400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
400-998-5282
专注多肽 服务科研
Potent constrictor of rat blood vessels in vitro and an effective pressor agent in vivo. Endothelin-3 (ET-3) has been found in high concentrations in the brain and may regulate important functions in neurons and astrocytes, such as proliferation and devel
编号:178999
CAS号:117399-93-6
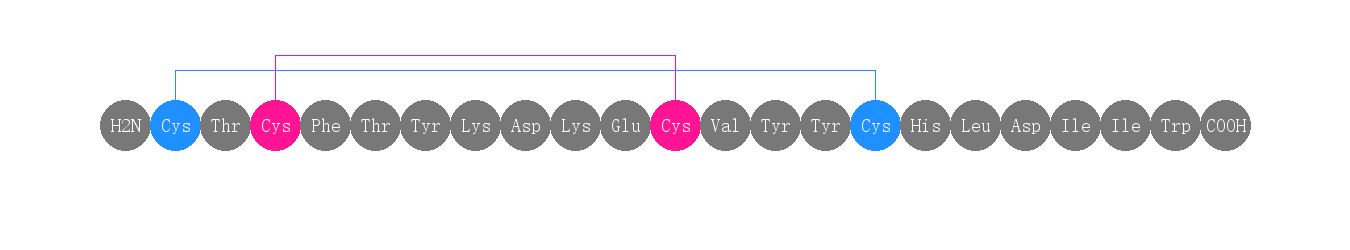
单字母:H2N-CTCFTYKDKECVYYCHLDIIW-OH(Disulfide Bridge:C1-C15 & C3-C11)
| 编号: | 178999 |
| 中文名称: | Endothelin-3, human、ET-3 |
| 英文名: | Endothelin-3, human、ET-3 |
| CAS号: | 117399-93-6 |
| 单字母: | H2N-CTCFTYKDKECVYYCHLDIIW-OH(Disulfide Bridge:C1-C15 & C3-C11) |
| 三字母: | H2N-Cys-Thr-Cys-Phe-Thr-Tyr-Lys-Asp-Lys-Glu-Cys-Val-Tyr-Tyr-Cys-His-Leu-Asp-Ile-Ile-Trp-OH(Disulfide Bridge:Cys1-Cys15 & Cys3-Cys11) |
| 氨基酸个数: | 21 |
| 分子式: | C121H168N26O33S4 |
| 平均分子量: | 2643.04 |
| 精确分子量: | 2641.11 |
| 等电点(PI): | 10.22 |
| pH=7.0时的净电荷数: | 7.09 |
| 平均亲水性: | -0.63333333333333 |
| 疏水性值: | 0.16 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色粉末状固体 |
| 消光系数: | 9970 |
| 来源: | 人工化学合成,仅限科学研究使用,不得用于人体。 |
| 纯度: | 95%、98% |
| 盐体系: | 可选TFA、HAc、HCl或其它 |
| 生成周期: | 2-3周 |
| 储存条件: | 负80℃至负20℃ |
| 标签: | 心血管(Cardiovascular)系统 内皮素(Endothelins) 二硫键环肽 |
| 参考文献(References): | K. Nakajima et al., J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 13, S8 (1989) A. Inoue, et al., PNAS, 86, 2863 (1989) M. Yanagisawa et al., PNAS, 85, 6964 (1988) |
体外有效的大鼠血管收缩剂和体内有效的升压剂。内皮素-3(ET-3)在大脑中浓度很高,可能调节神经元和星形胶质细胞的重要功能,如增殖和发育。ET-3显示对ETC受体的选择性。
Potent constrictor of rat blood vessels in vitro and an effective pressor agent in vivo. Endothelin-3 (ET-3) has been found in high concentrations in the brain and may regulate important functions in neurons and astrocytes, such as proliferation and development. ET-3 displays selectivity for the ETC receptor.
内皮素-3(ET-3)是属于内皮素肽大家族的蛋白质,其激活G蛋白偶联受体ETA和ETB。然而,与内皮素-1(ET-1)和内皮素-2(ET-2)相比,ET-3对ETA受体的亲和力较低,而所有三种内皮素对ETB受体具有相似的亲和力。由于ETB受体约占人类大脑皮层内皮素受体的90%,因此ET-3可以被称为“脑内皮素”。同样通过ET-3激活ETB受体,ET-3参与肠道神经系统的发育,该系统控制肠道内的血流,分泌和肠道运动。该产品在Cys1-Cys和Cys3-Cys11之间具有二硫键,来源于猪,大鼠和兔,可作为0.1mg小瓶获得。它可以用作研究内皮素受体功能的研究工具。
Endothelin-3 (ET-3) is a protein that belongs to the large family of endothelin peptides which activate the G-protein coupled receptors ETA and ETB. However ET-3 has lower affinity for the ETA receptors compared to Endothelin-1 (ET-1) and Endothelin-2 (ET-2), whereas all three endothelins have similar affinity for ETB receptors. As ETB receptors make up around 90% of the endothelin receptors found in the cerebral cortex in humans, ET-3 can be nicknamed the ‘brain endothelin’. Also through ET-3’s activation of ETB receptors, ET-3 is involved in the development of the enteric nervous system which controls within the gut, blood flow, secretion and intestinal motility. This product has disulfide bonds between Cys1-Cys and Cys3-Cys11, is sourced from Porcine, Rat and Rabbit and is available as a 0.1mg vial. It can be use\xa0as a research tool for studying the function of endothelin receptors.
Definition
A peptidergic activity produced in endothelial cells that caused coronary vasoconstriction was described in 1985, and a family of peptides, named the endothelins, was subsequently isolated and identified. The three members of the family — endothelin-1 (ET-1), endothelin-2 (ET-2), and endothelin-3 (ET-3 )— are produced in a variety of tissues, where they act as modulators of vasomotor tone, cell proliferation, and hormone production 1.
Related Peptides
The 21-amino acid peptide ET-1 is the predominant isoform of the endothelin peptide family, which includes ET-2, ET-3, and ET-4. It exerts various biological effects, including vasoconstriction and the stimulation of cell proliferation in tissues both within and outside of the cardiovascular system. ET-1 is synthesized by endothelin-converting enzymes (ECE), chymases, and non-ECE metalloproteases; it is regulated in an autocrine fashion in vascular and nonvascular cells 2.
Discovery
Endothelin, one of the most potent vasoconstrictors, was first discovered by Yanagisawa and co-workers in 1981. It was first isolated, characterized, and cloned in porcine aortic endothelial cells 3.
Structural Characteristics
First of the three isoforms, the ET-1, is a 21-amino acid peptide; it has a molecular weight of 2,492, free carboxyl and amino termini and has two intramolecular disulfide bonds. It is present in many mammalian species, including humans. Other two human endothelin isopeptides, ET-2 and ET-3 are encoded by separate genes. They contain two intramolecular disulfide bonds. They also contain a cluster of polar charged side chains in the hairpin loop and a hydrophobic COOH terminus, containing the aromatic indole side chain at trp21 3.
Mode of Action
Two endothelin receptors have been characterised in the mammals. They are classified according to the relative binding affinities of the 3-endothelin isopeptides to the receptors. The order of affinity of endothelins for 1st receptor type designated ETA is ET-1 > ET-2 > ET- 3. The second receptor subtype designated ETB shows equipotent affinity for all 3 endothelins 3.
Functions
Endothelins appear to act mainly as local paracrine/autocrine peptides, but circulating levels of endothelins also have great biological significance especially in pathological states of increased serum concentration.
Pathophysiology of Endothelins:
1. Renal haemodynamics: In various studies in dogs and rats it has been seen that endothelin peptides have both contractile and promitogenic actions in renal mesangial cells.
2. Renal disease: In various studies it has been shown that ET-1 plays a role in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure after renal ischaemia, i.e., plasma levels of ET-1 are increased in patients with acute renal failure.
3. Hypertension: ET-1 causes potent vasoconstriction and prolonged elevation of blood pressure in experimental models. But the relationship between the plasma levels of ET-1 and severity of hypertension is inconsistent in humans.
4. Heart failure: Plasma endothelin levels are increased in animal models of CHF (Chronic Heart Failure) and in patients with CHF. In patients, increased plasma endothelin levels correlate closely with the degree of haemodynamic and functional impairment, with higher levels predicting a greater likelihood of death or need for cardiac transplantation.
5. Ischaemic heart disease: In human studies, plasma endothelin levels are increased in unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction.
6. Variant angina: Patients with Prinzmetal’s angina are known to have endothelial dysfunction affecting the L-arginine nitric oxide system, and as a potent vasoconstrictor of coronary arteries, endothelin-1 has been implicated in the pathophysiology of this condition.
7. Primary pulmonary hypertension: In primary pulmonary hypertension there is proliferation of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle and endothelial injury. It has been observed that depending on the state of vasomotor tone, endothelin isopeptides can cause either pulmonary vasodilatation or vasoconstriction.
8. Raynaud’s disease: Raynaud’s disease is seen commonly in cold climates and is associated with vasospastic conditions like migraine and Prinzmetal’s angina. There has been exaggerated increase in endothelin levels in venous blood draining from the cold challenged arm, in cases with Raynaud’s disease as compared with responses in healthy volunteers.
9. Subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH): Endothelin-1 has a causative role in mediating sub-arachnoid hemorrhage induced vasospasm. Plasma and CSF endothelin levels are significantly increased in patients after SAH and plasma levels of endothelins are highest in those who develop vasospasm.
10. Migraine: In the recent studies it has been found that levels of endothelins are increased during migraine headaches 3.
References
1. Levin ER (1995). Endothelins. NEJM., 333:356-363.
2. Lüscher TF, Barton M (2000). Endothelins and Endothelin Receptor Antagonists Circulation., 102:2434:2440.
3. Jain SK, Yadava RK, Raikar R (2002). Role of Endothelins in Health and Disease. JIACM, 3(1):59-64.
二硫键广泛存在与蛋白结构中,对稳定蛋白结构具有非常重要的意义,二硫键一般是通过序列中的2个Cys的巯基,经氧化形成。
形成二硫键的方法很多:空气氧化法,DMSO氧化法,过氧化氢氧化法等。
二硫键的合成过程, 可以通过Ellman检测以及HPLC检测方法对其反应进程进行监测。
如果多肽中只含有1对Cys,那二硫键的形成是简单的。多肽经固相或液相合成,然后在pH8-9的溶液中进行氧化。
当需要形成2对或2对以上的二硫键时,合成过程则相对复杂。尽管二硫键的形成通常是在合成方案的最后阶段完成,但有时引入预先形成的二硫化物是有利于连合或延长肽链的。通常采用的巯基保护基有trt, Acm, Mmt, tBu, Bzl, Mob, Tmob等多种基团。我们分别列出两种以2-Cl树脂和Rink树脂为载体合成的多肽上多对二硫键形成路线:
二硫键反应条件选择
二硫键即为蛋白质或多肽分子中两个不同位点Cys的巯基(-SH)被氧化形成的S-S共价键。 一条肽链上不同位置的氨基酸之间形成的二硫键,可以将肽链折叠成特定的空间结构。多肽分 子通常分子量较大,空间结构复杂,结构中形成二硫键时要求两个半胱氨酸在空间距离上接近。 此外,多肽结构中还原态的巯基化学性质活泼,容易发生其他的副反应,而且肽链上其他侧链 也可能会发生一系列修饰,因此,肽链进行修饰所选取的氧化剂和氧化条件是反应的关键因素, 反应机理也比较复杂,既可能是自由基反应,也可能是离子反应。
反应条件有多种选择,比如空气氧化,DMSO氧化等温和的氧化过程,也可以采用H2O2,I2, 汞盐等激烈的反应条件。
空气氧化法: 空气氧化法形成二硫键是多肽合成中最经典的方法,通常是将巯基处于还原态的多肽溶于水中,在近中性或弱碱性条件下(PH值6.5-10),反应24小时以上。为了降低分子之间二硫键形成的可能,该方法通常需要在低浓度条件下进行。
碘氧化法:将多肽溶于25%的甲醇水溶液或30%的醋酸水溶液中,逐滴滴加10-15mol/L的碘进行氧化,反应15-40min。当肽链中含有对碘比较敏感的Tyr、Trp、Met和His的残基时,氧化条件要控制的更精确,氧化完后,立即加入维生素C或硫代硫酸钠除去过量的碘。 当序列中有两对或多对二硫键需要成环时,通常有两种情况:
自然随机成环: 序列中的Cys之间随机成环,与一对二硫键成环条件相似;
定点成环: 定点成环即序列中的Cys按照设计要求形成二硫键,反应过程相对复杂。在 固相合成多肽之前,需要提前设计几对二硫键形成的顺序和方法路线,选择不同的侧链 巯基保护基,利用其性质差异,分步氧化形成两对或多对二硫键。 通常采用的巯基保护 基有trt, Acm, Mmt, tBu, Bzl, Mob, Tmob等多种基团。
| DOI | 名称 | |
|---|---|---|
| 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23820.x | Endothelin-1 induces CXCL1 and CXCL8 secretion in human melanoma cells | 下载 |
| 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916094 | Endothelins | 下载 |
| 10.1096/fasebj.4.12.2168326 | Cellular signaling by peptides of the endothelin gene family | 下载 |
| 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00004 | Synthesis of endothelin-1 analogues, endothelin-3, and sarafotoxin S6b: structure-activity relationships | 下载 |
| 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863 | The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes | 下载 |
| 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90011-4 | Molecular biology and biochemistry of the endothelins | 下载 |
| 10.1016/j.peptides.2016.05.007 | Effects of endothelin family on ANP secretion | 下载 |
| 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6964 | Primary structure, synthesis, and biological activity of rat endothelin, an endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor peptide | 下载 |
| 10.1016/s0895-7061(03)00903-8 | Measurement of plasma endothelin-1 in experimental hypertension and in healthy subjects | 下载 |