: | H2N N端氨基 -Gly甘氨酸 -Ala丙氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Phe苯丙氨酸 -Tyr酪氨酸 -Ser丝氨酸 -Trp色氨酸 -Gly甘氨酸 -NH2C端酰胺化 |
| 氨基酸个数: | 8 |
| 分子式: | C42H52N10O11 |
| 平均分子量: | 872.92 |
| 精确分子量: | 872.38 |
| 等电点(PI): | - |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 1.97 |
| 平均亲水性: | -1.5333333333333 |
| 疏水性值: | 0.05 |
| 消光系数: | 6990 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 白细胞激肽(Leucokinin) |
Leucokinin VIII 是一种利尿八肽,从蟑螂头部提取物中得到。
Leucokinin VIII is an diuretic octapeptide isolated form head extracts of the cockroach.
Definition
The leucokinins are small insect neuropeptides which were originally isolated from head extracts of the Madeira cockroach, Leucophaea maderae. They stimulate the contractions of the cockroach's lower digestive tract.
Discovery
Identification of leucokinins and their cognate receptors has been successfully undertaken in cockroach, Leucophaea maderae, including the genetically tractable Dipteran, Drosophila Melanogaster, progress has been made in studies of leucokinin signalling in biomedically relevant insects.1, 2, 3.
Structural Characteristics
Leucokinins I and III are flanked by dibasic proteolytic cleavage sites, and in all three peptides a C-terminal Gly is present, which is predicted to be processed into a C-terminal amide group in the mature peptides. A different proteolytic cleavage site is present at the N terminus of leucokinin II, consisting of a single Arg with a Lys at residue –8. Four Cys residues are also present in the protein region before to the leucokinin peptide sequences. The position of the four Cys residues is identical, suggesting that these residues may play an important role in the function of the precursor protein, perhaps in the formation of disulphide bridges. It has been proposed that these residues are responsible for paraldehyde 4.
Mode of Action
Leucokinins in the cockroach increase motility of the isolated hindgut. Surprisingly, synthetic leucokinins have biological activity in a different insect and in a different tissue. In isolated Malpighian tubules of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti, leucokinins depolarize the transepithelial voltage. This effect on voltage is dependent on extracellular Cl. One leucokinin, LK-8, the effects of which were studied further in isolated Malpighian tubules, was found to inhibit transepithelial fluid secretion at low concentrations and to stimulate fluid secretion at high concentrations. The depolarizing effects on voltage and the stimulation of fluid secretion suggest that leucokinins increase the Cl permeability of the tubule wall thereby increasing the availability of Cl for secretion with Na, K and water. Structure-function comparisons of the seven leucokinins studied suggest that the active region of the octapeptide is segregated to the C-terminal pentapeptide. In view of the known effects of leucokinins on hindgut motility in the cockroach, finding of effects in mosquito Malpighian tubules suggests that leucokinins may be widely distributed in insects where they may have diverse functions in a variety of organs 5.
Functions
Leucokinins act on the leucokinin receptor to raise intracellular calcium having identified both leucokinins and a leucokinin-like receptor within Anopheles, it was established that they are a functional receptor–ligand pairing. The action of leucokinins on tubules were consistent with the existence of more than one receptor and that the broad concentration range of Drosophila leucokinin on Drosophila tubule was also taken as suggestive of multiple receptor classes.
Cross-specific leucokinin signaling, the effects of the Anopheles leucokinins on S2 cells expressing the Drosophila LKR, CG10626 were also established. Drosophila leucokinin was found to stimulate the A. stephensi receptor in a similar manner to the Anopheles leucokinins, displaying an EC50 value of 1.1•nmol, very similar to that of Anopheles leucokinin I.
Drosophila leucokinin was also found to activate the Anopheles receptor with a similar EC50 value to Anopheles leucokinin I. However, when the Anopheles peptides were applied to the Drosophila receptor, only Anopheles leucokinin I and II elicited a rise in Ca2+. This suggests that the Anopheles receptor has a broader specificity for leucokinin ligands than the Drosophila receptor 6. The insect leucokinins have attracted a great deal of interest as lead molecules for novel pesticides, including the development of peptidase resistant analogues of this family of peptides. Insect leucokinins have diverse roles; they act via their cognate G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Furthermore, as leucokinins have only been found in invertebrates, it is likely that careful design of leucokinin antagonist or agonist analogues will avoid interactions with mammalian species. Recent studies have suggested the involvement of leucokinins in dietary regulation and energy mobilisation 6.
References
1. Holman GM, Cook BJ, Wagner RM (1984). Isolation and partial characterization of five myotropic peptides present in head extracts of the cockroach, Leucophaea maderae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 77(1):1-5.
2. Holman GM, Nachman RJ Coast GM (1999). Isolation, characterization and biological activity of a diuretic myokinin neuropeptide from the housefly, Musca domestica. Peptides, 20:1-10.
3. Terhzaz S, O’Connell FC, Pollock, VP, Kean L, Davies SA, Veenstra, JA, Dow, JAT (1999). Isolation and characterization of a leucokinin-like peptide of Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Biol., 202:3667-3676.
4. Veenstra JA, Pattillo JM, Petzel DH (1997). A single cDNA encodes all three Aedes leucokinins, which stimulate both fluid secretion by the Malpighian tubules and hindgut contractions. J. Biol. Chem., 272:10402- 10407.
5. Hayes TK, Pannabecker TL, Hinckley DJ, Holman GM, Nachman RJ, Petzel DH, Beyenbach KW (1989). Leucokinins, a new family of ion transport stimulators and inhibitors in insect Malpighian tubules. Life Sci., 44(18):1259-1266.
6. Radford JC, Terhzaz S, Cabrero P, Davies SA, Dow JA (2004). Functional characterisation of the Anopheles leucokinins and their cognate G-protein coupled receptor. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 207
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1152/ajprenal.00041.2002 | Leucokinin activates Ca(2+)-dependent signal pathway in principal cells of Aedes aegypti Malpighian tubules | 下载 |
| 10.1007/BF00233052 | Regulation of epithelial shunt conductance by the peptide leucokinin | 下载 |
多肽H2N-Gly-Ala-Ser-Phe-Tyr-Ser-Trp-Gly-NH2的合成步骤:
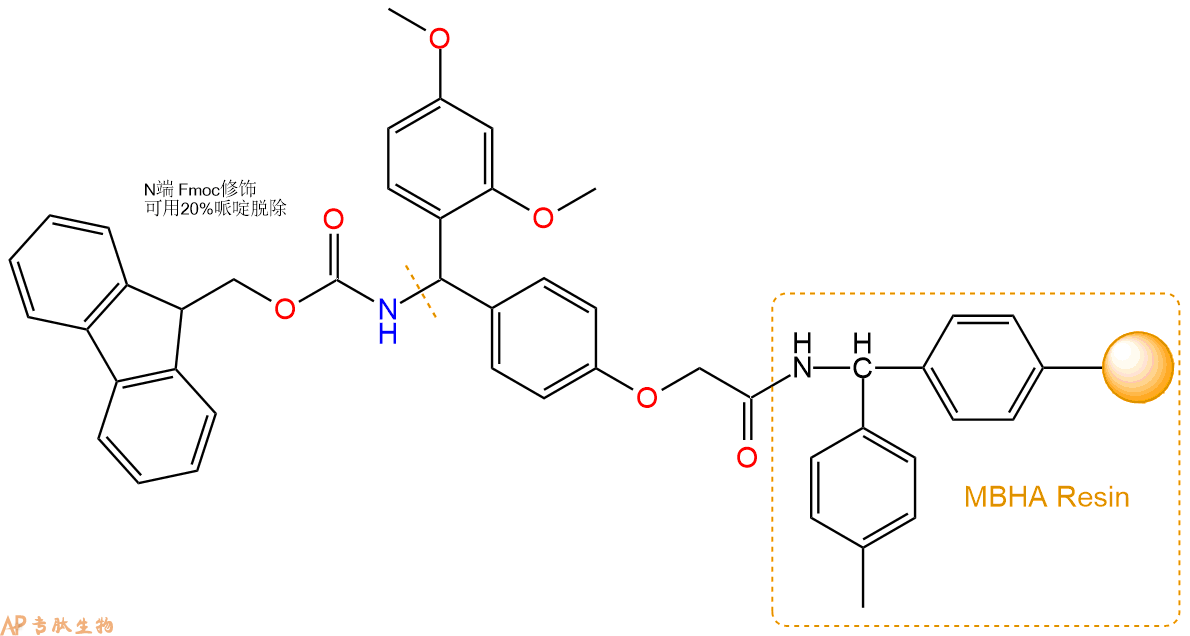
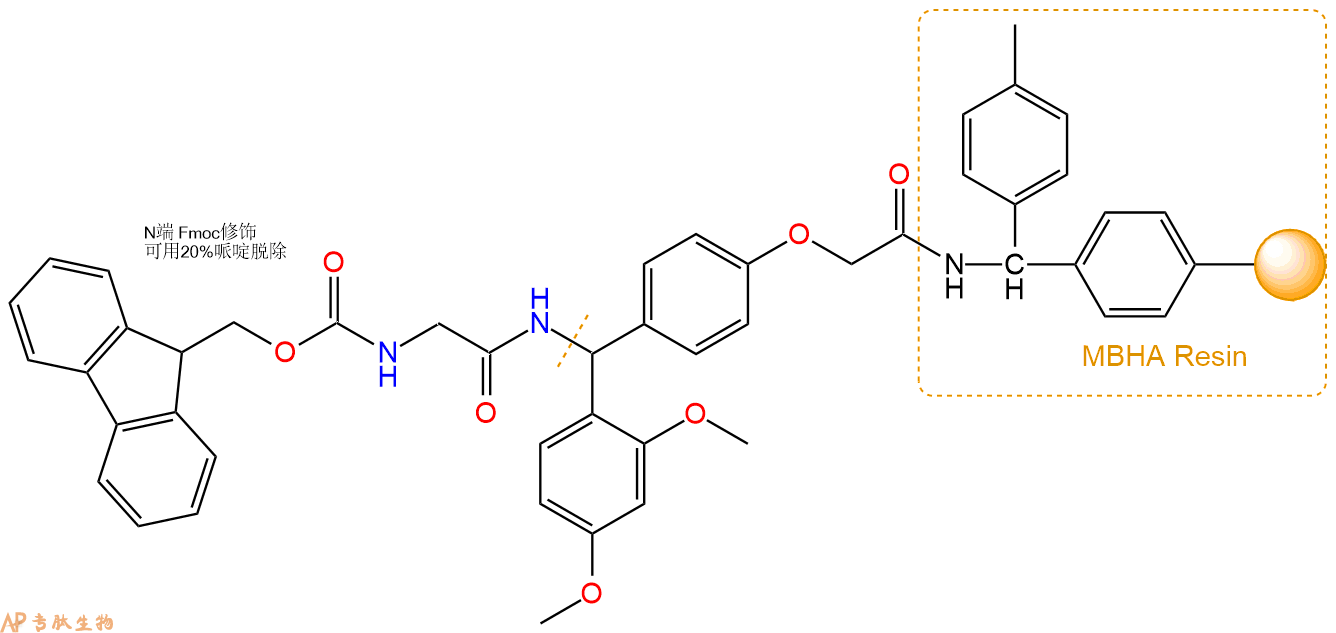
1、合成MBHA树脂:取若干克的MBHA树脂(如初始取代度为0.5mmol/g)和1倍树脂摩尔量的Fmoc-Linker-OH加入到反应器中,加入DMF,搅拌使氨基酸完全溶解。再加入树脂2倍量的DIEPA,搅拌混合均匀。再加入树脂0.95倍量的HBTU,搅拌混合均匀。反应3-4小时后,用DMF洗涤3次。用2倍树脂体积的10%乙酸酐/DMF 进行封端30分钟。然后再用DMF洗涤3次,甲醇洗涤2次,DCM洗涤2次,再用甲醇洗涤2次。真空干燥12小时以上,得到干燥的树脂{Fmoc-Linker-MHBA Resin},测定取代度。这里测得取代度为 0.3mmol/g。结构如下图:
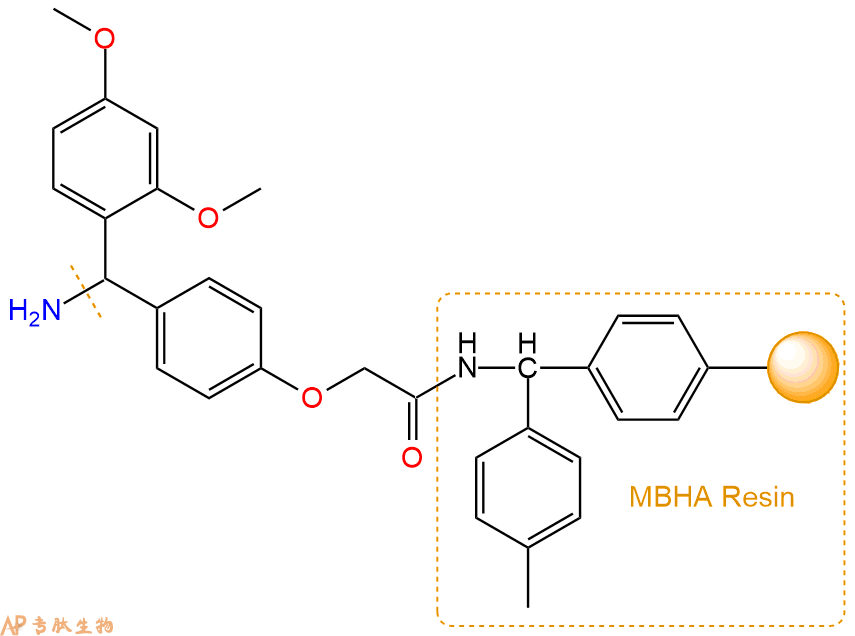
2、脱Fmoc:取1.02g的上述树脂,用DCM或DMF溶胀20分钟。用DMF洗涤2遍。加3倍树脂体积的20%Pip/DMF溶液,鼓氮气30分钟,然后2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤5次。得到 H2N-Linker-MBHA Resin 。(此步骤脱除Fmoc基团,茚三酮检测为蓝色,Pip为哌啶)。结构图如下:
3、缩合:取0.92mmol Fmoc-Gly-OH 氨基酸,加入到上述树脂里,加适当DMF溶解氨基酸,再依次加入1.84mmol DIPEA,0.87mmol HBTU。反应30分钟后,取小样洗涤,茚三酮检测为无色。用2倍树脂体积的DMF 洗涤3次树脂。(洗涤树脂,去掉残留溶剂,为下一步反应做准备)。得到Fmoc-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin。氨基酸:DIPEA:HBTU:树脂=3:6:2.85:1(摩尔比)。结构图如下:
4、依次循环步骤二、步骤三,依次得到
H2N-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Ser(tBu)-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Ala-Ser(tBu)-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
H2N-Ala-Ser(tBu)-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
Fmoc-Gly-Ala-Ser(tBu)-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin
以上中间结构,均可在专肽生物多肽计算器-多肽结构计算器中,一键画出。
最后再经过步骤二得到 H2N-Gly-Ala-Ser(tBu)-Phe-Tyr(tBu)-Ser(tBu)-Trp(Boc)-Gly-Linker-MBHA Resin,结构如下:
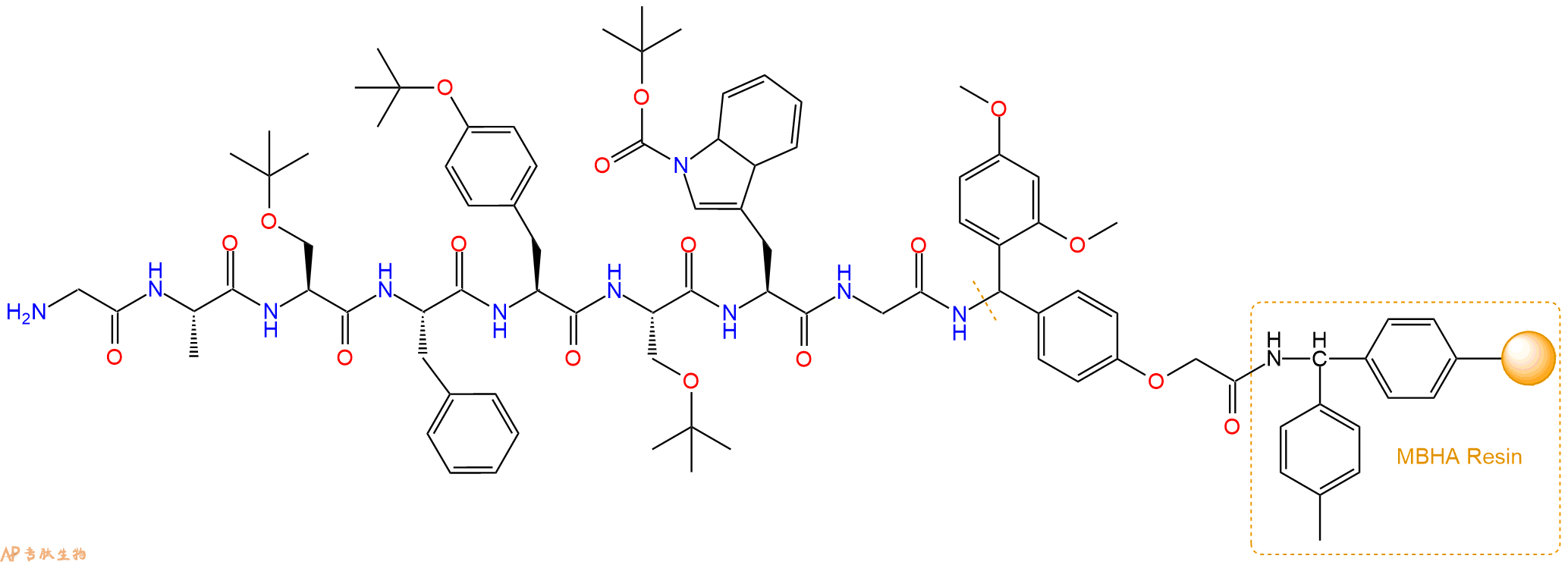
5、切割:6倍树脂体积的切割液(或每1g树脂加8ml左右的切割液),摇床摇晃 2小时,过滤掉树脂,用冰无水乙醚沉淀滤液,并用冰无水乙醚洗涤沉淀物3次,最后将沉淀物放真空干燥釜中,常温干燥24小试,得到粗品H2N-Gly-Ala-Ser-Phe-Tyr-Ser-Trp-Gly-NH2。结构图见产品结构图。
切割液选择:1)TFA:H2O=95%:5%
2)TFA:H2O:TIS=95%:2.5%:2.5%
3)三氟乙酸:茴香硫醚:1,2-乙二硫醇:苯酚:水=87.5%:5%:2.5%:2.5%:2.5%
(前两种适合没有容易氧化的氨基酸,例如Trp、Cys、Met。第三种适合几乎所有的序列。)
6、纯化冻干:使用液相色谱纯化,收集目标峰液体,进行冻干,获得蓬松的粉末状固体多肽。不过这时要取小样复测下纯度 是否目标纯度。
7、最后总结:
杭州专肽生物技术有限公司(ALLPEPTIDE https://www.allpeptide.com)主营定制多肽合成业务,提供各类长肽,短肽,环肽,提供各类修饰肽,如:荧光标记修饰(CY3、CY5、CY5.5、CY7、FAM、FITC、Rhodamine B、TAMRA等),功能基团修饰肽(叠氮、炔基、DBCO、DOTA、NOTA等),同位素标记肽(N15、C13),订书肽(Stapled Peptide),脂肪酸修饰肽(Pal、Myr、Ste),磷酸化修饰肽(P-Ser、P-Thr、P-Tyr),环肽(酰胺键环肽、一对或者多对二硫键环),生物素标记肽,PEG修饰肽,甲基化修饰肽等。
以上所有内容,为专肽生物原创内容,请勿发布到其他网站上。